Fatty liver causes: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ {{Fatty liver}} {{CMG}} ==Causes == Fatty liver is commonly associated with alcohol or metabolic syndrome (diabetes, hypertension and [[dyslipidemia...") |
(→Causes) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Causes == | ==Causes == | ||
Fatty liver is commonly associated with [[alcohol]] or [[metabolic syndrome]] ([[diabetes]], [[hypertension]] and [[dyslipidemia]]) but can also be due to any one of many causes<ref name="angulo"/><ref name="bayard"/>: | Fatty liver is commonly associated with [[alcohol]] or [[metabolic syndrome]] ([[diabetes]], [[hypertension]] and [[dyslipidemia]]) but can also be due to any one of many causes<ref name="angulo"/><ref name="bayard"/>: | ||
*Metabolic: [[Abetalipoproteinemia]], [[glycogen storage disease]]s, [[Weber-Christian disease]], [[Wolman disease|Wolmans disease]], [[acute fatty liver of pregnancy]], [[lipodystrophy]] | |||
*Nutritional:[[Malnutrition]], [[total parenteral nutrition]], severe [[weight loss]], [[refeeding syndrome]], [[jejuno-ileal bypass]], [[Gastric bypass surgery|gastric bypass]], jejunal [[diverticulosis]] with [[Small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome|bacterial overgrowth]] | |||
*Drugs and toxins:[[Amiodarone]], [[methotrexate]], [[diltiazem]], [[highly active antiretroviral therapy]], [[glucocorticoids]], [[tamoxifen]], environmental [[hepatotoxin]]s (e.g. [[phosphorus]], toxic [[mushroom]]) | |||
*Other:[[Inflammatory bowel disease]], [[HIV]] | |||
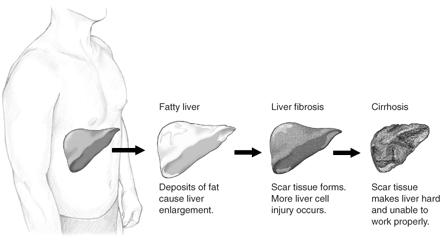
[[Image:Stage of liver damage.JPG|thumb|left|Different stages of liver damage]] | [[Image:Stage of liver damage.JPG|thumb|left|Different stages of liver damage]] | ||
Revision as of 21:27, 20 November 2012
|
Fatty Liver Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Fatty liver causes On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Fatty liver causes |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Causes
Fatty liver is commonly associated with alcohol or metabolic syndrome (diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia) but can also be due to any one of many causes[1][2]:
- Metabolic: Abetalipoproteinemia, glycogen storage diseases, Weber-Christian disease, Wolmans disease, acute fatty liver of pregnancy, lipodystrophy
- Nutritional:Malnutrition, total parenteral nutrition, severe weight loss, refeeding syndrome, jejuno-ileal bypass, gastric bypass, jejunal diverticulosis with bacterial overgrowth
- Drugs and toxins:Amiodarone, methotrexate, diltiazem, highly active antiretroviral therapy, glucocorticoids, tamoxifen, environmental hepatotoxins (e.g. phosphorus, toxic mushroom)
- Other:Inflammatory bowel disease, HIV