Eseroline
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
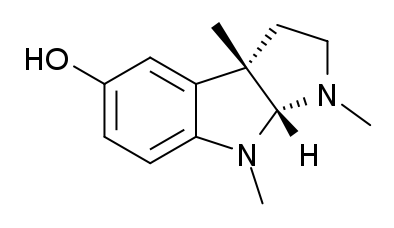 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Eseroline |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H18N2O |
| Molar mass | 218.295 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Overview
Eseroline is a drug which acts as an opioid agonist.[1] It is a metabolite of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor physostigmine but unlike physostigmine, the acetylcholinesterase inhibition produced by eseroline is weak and easily reversible,[2][3] and it produces fairly potent analgesic effects mediated through the μ-opioid receptor.[4] This mixture of activities gives eseroline an unusual pharmacological profile,[5][6] although its uses are limited by side effects such as respiratory depression[7] and neurotoxicity.[8]
References
- ↑ Fürst S, Friedmann T, Bartolini A, Bartolini R, Aiello-Malmberg P, Galli A, Somogyi GT, Knoll J. Direct evidence that eseroline possesses morphine-like effects. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1982 Sep 24;83(3-4):233-41. PMID 6293841
- ↑ Jhamandas K, Elliott J, Sutak M. Opiatelike actions of eseroline, an eserine derivative. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 1981 Mar;59(3):307-10. PMID 7194726
- ↑ Galli A, Renzi G, Grazzini E, Bartolini R, Aiello-Malmberg P, Bartolini A. Reversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by eseroline, an opioid agonist structurally related to physostigmine (eserine) and morphine. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1982 Apr 1;31(7):1233-8. PMID 7092918
- ↑ Agresti A, Buffoni F, Kaufman JJ, Petrongolo C. Structure-activity relationships of eseroline and morphine: ab initio quantum-chemical study of the electrostatic potential and of the interaction energy with water. Molecular Pharmacology. 1980 Nov;18(3):461-7. PMID 7464812
- ↑ Galli A, Ranaudo E, Giannini L, Costagli C. Reversible inhibition of cholinesterases by opioids: possible pharmacological consequences. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 1996 Nov;48(11):1164-8. PMID 8961166
- ↑ Liu WF. Effect of eseroline on schedule-controlled behavior in the rat. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behaviour. 1991 Apr;38(4):747-51. PMID 1871191
- ↑ Berkenbosch A, Rupreht J, DeGoede J, Olievier CN, Wolsink JG. Effects of eseroline on the ventilatory response to CO2. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1993 Feb 23;232(1):21-8. PMID 8458393
- ↑ Somani SM, Kutty RK, Krishna G. Eseroline, a metabolite of physostigmine, induces neuronal cell death. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 1990 Oct;106(1):28-37. PMID 2251681
Categories:
- Pages with script errors
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Opioids