Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia
| Choriocarcinoma | |
 | |
|---|---|
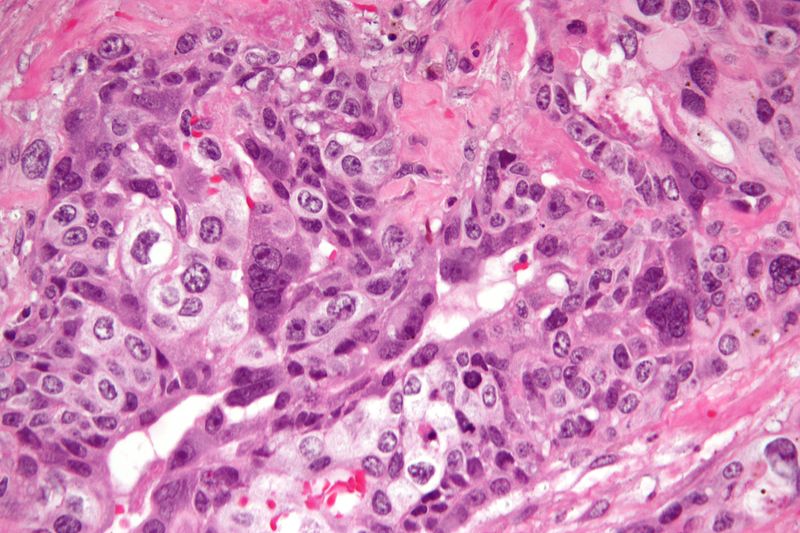
| Micrograph of choriocarcinoma showing both of the components necessary for the diagnosis - cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts. The syncytiotrophoblasts are multinucleated and have a dark staining cytoplasm. The cytotrophoblasts are mononuclear and have a pale staining cytoplasm. H&E stain. |
For patient information, click here Template:Choriocarcinoma Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Monalisa Dmello, M.B,B.S., M.D. [2]
Synonyms and Keywords: Chorioblastoma; trophoblastic tumor; chorioepithelioma; gestational trophoblastic neoplasia; Gestational trophoblastic tumor; Placental site trophoblastic tumor; Epithelioid trophoblastic tumor; Exaggerated placenta site (EPS) tumor; Placental site nodule (PSN) tumor.
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia from other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | Chest X Ray CT | MRI | Ultrasound | Other Imaging Findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Staging | Medical Therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies