HIV AIDS cost-effectiveness of therapy: Difference between revisions
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| publisher = IAEN | | publisher = IAEN | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
===Economic impact=== | |||
[[Image:Life expectancy in some Southern African countries 1958 to 2003.jpg|left|295px|thumb|Changes in life expectancy in some hard-hit African countries. | |||
{{legend-line|red solid 2px|Botswana}}{{legend-line|darkgreen solid 2px|Zimbabwe}}{{legend-line|blue solid 2px|Kenya}}{{legend-line|black solid 2px|South Africa}}{{legend-line|grey solid 2px|Uganda}}]] | |||
The increased mortality in this region will result in a smaller skilled population and labor force.<ref name=Greener /> This smaller labor force will be predominantly young people, with reduced knowledge and work experience leading to reduced productivity. An increase in workers’ time off to look after sick family members or for sick leave will also lower productivity. Increased mortality will also weaken the mechanisms that generate human capital and investment in people, through loss of income and the death of parents.<ref name=Greener /> By killing off mainly young adults, AIDS seriously weakens the taxable population, reducing the resources available for public expenditures such as education and health services not related to AIDS resulting in increasing pressure for the state's finances and slower growth of the economy. This results in a slower growth of the tax base, an effect that will be reinforced if there are growing expenditures on treating the sick, training (to replace sick workers), sick pay and caring for AIDS orphans. This is especially true if the sharp increase in adult mortality shifts the responsibility and blame from the family to the government in caring for these orphans.<ref name=Greener /> | |||
On the level of the household, AIDS results in both the loss of income and increased spending on healthcare by the household. The income effects of this lead to spending reduction as well as a substitution effect away from education and towards healthcare and funeral spending. A study in Côte d'Ivoire showed that households with an HIV/AIDS patient spent twice as much on medical expenses as other households.<ref name=WBank>{{ | |||
cite journal | | |||
author=Over M | | |||
title=The macroeconomic impact of AIDS in Sub-Saharan Africa, Population and Human Resources Department | | |||
journal=The World Bank | year=1992 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
UNAIDS, WHO and the United Nations Development Programme have documented a correlation between the decreasing life expectancies and the lowering of gross national product in many African countries with prevalence rates of 10% or more. Indeed, since 1992 predictions that AIDS would slow economic growth in these countries have been published. The degree of impact depended on assumptions about the extent to which illness would be funded by savings and who would be infected.<ref name=WBank /> Conclusions reached from models of the growth trajectories of 30 sub-Saharan economies over the period 1990–2025 were that the economic growth rates of these countries would be between 0.56 and 1.47% lower. The impact on gross domestic product (GDP) per capita was less conclusive. However, in 2000, the rate of growth of Africa's per capita GDP was in fact reduced by 0.7% per year from 1990–1997 with a further 0.3% per year lower in countries also affected by [[malaria]].<ref name=Bonnel>{{ | |||
cite journal | | |||
author=Bonnel R | | |||
title=HIV/AIDS and Economic Growth: A Global Perspective | | |||
journal=S. A. J. Economics | year=2000 | pages=820–855 | volume=68 | issue=5 | | |||
}}</ref> The forecast now is that the growth of GDP for these countries will undergo a further reduction of between 0.5 and 2.6% per annum.<ref name=Greener /> However, these estimates may be an underestimate, as they do not look at the effects on output per capita.<ref name=Bell-et-al-2003>{{ | |||
cite paper | |||
|author= Bell C, Devarajan S, Gersbach H |date=2003 | |||
|url=http://ssrn.com/abstract=636571 | |||
| title=The long-run economic costs of AIDS: theory and an application to South Africa | |||
|accessdate= 2008-03-12 | |||
|version= World Bank Policy Research Working Paper No. 3152 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
Many governments in sub-Saharan Africa denied that there was a problem for years, and are only now starting to work towards solutions. Underfunding is a problem in all areas of HIV prevention when compared to even conservative estimates of the problems. | |||
Recent research by the Overseas Development Institute (ODI) has suggested that the private sector has begun to recognize the impact of HIV/AIDS on the bottom line, both directly and indirectly. It is estimated that a company can generate an average return of US$3 for every US$1 invested in employee health due to a reduced absenteeism, better productivity and reduction in employee turnover.<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| author = Goetzel RZ, Ozminkowski RJ, Baase CM, Billotti GM | |||
| title = Estimating the return-on-investment from changes in employee health risks on the Dow Chemical Company’s health care costs | |||
| journal = Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine | |||
| volume = 47 | |||
| year = 2005 | |||
| pages = 759-68 | |||
| pmid = 16093925}}</ref> Indirectly there are also important implications on the supply chain. Many multi-national corporations (MNCs) have therefore gotten involved in HIV/AIDS initiatives of three main types: a community-based partnerships, supply chain support, and sector-based initiatives.<ref name="odi">{{cite web|url=http://www.odi.org.uk/publications/briefing/bp_hiv_privatesector_nov07.pdf |format=PDF|title= AIDS and the private sector: The case of South Africa |accessyear=2007 |year=2007 |publisher=Overseas Development Institute}}</ref> | |||
The launching of the world's first official HIV/AIDS Toolkit in Zimbabwe on October 3 2006 is a product of collaborative work between the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, World Health Organization and the Southern Africa HIV/AIDS Information Dissemination Service. It is for the strengthening of people living with HIV/AIDS and nurses by minimal external support. The package, which is in form of eight modules focusing on basic facts about HIV and AIDS, was pre-tested in Zimbabwe in March 2006 to determine its adaptability. It disposes, among other things, categorized guidelines on clinical management, education and counseling of AIDS victims at community level.<ref name=xinhua>{{ | |||
cite web | |||
| author=Mu Xuequan | publisher=xinhua | year= 2006 | |||
| url=http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2006-10/04/content_5167991.htm | |||
| title=Zimbabwe launches world's first AIDS training package | |||
| accessdate = 2006-10-03 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
The Copenhagen Consensus is a project that seeks to establish priorities for advancing global welfare using methodologies based on the theory of welfare economics. The participants are all economists, with the focus of the project being a rational prioritization based on economic analysis. The project is based on the contention that, in spite of the billions of dollars spent on global challenges by the United Nations, the governments of wealthy nations, foundations, charities, and non-governmental organizations, the money spent on problems such as malnutrition and climate change is not sufficient to meet many internationally-agreed targets. The highest priority was assigned to implementing new measures to prevent the spread of HIV and AIDS. The economists estimated that an investment of $27 billion could avert nearly 30 million new infections by 2010.<ref name=Kaiserfunds>{{ | |||
cite web | |||
| publisher=kaisernetwork.org | year= 2002 | |||
| url=http://kaisernetwork.org/aids2002/syndication.asp?show=daily_report_1.html | |||
| title=$27 Billion Boost for HIV Prevention Programs Could Avert Majority of Projected HIV Infections Worldwide | |||
| accessdate = 2008-03-10 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
Revision as of 18:41, 2 March 2012
|
AIDS Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
HIV AIDS cost-effectiveness of therapy On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of HIV AIDS cost-effectiveness of therapy |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for HIV AIDS cost-effectiveness of therapy |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editors-in-Chief: Ujjwal Rastogi, MBBS [2]
Overview
HIV and AIDS retard economic growth by destroying human capital. Without proper nutrition, health care and medicine that is available in developed countries, large numbers of people are falling victim to AIDS. They will not only be unable to work, but will also require significant medical care. The forecast is that this will likely cause a collapse of economies and societies in the region. In some heavily infected areas, the epidemic has left behind many orphans cared for by elderly grandparents.[1]
Economic impact
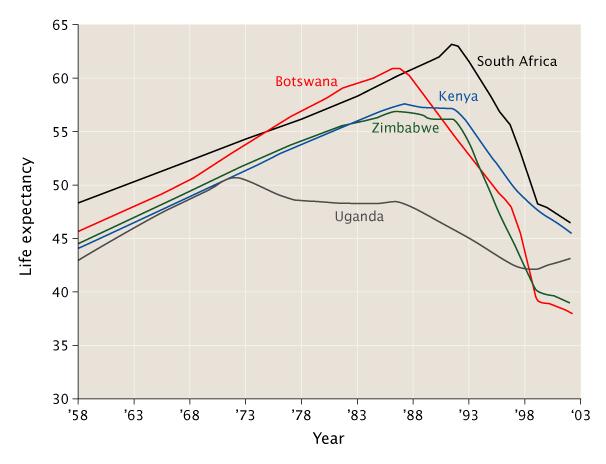
The increased mortality in this region will result in a smaller skilled population and labor force.[1] This smaller labor force will be predominantly young people, with reduced knowledge and work experience leading to reduced productivity. An increase in workers’ time off to look after sick family members or for sick leave will also lower productivity. Increased mortality will also weaken the mechanisms that generate human capital and investment in people, through loss of income and the death of parents.[1] By killing off mainly young adults, AIDS seriously weakens the taxable population, reducing the resources available for public expenditures such as education and health services not related to AIDS resulting in increasing pressure for the state's finances and slower growth of the economy. This results in a slower growth of the tax base, an effect that will be reinforced if there are growing expenditures on treating the sick, training (to replace sick workers), sick pay and caring for AIDS orphans. This is especially true if the sharp increase in adult mortality shifts the responsibility and blame from the family to the government in caring for these orphans.[1]
On the level of the household, AIDS results in both the loss of income and increased spending on healthcare by the household. The income effects of this lead to spending reduction as well as a substitution effect away from education and towards healthcare and funeral spending. A study in Côte d'Ivoire showed that households with an HIV/AIDS patient spent twice as much on medical expenses as other households.[2]
UNAIDS, WHO and the United Nations Development Programme have documented a correlation between the decreasing life expectancies and the lowering of gross national product in many African countries with prevalence rates of 10% or more. Indeed, since 1992 predictions that AIDS would slow economic growth in these countries have been published. The degree of impact depended on assumptions about the extent to which illness would be funded by savings and who would be infected.[2] Conclusions reached from models of the growth trajectories of 30 sub-Saharan economies over the period 1990–2025 were that the economic growth rates of these countries would be between 0.56 and 1.47% lower. The impact on gross domestic product (GDP) per capita was less conclusive. However, in 2000, the rate of growth of Africa's per capita GDP was in fact reduced by 0.7% per year from 1990–1997 with a further 0.3% per year lower in countries also affected by malaria.[3] The forecast now is that the growth of GDP for these countries will undergo a further reduction of between 0.5 and 2.6% per annum.[1] However, these estimates may be an underestimate, as they do not look at the effects on output per capita.[4]
Many governments in sub-Saharan Africa denied that there was a problem for years, and are only now starting to work towards solutions. Underfunding is a problem in all areas of HIV prevention when compared to even conservative estimates of the problems.
Recent research by the Overseas Development Institute (ODI) has suggested that the private sector has begun to recognize the impact of HIV/AIDS on the bottom line, both directly and indirectly. It is estimated that a company can generate an average return of US$3 for every US$1 invested in employee health due to a reduced absenteeism, better productivity and reduction in employee turnover.[5] Indirectly there are also important implications on the supply chain. Many multi-national corporations (MNCs) have therefore gotten involved in HIV/AIDS initiatives of three main types: a community-based partnerships, supply chain support, and sector-based initiatives.[6]
The launching of the world's first official HIV/AIDS Toolkit in Zimbabwe on October 3 2006 is a product of collaborative work between the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, World Health Organization and the Southern Africa HIV/AIDS Information Dissemination Service. It is for the strengthening of people living with HIV/AIDS and nurses by minimal external support. The package, which is in form of eight modules focusing on basic facts about HIV and AIDS, was pre-tested in Zimbabwe in March 2006 to determine its adaptability. It disposes, among other things, categorized guidelines on clinical management, education and counseling of AIDS victims at community level.[7]
The Copenhagen Consensus is a project that seeks to establish priorities for advancing global welfare using methodologies based on the theory of welfare economics. The participants are all economists, with the focus of the project being a rational prioritization based on economic analysis. The project is based on the contention that, in spite of the billions of dollars spent on global challenges by the United Nations, the governments of wealthy nations, foundations, charities, and non-governmental organizations, the money spent on problems such as malnutrition and climate change is not sufficient to meet many internationally-agreed targets. The highest priority was assigned to implementing new measures to prevent the spread of HIV and AIDS. The economists estimated that an investment of $27 billion could avert nearly 30 million new infections by 2010.[8]
Reference
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Greener R (2002). "AIDS and macroeconomic impact". In S, Forsyth (ed.). State of The Art: AIDS and Economics. IAEN. pp. 49&ndash, 55.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Over M (1992). "The macroeconomic impact of AIDS in Sub-Saharan Africa, Population and Human Resources Department". The World Bank.
- ↑ Bonnel R (2000). "HIV/AIDS and Economic Growth: A Global Perspective". S. A. J. Economics. 68 (5): 820&ndash, 855.
- ↑ Template:Cite paper
- ↑ Goetzel RZ, Ozminkowski RJ, Baase CM, Billotti GM (2005). "Estimating the return-on-investment from changes in employee health risks on the Dow Chemical Company's health care costs". Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 47: 759–68. PMID 16093925.
- ↑ "AIDS and the private sector: The case of South Africa" (PDF). Overseas Development Institute. 2007. Unknown parameter
|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ↑ Mu Xuequan (2006). "Zimbabwe launches world's first AIDS training package". xinhua. Retrieved 2006-10-03.
- ↑ "$27 Billion Boost for HIV Prevention Programs Could Avert Majority of Projected HIV Infections Worldwide". kaisernetwork.org. 2002. Retrieved 2008-03-10.
Template:Viral diseases Template:STD/STI
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA af:Vigs als:AIDS am:ኤድስ an:SIDA ar:متلازمة العوز المناعي المكتسب ast:SIDA az:QİÇS bat-smg:AIDS be-x-old:СНІД bg:Синдром на придобитата имунна недостатъчност bm:Sida bn:এইডস bs:Sida ca:SIDA cs:AIDS da:Aids de:Aids dv:އެއިޑްސް ބަލި el:AIDS eo:Aidoso et:AIDS eu:Hartutako Immuno Eskasiaren Sindromea fa:ایدز fi:AIDS fur:AIDS ga:SEIF gd:AIDS gl:SIDA gu:એડ્સ he:איידס hi:एड्स hr:Sindrom stečene imunodeficijencije ht:Sida hu:AIDS hy:ՁԻԱՀ id:AIDS is:Alnæmi it:AIDS ka:შიდსი ki:AIDS km:ជំងឺអេដស៍ kn:ಏಡ್ಸ್ ರೋಗ ko:에이즈 ku:AIDS la:SCDI lb:Aids ln:Sida lo:ເອດສ໌ lt:AIDS lv:AIDS mk:СИДА ml:എയ്ഡ്സ് mn:Дархлалын олдмол хомсдол mr:एड्स ms:AIDS mt:AIDS new:एड्स nl:Aids nn:Hiv/aids no:Aids oc:SIDA ps:اېډز qu:Unquy hark'aypa chaskisqa waqlliynin scn:AIDS sh:AIDS si:ඒඩ්ස් simple:AIDS sk:Aids sl:Aids sr:Сида sv:Aids sw:Ukimwi ta:எய்ட்ஸ் te:ఎయిడ్స్ tg:СПИД th:เอดส์ tt:AİDS uk:СНІД ur:محصولی کسرمناعی متلازمہ uz:Orttirilgan Imunitet Tanqisligi Sindromi vec:AIDS yi:עידס yo:AIDS zh-min-nan:AIDS zh-yue:愛滋病