Fibrosarcoma: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Risk Factors== | ==Risk Factors== | ||
Common risk factors in the development of Fibrosarcoma are preexisting benign lesions such as | Common risk factors in the development of Fibrosarcoma are preexisting benign lesions such as giant cell tumor, [[enchondroma]], [[fibrous dysplasia]], bizarre parosteal osteochondromatous proliferation or chronic osteomyelitis. Other risk factors include [[Paget's disease]], radiation therapy, surgically treated fracture and infarction of bone . | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 01:12, 21 August 2015
|
WikiDoc Resources for Fibrosarcoma |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Fibrosarcoma Most cited articles on Fibrosarcoma |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Fibrosarcoma |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Fibrosarcoma at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Fibrosarcoma at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Fibrosarcoma
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Fibrosarcoma Discussion groups on Fibrosarcoma Patient Handouts on Fibrosarcoma Directions to Hospitals Treating Fibrosarcoma Risk calculators and risk factors for Fibrosarcoma
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Fibrosarcoma |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Malignant fibromatous neoplasm, fibroblastic sarcoma
Overview
Fibrosarcoma (fibroblastic sarcoma) is a malignant tumor derived from fibrous connective tissue and characterized by immature proliferating fibroblasts or undifferentiated anaplastic spindle cells.
Classificaion
Fibrosarcoma may be classified according to degrees of differentiation into three subtypes: low grade malignancy (differentiated), intermediate malignancy and high grade malignancy (anaplastic)
Pathophysiology
Tumor cells may resemble mature fibroblasts (spindle-shaped), secreting collagen, with rare mitoses. These cells are arranged in short fascicles which split and merge, giving the appearance of "fish bone". Poorly differentiated tumors consist in more atypical cells, pleomorphic, giant cells, multinucleated, numerous atypical mitoses and reduced collagen production. Presence of immature blood vessels (sarcomatous vessels lacking endothelial cells) favors the bloodstream metastasizing.
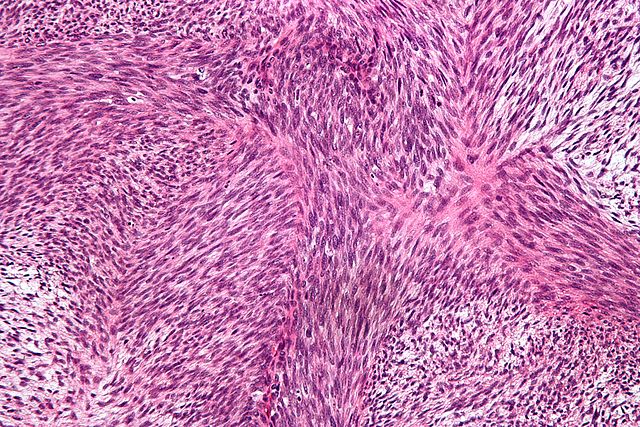 |
Epidemiology and Demographics
Patients of all age groups may develop Fibrosarcoma, but are most common between the third and sixth decades of life. In infants, fibrosarcoma is usually congenital. Infants presenting with fibrosarcoma usually do so in the first two years of their life.
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Prognosis
Fibrosarcoma is associated with a 5 year survival rates of 30% among patients with high grade medullary lesions and 50-80% in surface fibrosarcomas and low grade fibrosarcomas. The presence of eccentric permeative lesions, primary tumor in the axial skeleton is associated with a particularly poor prognosis among patients with fibrosarcoma.
Risk Factors
Common risk factors in the development of Fibrosarcoma are preexisting benign lesions such as giant cell tumor, enchondroma, fibrous dysplasia, bizarre parosteal osteochondromatous proliferation or chronic osteomyelitis. Other risk factors include Paget's disease, radiation therapy, surgically treated fracture and infarction of bone .
See also
References