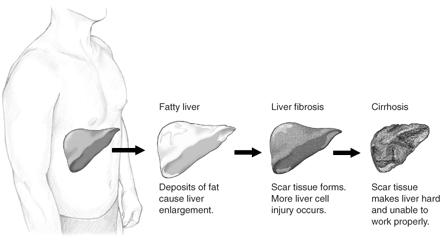
Fatty liver causes
|
Fatty Liver Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Fatty liver causes On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Fatty liver causes |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Causes
Fatty liver is commonly associated with alcohol or metabolic syndrome (diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia) but can also be due to any one of many causes[1][2]:
- Metabolic
- Abetalipoproteinemia, glycogen storage diseases, Weber-Christian disease, Wolmans disease, acute fatty liver of pregnancy, lipodystrophy
- Nutritional
- Malnutrition, total parenteral nutrition, severe weight loss, refeeding syndrome, jejuno-ileal bypass, gastric bypass, jejunal diverticulosis with bacterial overgrowth
- Drugs and toxins
- Amiodarone, methotrexate, diltiazem, highly active antiretroviral therapy, glucocorticoids, tamoxifen, environmental hepatotoxins (e.g. phosphorus, toxic mushroom)
- Other
- Inflammatory bowel disease, HIV