Ethanolamine oleate: Difference between revisions
Kiran Singh (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kiran Singh (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|indicationType=treatment | |indicationType=treatment | ||
|indication=bleeding esophageal varices | |indication=bleeding esophageal varices | ||
|adverseReactions=[[pleural effusion]], | |adverseReactions=[[pleural effusion]], retrosternal pain, [[esophageal ulcer]], [[fever]] and [[stricture]] | ||
|blackBoxWarningTitle=<span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span> | |blackBoxWarningTitle=<span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span> | ||
|blackBoxWarningBody=<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | |blackBoxWarningBody=<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
* The practice of injecting varicosities of the leg with ETHAMOLlN Injection is not supported by adequately-controlled clinical trials. Therefore, such use is not recommended. | * The practice of injecting varicosities of the leg with ETHAMOLlN Injection is not supported by adequately-controlled clinical trials. Therefore, such use is not recommended. | ||
|clinicalTrials=* The reported frequency of complications/adverse events per injection session was 13%. The most common complications were [[pleural effusion]]/infiltration (2.1%), [[esophageal ulcer]] (2.1 %), [[pyrexia]] (1.8%), | |clinicalTrials=* The reported frequency of complications/adverse events per injection session was 13%. The most common complications were [[pleural effusion]]/infiltration (2.1%), [[esophageal ulcer]] (2.1 %), [[pyrexia]] (1.8%), retrosterual pain (1.6%), [[esophageal stricture]] .(1.3%), and [[pneumonia]] (1.2%). | ||
* Other adverse local esophageal reactions have also been reported at rates of 0.1 to 0.4%, including [[esophagitis]], tearing of the esophagus, sloughing of the mucosa overlying the injected varix, [[ulceration]], [[stricture]], [[necrosis]], periesophageal abscess and perforation. These complications appear to be dependent upon the dose and the patient's clinical state. | * Other adverse local esophageal reactions have also been reported at rates of 0.1 to 0.4%, including [[esophagitis]], tearing of the esophagus, sloughing of the mucosa overlying the injected varix, [[ulceration]], [[stricture]], [[necrosis]], periesophageal abscess and perforation. These complications appear to be dependent upon the dose and the patient's clinical state. | ||
* Bacteremia has been observed in patients following injection of [[esophageal varices]] with ETHAMOLlN. [[Pyrexia]] and | * Bacteremia has been observed in patients following injection of [[esophageal varices]] with ETHAMOLlN. [[Pyrexia]] and retrosternal pain are not infrequently observed during the post-injection period. Fatal aspiration pneumonia has occurred in patients with [[esophageal varices]] who underwent ETHAMOLIN Injection [[Sclerotherapy]]. [[Anaphylactic shock]] and acute renal failure with spontaneous recovery have occurred . A case of [[disseminated intravascular coagulation]] has been reported. | ||
* Spinal cord paralysis due to occlusion of the anterior spinal artery has been reported in one child eight hours after ETHAMOLIN sclerotherapy | * Spinal cord paralysis due to occlusion of the anterior spinal artery has been reported in one child eight hours after ETHAMOLIN sclerotherapy | ||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
<!--Category--> | <!--Category--> | ||
[[Category:Drug]] | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
Revision as of 19:22, 30 March 2015
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag=Kiran Singh, M.D. [1] |genericName=ethanolamine oleate |aOrAn=a |drugClass=cardiovascular agent |indicationType=treatment |indication=bleeding esophageal varices |adverseReactions=pleural effusion, retrosternal pain, esophageal ulcer, fever and stricture |blackBoxWarningTitle=ConditionName: |blackBoxWarningBody=ConditionName:
- Content
|fdaLIADAdult===Indications==
- ETHAMOLIN Injection is indicated for the treatment of patients with esophageal varices that have recently bled, to prevent rebleeding.
Dosage
- Local ETHAMOLIN Injection sclerotherapy of esophageal varices should be performed by physicians who are famillar with an acceptable technique. The usual intravenous dose is 1.5 to 5.0 mL per varix. The maximum dose per treatment session should not exceed 20 mL. Patients with significant liver dysfunction (Child Class C) or concomitant cardiopulmonary disease should usually receive less than the recommended maximum dose. Submucosal injections are not recommended, as they reportedly are more likely to result in ulceration at the site of injection.
- To obliterate the varix, injections may be made at the time of theacute bleeding episode and then after oIie week, six weeks, three months, and six months, as indicated.
- Note: Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration whenever solution and container permit.
- ETHAMOLIN is not indicated for the treatment of patients with esophageal varices that have not bled. There is no evidence that treatment of this population decreases the likelihood of bleeding.
- Sclerotherapy with ETHAMOLIN has no beneficial effect upon portal hypertension, the cause of esophageal varices, so that recanalization and collateralization may occur, necessitating reinjection.
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport=* There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ethanolamine oleate in adult patients. |offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=* There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ethanolamine oleate in adult patients. |fdaLIADPed=* There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Ethanolamine oleate in pediatric patients. |offLabelPedGuideSupport=* There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ethanolamine oleate in pediatric patients. |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=* There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ethanolamine oleate in pediatric patients. |contraindications=* ETHAMOLIN Injection should not be administered to subjects with a known hypersensitivity to ethanolamine, oleic acid, or ethanolamine oleate. |warnings=* ETHAMOLlN Injection should be used in pregnant women only when clearly needed.
- The practice of injecting varicosities of the leg with ETHAMOLlN Injection is not supported by adequately-controlled clinical trials. Therefore, such use is not recommended.
|clinicalTrials=* The reported frequency of complications/adverse events per injection session was 13%. The most common complications were pleural effusion/infiltration (2.1%), esophageal ulcer (2.1 %), pyrexia (1.8%), retrosterual pain (1.6%), esophageal stricture .(1.3%), and pneumonia (1.2%).
- Other adverse local esophageal reactions have also been reported at rates of 0.1 to 0.4%, including esophagitis, tearing of the esophagus, sloughing of the mucosa overlying the injected varix, ulceration, stricture, necrosis, periesophageal abscess and perforation. These complications appear to be dependent upon the dose and the patient's clinical state.
- Bacteremia has been observed in patients following injection of esophageal varices with ETHAMOLlN. Pyrexia and retrosternal pain are not infrequently observed during the post-injection period. Fatal aspiration pneumonia has occurred in patients with esophageal varices who underwent ETHAMOLIN Injection Sclerotherapy. Anaphylactic shock and acute renal failure with spontaneous recovery have occurred . A case of disseminated intravascular coagulation has been reported.
- Spinal cord paralysis due to occlusion of the anterior spinal artery has been reported in one child eight hours after ETHAMOLIN sclerotherapy
|postmarketing=* There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Ethanolamine oleate in the drug label. |useInPregnancyFDA=Pregnancy: (Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C)
- Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with ETHAMOLlN Injection. It is also not known whether ETHAMOLIN Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. ETHAMOLIN Injection should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
|useInPregnancyAUS=* There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Ethanolamine oleate in women who are pregnant. |useInLaborDelivery=* There is no FDA guidance on use of Ethanolamine oleate during labor and delivery. |useInNursing=* It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ETHAMOLlN Injection is administered to a nursing woman. |useInPed=* Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established |useInGeri=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethanolamine oleate with respect to geriatric patients. |useInGender=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethanolamine oleate with respect to specific gender populations. |useInRace=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethanolamine oleate with respect to specific racial populations. |useInRenalImpair=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethanolamine oleate in patients with renal impairment. |useInHepaticImpair=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethanolamine oleate in patients with hepatic impairment. |useInReproPotential=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ethanolamine oleate in women of reproductive potentials and males. |useInImmunocomp=There is no FDA guidance one the use of Ethanolamine oleate in patients who are immunocompromised.
|administration=* Oral
- Intravenous
|monitoring=There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Ethanolamine oleate in the drug label.
- Description
|IVCompat=There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Ethanolamine oleate in the drug label. |overdose=* Overdosage of ETHAMOLIN Injection can result in severe intramural necrosis of the esophagus. Complications resulting from such overdosage have resulted in death.
|drugBox=*
|structure=* ETHAMOLIN® (Ethanolamine Oleate) Injection is a mild sclerosing agent. Chemically it is C17H33COOH•NH2CH2CH2OH. It has the following structure:
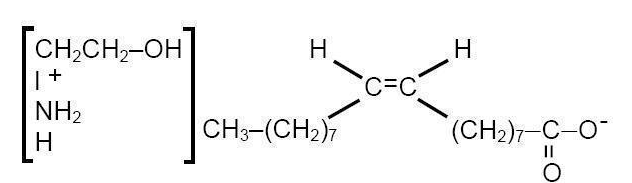
- The empirical formula is C20H41NO3, representing a molecular weight of 343.55.
- ETHAMOLIN Injection consists of ethanolamine, a basic substance, which when combined with oleic acid, forms a clear pale-yellow to straw-colored, deliquescent oleate. The pH ranges from 8.0 to 9.0.
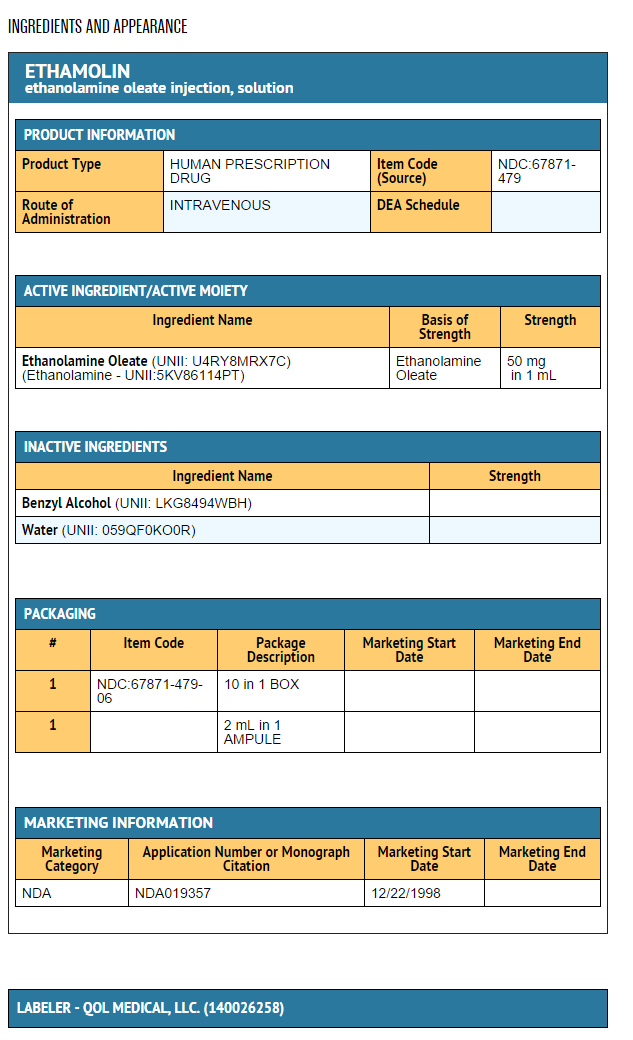
- ETHAMOLIN Injection is a sterile, apyrogenic, aqueous solution containing in each mL approximately 50 mg of ethanolamine oleate with benzyl alcohol 2% by volume as preservative.
|PD=* There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Ethanolamine oleate in the drug label. |PK=There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Ethanolamine oleate in the drug label. |nonClinToxic=There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Ethanolamine oleate in the drug label. |clinicalStudies=There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Ethanolamine oleate in the drug label.
|howSupplied=*
|storage=* Store at controlled room temperature, 15°- 30°C (59°- 86°F). Protect from light.
|packLabel=

|fdaPatientInfo=* There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Ethanolamine oleate in the drug label. |alcohol=* Alcohol-Ethanolamine oleate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
|brandNames=* ETHAMOLIN®[1] |drugShortage= {{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ethanolamine oleate |Label Name=Ethanolamine oleate11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Ethanolamine oleate |Label Name=Ethanolamine oleate11.png
}}