Hepatitis B ultrasound: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Varun Kumar (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Varun Kumar (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | [[Category:Infectious disease]] | ||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] | ||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
Revision as of 16:06, 16 March 2012
|
Hepatitis B |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hepatitis B ultrasound On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hepatitis B ultrasound |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Hepatitis B ultrasound |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S. [2]
Ultrasound
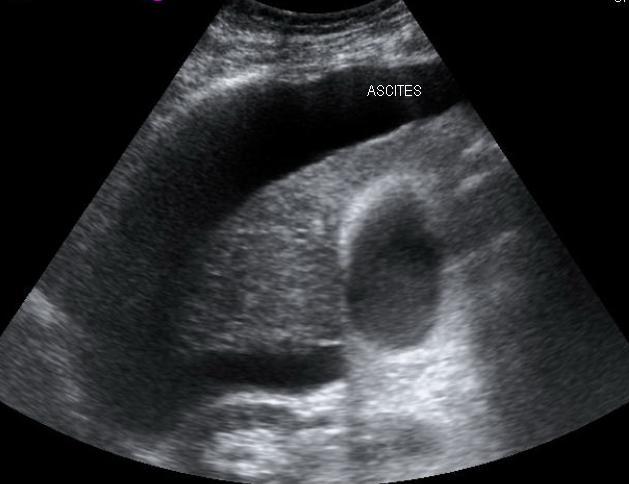
Ultrasound may be used as a screening tool in patients with hepatitis for early detection of hepatic cirrhosis. Coarse echogenicity and segmental hypertrophy with nodular appearance of liver may be noted along with other findings of portal hypertension such as splenomegaly, ascites and pleural effusion.