GNB2
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 2 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 1b9x. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | GNB2 ; | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 68451 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
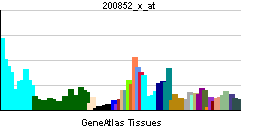 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 2, also known as GNB2, is a human gene.[1]
Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins), which integrate signals between receptors and effector proteins, are composed of an alpha, a beta, and a gamma subunit. These subunits are encoded by families of related genes. This gene encodes a beta subunit. Beta subunits are important regulators of alpha subunits, as well as of certain signal transduction receptors and effectors. This gene contains a trinucleotide (CCG) repeat length polymorphism in its 5' UTR.[1]
References
Further reading
- Downes GB, Gautam N (2000). "The G protein subunit gene families". Genomics. 62 (3): 544–52. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5992. PMID 10644457.
- Dawson SJ, White LA (1992). "Treatment of Haemophilus aphrophilus endocarditis with ciprofloxacin". J. Infect. 24 (3): 317–20. PMID 1602151.
- Lovett M, Kere J, Hinton LM (1991). "Direct selection: a method for the isolation of cDNAs encoded by large genomic regions". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (21): 9628–32. PMID 1946378.
- Blatt C, Eversole-Cire P, Cohn VH; et al. (1988). "Chromosomal localization of genes encoding guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunits in mouse and human". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (20): 7642–6. PMID 2902634.
- Fong HK, Amatruda TT, Birren BW, Simon MI (1987). "Distinct forms of the beta subunit of GTP-binding regulatory proteins identified by molecular cloning". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (11): 3792–6. PMID 3108879.
- Gao B, Gilman AG, Robishaw JD (1987). "A second form of the beta subunit of signal-transducing G proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (17): 6122–5. PMID 3114742.
- Buhl AM, Osawa S, Johnson GL (1995). "Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation requires two signal inputs from the human anaphylatoxin C5a receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (34): 19828–32. PMID 7649993.
- Ray K, Kunsch C, Bonner LM, Robishaw JD (1995). "Isolation of cDNA clones encoding eight different human G protein gamma subunits, including three novel forms designated the gamma 4, gamma 10, and gamma 11 subunits". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (37): 21765–71. PMID 7665596.
- Pumiglia KM, LeVine H, Haske T; et al. (1995). "A direct interaction between G-protein beta gamma subunits and the Raf-1 protein kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (24): 14251–4. PMID 7782277.
- Ueda N, Iñiguez-Lluhi JA, Lee E; et al. (1994). "G protein beta gamma subunits. Simplified purification and properties of novel isoforms". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (6): 4388–95. PMID 8308009.
- Liang JJ, Cockett M, Khawaja XZ (1998). "Immunohistochemical localization of G protein beta1, beta2, beta3, beta4, beta5, and gamma3 subunits in the adult rat brain". J. Neurochem. 71 (1): 345–55. PMID 9648884.
- Glöckner G, Scherer S, Schattevoy R; et al. (1998). "Large-scale sequencing of two regions in human chromosome 7q22: analysis of 650 kb of genomic sequence around the EPO and CUTL1 loci reveals 17 genes". Genome Res. 8 (10): 1060–73. PMID 9799793.
- Kleiderlein JJ, Nisson PE, Jessee J; et al. (1999). "CCG repeats in cDNAs from human brain". Hum. Genet. 103 (6): 666–73. PMID 9921901.
- Asano T, Morishita R, Ueda H, Kato K (1999). "Selective association of G protein beta(4) with gamma(5) and gamma(12) subunits in bovine tissues". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (30): 21425–9. PMID 10409705.
- Suzuki H, Fukunishi Y, Kagawa I; et al. (2001). "Protein-protein interaction panel using mouse full-length cDNAs". Genome Res. 11 (10): 1758–65. doi:10.1101/gr.180101. PMID 11591653.
- Blake BL, Wing MR, Zhou JY; et al. (2002). "G beta association and effector interaction selectivities of the divergent G gamma subunit G gamma(13)". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (52): 49267–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106565200. PMID 11675383.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
- Cuello F, Schulze RA, Heemeyer F; et al. (2003). "Activation of heterotrimeric G proteins by a high energy phosphate transfer via nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) B and Gbeta subunits. Complex formation of NDPK B with Gbeta gamma dimers and phosphorylation of His-266 IN Gbeta". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (9): 7220–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210304200. PMID 12486123.
- Sprague RS, Bowles EA, Olearczyk JJ; et al. (2003). "The role of G protein beta subunits in the release of ATP from human erythrocytes". J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 53 (4 Pt 1): 667–74. PMID 12512701.
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |