Indinavir: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
Concomitant use of CRIXIVAN and [[St. John's wort]] ([[Hypericum perforatum]]) or products containing [[St. John's wort]] is not recommended. Coadministration of CRIXIVAN and [[St. John's wort]] has been shown to substantially decrease indinavir concentrations and may lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to CRIXIVAN or to the class of [[protease inhibitors]]. | Concomitant use of CRIXIVAN and [[St. John's wort]] ([[Hypericum perforatum]]) or products containing [[St. John's wort]] is not recommended. Coadministration of CRIXIVAN and [[St. John's wort]] has been shown to substantially decrease indinavir concentrations and may lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to CRIXIVAN or to the class of [[protease inhibitors]]. | ||
|clinicalTrials=====Clinical Trials in Adults==== | |||
[[Nephrolithiasis]]/[[urolithiasis]], including [[flank pain]] with or without [[hematuria]] (including [[microscopic hematuria]]), has been reported in approximately 12.4% (301/2429; range across individual trials: 4.7% to 34.4%) of patients receiving CRIXIVAN at the recommended dose in clinical trials with a median follow-up of 47 weeks (range: 1 day to 242 weeks; 2238 patient-years follow-up). The cumulative frequency of nephrolithiasis events increases with duration of exposure to CRIXIVAN; however, the risk over time remains relatively constant. Of the patients treated with CRIXIVAN who developed [[nephrolithiasis]]/[[urolithiasis]] in clinical trials during the double-blind phase, 2.8% (7/246) were reported to develop hydronephrosis and 4.5% (11/246) underwent stent placement. Following the acute episode, 4.9% (12/246) of patients discontinued therapy. | |||
Asymptomatic [[hyperbilirubinemia]] ([[total bilirubin]] ≥2.5 mg/dL), reported predominantly as elevated [[indirect bilirubin]], has occurred in approximately 14% of patients treated with CRIXIVAN. In <1% this was associated with elevations in [[ALT]] or [[AST]]. | |||
[[Hyperbilirubinemia]] and [[nephrolithiasis]]/[[urolithiasis]] occurred more frequently at doses exceeding 2.4 g/day compared to doses ≤2.4 g/day. | |||
Clinical adverse experiences reported in ≥2% of patients treated with CRIXIVAN alone, CRIXIVAN in combination with [[zidovudine]] or [[zidovudine]] plus [[lamivudine]], [[zidovudine]] alone, or [[zidovudine]] plus [[lamivudine]] are presented in TABLE 10. | |||
[[file:Indinavir AR1.png|none|400px]] | |||
|alcohol=Alcohol-Indinavir interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |alcohol=Alcohol-Indinavir interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 15:40, 2 February 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alberto Plate [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Indinavir is an antiretroviral agent and protease inhibitor that is FDA approved for the treatment of HIV infection in combination with other antiretroviral agents. Common adverse reactions include abdominal pain, heartburn, loss of appetite, nausea, taste sense altered, vomiting, neutrophil count abnormal, hyperbilirubinemia and headache.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
There is limited information regarding Indinavir FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Indinavir in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Indinavir in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Indinavir FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Indinavir in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Indinavir in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
CRIXIVAN is contraindicated in patients with clinically significant hypersensitivity to any of its components.
Inhibition of CYP3A4 by CRIXIVAN can result in elevated plasma concentrations of the following drugs, potentially causing serious or life-threatening reactions:
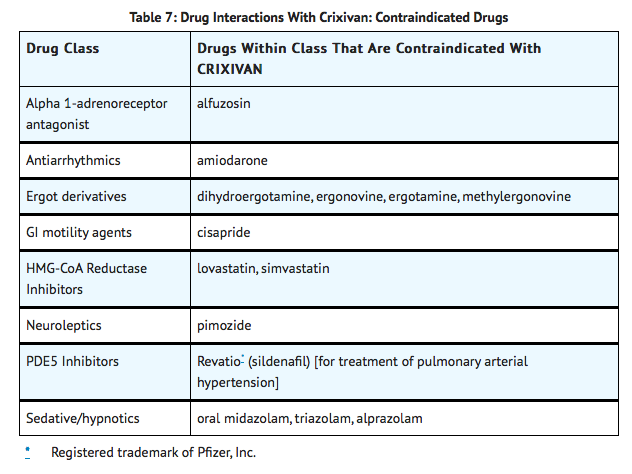
Warnings
ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with CRIXIVAN. This statement is included on the product's bottle label.
Nephrolithiasis/Urolithiasis
Nephrolithiasis/urolithiasis has occurred with CRIXIVAN therapy. The cumulative frequency of nephrolithiasis is substantially higher in pediatric patients (29%) than in adult patients (12.4%; range across individual trials: 4.7% to 34.4%). The cumulative frequency of nephrolithiasis events increases with increasing exposure to CRIXIVAN; however, the risk over time remains relatively constant. In some cases, nephrolithiasis/urolithiasis has been associated with renal insufficiency or acute renal failure, pyelonephritis with or without bacteremia. If signs or symptoms of nephrolithiasis/urolithiasis occur, (including flank pain, with or without hematuria or microscopic hematuria), temporary interruption (e.g., 1-3 days) or discontinuation of therapy may be considered. Adequate hydration is recommended in all patients treated with CRIXIVAN.
Hemolytic Anemia
Acute hemolytic anemia, including cases resulting in death, has been reported in patients treated with CRIXIVAN. Once a diagnosis is apparent, appropriate measures for the treatment of hemolytic anemia should be instituted, including discontinuation of CRIXIVAN.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis including cases resulting in hepatic failure and death has been reported in patients treated with CRIXIVAN. Because the majority of these patients had confounding medical conditions and/or were receiving concomitant therapy(ies), a causal relationship between CRIXIVAN and these events has not been established.
Hyperglycemia
New onset diabetes mellitus, exacerbation of pre-existing diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia have been reported during post-marketing surveillance in HIV-infected patients receiving protease inhibitor therapy. Some patients required either initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents for treatment of these events. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis has occurred. In those patients who discontinued protease inhibitor therapy, hyperglycemia persisted in some cases. Because these events have been reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made and a causal relationship between protease inhibitor therapy and these events has not been established.
Drug Interactions
Concomitant use of CRIXIVAN with lovastatin or simvastatin is contraindicated due to an increased risk of myopathy including rhabdomyolysis. Caution should be exercised if CRIXIVAN is used concurrently with atorvastatin or rosuvastatin. Titrate the atorvastatin and rosuvastatin doses carefully and use the lowest necessary dose with CRIXIVAN.
Midazolam is extensively metabolized by CYP3A4. Co-administration with CRIXIVAN with or without ritonavir may cause a large increase in the concentration of this benzodiazepine. No drug interaction study has been performed for the co-administration of CRIXIVAN with benzodiazepines. Based on data from other CYP3A4 inhibitors, plasma concentrations of midazolam are expected to be significantly higher when midazolam is given orally. Therefore CRIXIVAN should not be co-administered with orally administered midazolam, whereas caution should be used with co-administration of CRIXIVAN and parenteral midazolam. Data from concomitant use of parenteral midazolam with other protease inhibitors suggest a possible 3-4 fold increase in midazolam plasma levels. If CRIXIVAN with or without ritonavir is co-administered with parenteral midazolam, it should be done in a setting which ensures close clinical monitoring and appropriate medical management in case of respiratory depression and/or prolonged sedation. Dosage reduction for midazolam should be considered, especially if more than a single dose of midazolam is administered.
Particular caution should be used when prescribing sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil in patients receiving indinavir. Coadministration of CRIXIVAN with these medications is expected to substantially increase plasma concentrations of sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil and may result in an increase in adverse events, including hypotension, visual changes, and priapism, which have been associated with sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil.
Concomitant use of CRIXIVAN and St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) or products containing St. John's wort is not recommended. Coadministration of CRIXIVAN and St. John's wort has been shown to substantially decrease indinavir concentrations and may lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to CRIXIVAN or to the class of protease inhibitors.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Clinical Trials in Adults
Nephrolithiasis/urolithiasis, including flank pain with or without hematuria (including microscopic hematuria), has been reported in approximately 12.4% (301/2429; range across individual trials: 4.7% to 34.4%) of patients receiving CRIXIVAN at the recommended dose in clinical trials with a median follow-up of 47 weeks (range: 1 day to 242 weeks; 2238 patient-years follow-up). The cumulative frequency of nephrolithiasis events increases with duration of exposure to CRIXIVAN; however, the risk over time remains relatively constant. Of the patients treated with CRIXIVAN who developed nephrolithiasis/urolithiasis in clinical trials during the double-blind phase, 2.8% (7/246) were reported to develop hydronephrosis and 4.5% (11/246) underwent stent placement. Following the acute episode, 4.9% (12/246) of patients discontinued therapy.
Asymptomatic hyperbilirubinemia (total bilirubin ≥2.5 mg/dL), reported predominantly as elevated indirect bilirubin, has occurred in approximately 14% of patients treated with CRIXIVAN. In <1% this was associated with elevations in ALT or AST.
Hyperbilirubinemia and nephrolithiasis/urolithiasis occurred more frequently at doses exceeding 2.4 g/day compared to doses ≤2.4 g/day.
Clinical adverse experiences reported in ≥2% of patients treated with CRIXIVAN alone, CRIXIVAN in combination with zidovudine or zidovudine plus lamivudine, zidovudine alone, or zidovudine plus lamivudine are presented in TABLE 10.
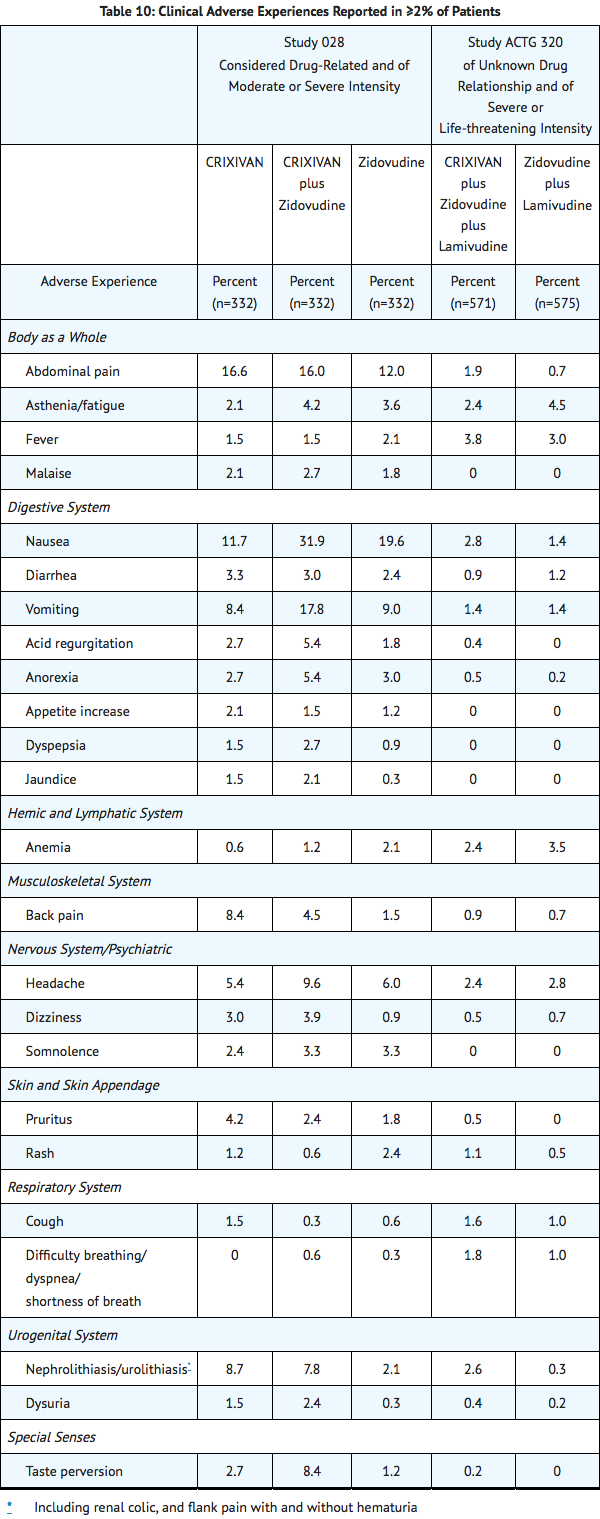
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Indinavir in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Indinavir in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Indinavir during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indinavir in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indinavir in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indinavir in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indinavir with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indinavir with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indinavir in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indinavir in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indinavir in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Indinavir in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Indinavir and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Indinavir overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Indinavir How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Indinavir |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Indinavir |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Indinavir interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Indinavir Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [3]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mohamed Moubarak, M.D. [4]
Overview
Indinavir (IDV; trade name Crixivan, manufactured by Merck) is a protease inhibitor used as a component of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) to treat HIV infection and AIDS.
Category
US Brand Names
CRIXIVAN®
FDA Package Insert
Description | Clinical Pharmacology | Microbiology | Indications and Usage | Contraindications | Warnings and Precautions | Adverse Reactions | Overdosage | Dosage and Administration | How Supplied
Mechanism of Action
HIV-1 protease is an enzyme required for the proteolytic cleavage of the viral polyprotein precursors into the individual functional proteins found in infectious HIV-1. Indinavir binds to the protease active site and inhibits the activity of the enzyme. This inhibition prevents cleavage of the viral polyproteins resulting in the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles.[1]
References
- ↑ "CRIXIVAN (INDINAVIR SULFATE) CAPSULE [MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP.]". Text " accessdate" ignored (help)