Indapamide: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :* '''2.5 mg/d'''<ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0160-2446 | volume = 22 Suppl 6 | pages = –78-86 | last = Borghi | first = L. | coauthors = T. Meschi, A. Guerra, A. Novarini | title = Randomized prospective study of a nonthiazide diuretic, indapamide, in preventing calcium stone recurrences | journal = Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology | date = 1993 | pmid = 7508066 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0820-3946 | volume = 135 | issue = 2 | pages = 119–121 | last = Lemieux | first = G. | title = Treatment of idiopathic hypercalciuria with indapamide | journal = CMAJ: Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne | date = 1986-07-15 | pmid = 3719496 | pmc = PMC1491209 }}</ref> | ||
=====Neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus===== | =====Neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus===== | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :* '''2.5 mg/d'''<ref>{{Cite journal | issn = 0003-9926 | volume = 159 | issue = 17 | pages = 2085–2087 | last = Tetiker | first = T. | coauthors = M. Sert, M. Koçak | title = Efficacy of indapamide in central diabetes insipidus | journal = Archives of Internal Medicine | date = 1999-09-27 | pmid = 10510995 }}</ref> | ||
<!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | <!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | ||
Revision as of 20:38, 6 July 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Indapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of hypertension and salt and fluid retention associated with congestive heart failure. Common adverse reactions include hypokalemia, cramp, asthenia, dizziness, headache, lethargy, numbness, fatigue, and malaise.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Hypertension
- Dosing Information
- The adult starting indapamide dose for hypertension is 1.25 mg as a single daily dose taken in the morning.
- If the response to 1.25 mg is not satisfactory after four weeks, the daily dose may be increased to 2.5 mg taken once daily.
- If the response to 2.5 mg is not satisfactory after four weeks, the daily dose may be increased to 5 mg taken once daily, but adding another antihypertensive should be considered.
Edema Of Congestive Heart Failure
- Dosing Information
- The adult starting indapamide dose for edema of congestive heart failure is 2.5 mg as a single daily dose taken in the morning.
- If the response to 2.5 mg is not satisfactory after one week, the daily dose may be increased to 5 mg taken once daily.
- If the antihypertensive response to indapamide is insufficient, indapamide may be combined with other antihypertensive drugs, with careful monitoring of blood pressure. It is recommended that the usual dose of other agents be reduced by 50% during initial combination therapy. As the blood pressure response becomes evident, further dosage adjustments may be necessary.
- In general, doses of 5 mg and larger have not appeared to provide additional effects on blood pressure or heart failure, but are associated with a greater degree of hypokalemia. There is minimal clinical trial experience in patients with doses greater than 5 mg once a day.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Indapamide in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Hypercalciuria
- Dosing Information
Neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus
- Dosing Information
- 2.5 mg/d[3]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Safety and effectiveness of indapamide in pediatric patients have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Indapamide in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Indapamide in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Condition1
Warnings
- Description
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Indapamide in the drug label.
Central Nervous System
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Gastrointestinal
Hypersensitivity
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Indapamide in the drug label.
Central Nervous System
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Gastrointestinal
Hypersensitivity
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Usage in Pregnancy
- The routine use of diuretics in an otherwise healthy woman is inappropriate and exposes mother and fetus to unnecessary hazard (see PRECAUTIONS). Diuretics do not prevent development of toxemia of pregnancy, and there is no satisfactory evidence that they are useful in the treatment of developed toxemia.
- Edema during pregnancy may arise from pathological causes or from the physiologic and mechanical consequences of pregnancy. Indapamide is indicated in pregnancy when edema is due to pathologic causes, just as it is in the absence of pregnancy (however, see PRECAUTIONS). Dependent edema in pregnancy, resulting from restriction of venous return by the expanded uterus, is properly treated through elevation of the lower extremities and use of support hose; use of diuretics to lower intravascular volume in this case is illogical and unnecessary. There is hypervolemia during normal pregnancy which is not harmful to either the fetus or the mother (in the absence of cardiovascular disease), but which is associated with edema, including generalized edema in the majority of pregnant women. If this edema produces discomfort, increased recumbency will often provide relief. In rare instances, this edema may cause extreme discomfort which is not relieved by rest. In these cases, a short course of diuretics may provide relief and may be appropriate.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Indapamide in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Indapamide during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indapamide with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indapamide with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indapamide with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indapamide with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indapamide with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indapamide in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indapamide in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Indapamide in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Indapamide in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Indapamide in the drug label.
Condition1
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Indapamide in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Indapamide in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Indapamide Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
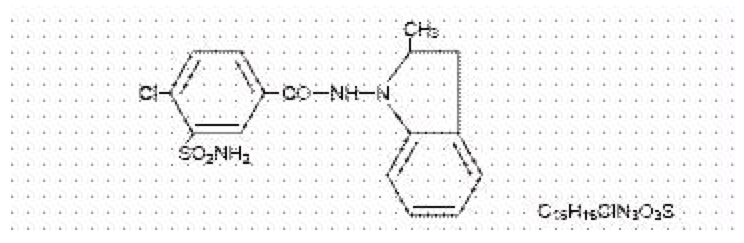
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Indapamide in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Indapamide in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Indapamide in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Indapamide in the drug label.
Condition1
- Description
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Indapamide Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Indapamide |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Indapamide |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Indapamide in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Indapamide interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Lozol®[4]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- N/A[5]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Borghi, L. (1993). "Randomized prospective study of a nonthiazide diuretic, indapamide, in preventing calcium stone recurrences". Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 22 Suppl 6: –78-86. ISSN 0160-2446. PMID 7508066. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Lemieux, G. (1986-07-15). "Treatment of idiopathic hypercalciuria with indapamide". CMAJ: Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne. 135 (2): 119–121. ISSN 0820-3946. PMC 1491209. PMID 3719496.
- ↑ Tetiker, T. (1999-09-27). "Efficacy of indapamide in central diabetes insipidus". Archives of Internal Medicine. 159 (17): 2085–2087. ISSN 0003-9926. PMID 10510995. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ "INDAPAMIDE tablet, film coated".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Indapamide |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Indapamide |Label Name=Indapamide11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Indapamide |Label Name=Indapamide11.png
}}