Hemolytic anemia: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (10 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{| class="infobox" style="float:right;" | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Siren.gif|30px|link=Hemolytic anemia resident survival guide]]|| <br> || <br> | |||
| [[Hemolytic anemia resident survival guide|'''Resident'''<br>'''Survival'''<br>'''Guide''']] | |||
|} | |||
{{Infobox_Disease | {{Infobox_Disease | ||
| Name = Hemolytic anemia | | Name = Hemolytic anemia | ||
| Line 16: | Line 21: | ||
'''For patient information on this, click [[Hemolytic anemia (patient information)|here]]''' | '''For patient information on this, click [[Hemolytic anemia (patient information)|here]]''' | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} {{shyam}} | ||
{{SK}} Haemolytic anaemia | {{SK}} Haemolytic anaemia | ||
==Overview== | ==[[Hemolytic anemia overview|Overview]]== | ||
==[[Hemolytic anemia historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | |||
==[[Hemolytic anemia classification|Classification]]== | |||
== | ==[[Hemolytic anemia pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | ||
== | ==[[Hemolytic anemia causes|Causes]]== | ||
==[[Hemolytic anemia epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | |||
==[[Hemolytic anemia risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | |||
==[[Hemolytic anemia screening|Screening]]== | |||
==[[Hemolytic anemia differential diagnosis|Differentiating Hemolytic anemia from other Diseases]]== | |||
==[[Hemolytic anemia natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== | |||
==Diagnosis== | |||
[[Hemolytic anemia history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Hemolytic anemia physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Hemolytic anemia laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Hemolytic anemia x ray|X Ray]] | [[Hemolytic anemia CT scan|CT Scan]] | [[Hemolytic anemia MRI scan|MRI Scan]] | [[Hemolytic anemia Echocardiography or ultrasound|Echocardiography or Ultrasound]] | [[Hemolytic anemia imaging findings|Imaging Findings]] | [[Hemolytic anemia Other Imaging Findings|Other imaging findings]] | [[Hemolytic anemia other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] | |||
==Treatment== | |||
[[Hemolytic anemia medical therapy|Medical therapy]] | [[Hemolytic anemia surgery|Surgery]] | [[Hemolytic anemia primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Hemolytic anemia cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Hemolytic anemia future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] | |||
==Case Studies== | |||
[[Hemolytic anemia case study one|Case #1]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:53, 31 October 2017
| Resident Survival Guide |
| Hemolytic anemia | |
 | |
|---|---|
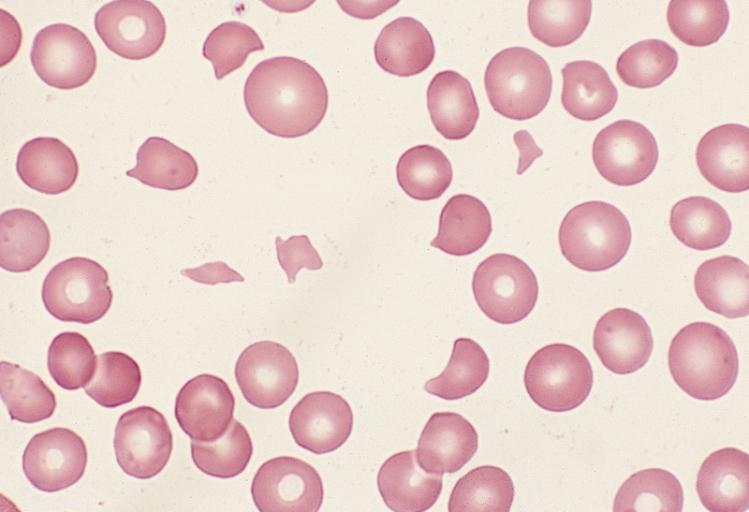
| Bone Marrow: Leukoerythroblastic Reaction and Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia in a Patient with Bone Marrow Metastasis Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology | |
| ICD-10 | D55-D59 |
| ICD-9 | 282, 283, 773 |
| DiseasesDB | 5534 |
| MedlinePlus | 000571 |
|
Hemolytic anemia Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hemolytic anemia On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hemolytic anemia |
For patient information on this, click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Shyam Patel [2]
Synonyms and keywords: Haemolytic anaemia
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Differentiating Hemolytic anemia from other Diseases
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | X Ray | CT Scan | MRI Scan | Echocardiography or Ultrasound | Imaging Findings | Other imaging findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies
Case Studies
ar:فقر الدم التحللي de:Hämolytische Anämie sr:Хемолитичка анемија