Eplerenone: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 208: | Line 208: | ||
[[File:Eplerenone006.jpg|thumb|400px|none|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | [[File:Eplerenone006.jpg|thumb|400px|none|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
* The table below shows the rates of hyperkalemia in EPHESUS as assessed by two baseline characteristics: presence/absence of proteinuria from baseline urinalysis and presence/absence of diabetes. | * The table below shows the rates of hyperkalemia in EPHESUS as assessed by two baseline characteristics: presence/absence of proteinuria from baseline urinalysis and presence/absence of diabetes. | ||
| Line 223: | Line 222: | ||
* Patients with both type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria are at increased risk of developing persistent hyperkalemia. In a study of such patients taking eplerenone tablets 200 mg, the frequencies of maximum serum potassium levels >5.5 mEq/L were 33% with eplerenone tablets given alone and 38% when eplerenone tablets were given with enalapril. | * Patients with both type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria are at increased risk of developing persistent hyperkalemia. In a study of such patients taking eplerenone tablets 200 mg, the frequencies of maximum serum potassium levels >5.5 mEq/L were 33% with eplerenone tablets given alone and 38% when eplerenone tablets were given with enalapril. | ||
Rates of hyperkalemia increased with decreasing renal function. In all studies, serum potassium elevations >5.5 mEq/L were observed in 10.4% of patients treated with eplerenone tablets with baseline calculated creatinine clearance <70 mL/min, 5.6% of patients with baseline creatinine clearance of 70 to 100 mL/min, and 2.6% of patients with baseline creatinine clearance of >100 mL/min. | Rates of hyperkalemia increased with decreasing renal function. In all studies, serum potassium elevations >5.5 mEq/L were observed in 10.4% of patients treated with eplerenone tablets with baseline calculated creatinine clearance <70 mL/min, 5.6% of patients with baseline creatinine clearance of 70 to 100 mL/min, and 2.6% of patients with baseline creatinine clearance of >100 mL/min. | ||
* Sodium | * Sodium | ||
| Line 235: | Line 233: | ||
:* Serum cholesterol increased in a dose-related manner. Mean changes ranged from a decrease of 0.4 mg/dL at 50 mg daily to an increase of 11.6 mg/dL at 400 mg daily. Increases in serum cholesterol values greater than 200 mg/dL were reported for 0.3% of patients administered eplerenone tablets and 0% of placebo-treated patients. | :* Serum cholesterol increased in a dose-related manner. Mean changes ranged from a decrease of 0.4 mg/dL at 50 mg daily to an increase of 11.6 mg/dL at 400 mg daily. Increases in serum cholesterol values greater than 200 mg/dL were reported for 0.3% of patients administered eplerenone tablets and 0% of placebo-treated patients. | ||
* Liver Function Tests | * Liver Function Tests | ||
Revision as of 01:37, 1 July 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Eplerenone is a aldosterone antagonist that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of hypertension and congestive heart failure after myocardial infarction. Common adverse reactions include hyperkalemia, diarrhea, dizziness, elevated serum creatinine, cough, and fatigue.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Congestive Heart Failure Post-Myocardial Infarction
Eplerenone tablets are indicated to improve survival of stable patients with left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction (ejection fraction ≤40%) and clinical evidence of congestive heart failure (CHF) after an acute myocardial infarction.
- Dosing Information
- Treatment should be initiated at 25 mg once daily and titrated to the recommended dose of 50 mg once daily, preferably within 4 weeks as tolerated by the patient.
- Eplerenone tablets may be administered with or without food.
- Once treatment with eplerenone tablets have begun, adjust the dose based on the serum potassium level as shown in the table below.

Hypertension
- Dosing Information
- The recommended starting dose of eplerenone tablets are 50 mg once daily.
- The full therapeutic effect of eplerenone tablets is apparent within 4 weeks.
- For patients with an inadequate blood pressure response to 50 mg once daily the dosage of eplerenone tablets should be increased to 50 mg twice daily. Higher dosages of eplerenone tablets are not recommended because they have no greater effect on blood pressure than 100 mg and are associated with an increased risk of hyperkalemia.
Dose Modifications for Specific Populations
- Serum potassium levels should be measured before initiating eplerenone tablet therapy, and eplerenone tablets should not be prescribed if serum potassium is >5.5 mEq/L.
- For hypertensive patients receiving moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, saquinavir, verapamil, and fluconazole), the starting dose of eplerenone tablets should be reduced to 25 mg once daily.
- No adjustment of the starting dose is recommended for the elderly or for patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Heart Failure, Myocardial infarction with Complication
- Developed by: American College of Cardiology (ACC) and American Heart Association (AHA)
- Class of Recommendation: Class IIa
- Strength of Evidence: Category A
- Dosing Information
- 25 mg daily initially, titrated to a maximum of 50 mg/day[1]
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Albuminuria in Diabetes Mellitus
- Dosing Information
- 50 mg once daily[2]
Low-Renin Essential Hypertension
- Dosing Information
- 100 mg once daily[3]
Systolic Heart Failure (Mild)
- Dosing Information
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Eplerenone tablets has not been studied in hypertensive patients less than 4 years old because the study in older pediatric patients did not demonstrate effectiveness.
- Eplerenone has not been studied in pediatric patients with heart failure.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Eplerenone in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Eplerenone in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
For All Patients
- Serum potassium >5.5 mEq/L at initiation
- Creatinine clearance ≤30 mL/min
- Concomitant administration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, nefazodone, troleandomycin, clarithromycin, ritonavir, and nelfinavir)
For Patients Treated for Hypertension
- Type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria
- Serum creatinine >2.0 mg/dL in males or >1.8 mg/dL in females
- Creatinine clearance <50 mL/min
- Concomitant administration of potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., amiloride, spironolactone, or triamterene)
Warnings
Hyperkalemia
- Minimize the risk of hyperkalemia with proper patient selection and monitoring, and avoidance of certain concomitant medications. Monitor patients for the development of hyperkalemia until the effect of eplerenone tablets are established. Patients who develop hyperkalemia (>5.5 mEq/L) may continue eplerenone tablets therapy with proper dose adjustment. Dose reduction decreases potassium levels.
- The rates of hyperkalemia increase with declining renal function. Patients with hypertension who have serum creatinine levels >2.0 mg/dL (males) or >1.8 mg/dL (females) or creatinine clearance ≤50 mL/min should not be treated with eplerenone tablets. Patients with CHF post-MI who have serum creatinine levels >2.0 mg/dL (males) or >1.8 mg/dL (females) or creatinine clearance ≤50 mL/min should be treated with eplerenone tablets with caution.
- Diabetic patients with CHF post-MI should also be treated with caution, especially those with proteinuria. The subset of patients in the EPHESUS study with both diabetes and proteinuria on the baseline urinalysis had increased rates of hyperkalemia compared to patients with either diabetes or proteinuria.
- The risk of hyperkalemia may increase when eplerenone is used in combination with an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor and/or an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB).
Impaired Hepatic Function
- Mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment did not increase the incidence of hyperkalemia. In 16 subjects with mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment who received 400 mg of eplerenone, no elevations of serum potassium above 5.5 mEq/L were observed. The mean increase in serum potassium was 0.12 mEq/L in patients with hepatic impairment and 0.13 mEq/L in normal controls. The use of eplerenone tablets in patients with severe hepatic impairment has not been evaluated.
Impaired Renal Function
- Patients with decreased renal function are at increased risk of hyperkalemia.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Congestive Heart Failure Post-Myocardial Infarction
- In EPHESUS, safety was evaluated in 3307 patients treated with eplerenone tablets and 3301 placebo-treated patients. The overall incidence of adverse events reported with eplerenone tablets (78.9%) was similar to placebo (79.5%). Adverse events occurred at a similar rate regardless of age, gender, or race. Patients discontinued treatment due to an adverse event at similar rates in either treatment group (4.4% eplerenone tablets vs. 4.3% placebo), with the most common reasons for discontinuation being hyperkalemia, myocardial infarction, and abnormal renal function.
- Adverse reactions that occurred more frequently in patients treated with eplerenone tablets than placebo were hyperkalemia (3.4% vs. 2.0%) and increased creatinine (2.4% vs. 1.5%). Discontinuations due to hyperkalemia or abnormal renal function were less than 1.0% in both groups. Hypokalemia occurred less frequently in patients treated with eplerenone tablets (0.6% vs. 1.6%).
- The rates of sex hormone-related adverse events are shown in the table below.

Hypertension
- Eplerenone tablets has been evaluated for safety in 3091 patients treated for hypertension. A total of 690 patients were treated for over 6 months and 106 patients were treated for over 1 year.
- In placebo-controlled studies, the overall rates of adverse events were 47% with eplerenone tablets and 45% with placebo. Adverse events occurred at a similar rate regardless of age, gender, or race. Therapy was discontinued due to an adverse event in 3% of patients treated with eplerenone tablets and 3% of patients given placebo. The most common reasons for discontinuation of eplerenone tablets were headache, dizziness, angina pectoris/myocardial infarction, and increased GGT. The adverse events that were reported at a rate of at least 1% of patients and at a higher rate in patients treated with eplerenone tablets in daily doses of 25 to 400 mg versus placebo are shown in the table below.
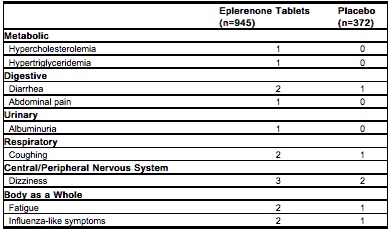
- Gynecomastia and abnormal vaginal bleeding were reported with eplerenone tablets but not with placebo. The rates of these sex hormone-related adverse events are shown in the table below. The rates increased slightly with increasing duration of therapy. In females, abnormal vaginal bleeding was also reported in 0.8% of patients on antihypertensive medications (other than spironolactone) in active control arms of the studies with eplerenone tablets.

Clinical Laboratory Test Findings
Congestive Heart Failure Post-Myocardial Infarction
- Creatinine
- Increases of more than 0.5 mg/dL were reported for 6.5% of patients administered eplerenone tablets and for 4.9% of placebo-treated patients.
- Potassium
- In EPHESUS, the frequencies of patients with changes in potassium (<3.5 mEq/L or >5.5 mEq/L or ≥6.0 mEq/L) receiving eplerenone tablets compared with placebo are displayed in the table below.

- The table below shows the rates of hyperkalemia in EPHESUS as assessed by baseline renal function (creatinine clearance).

- The table below shows the rates of hyperkalemia in EPHESUS as assessed by two baseline characteristics: presence/absence of proteinuria from baseline urinalysis and presence/absence of diabetes.

Hypertension
- Potassium
- In placebo-controlled fixed-dose studies, the mean increases in serum potassium were dose-related and are shown in the table below along with the frequencies of values >5.5 mEq/L.

- Patients with both type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria are at increased risk of developing persistent hyperkalemia. In a study of such patients taking eplerenone tablets 200 mg, the frequencies of maximum serum potassium levels >5.5 mEq/L were 33% with eplerenone tablets given alone and 38% when eplerenone tablets were given with enalapril.
Rates of hyperkalemia increased with decreasing renal function. In all studies, serum potassium elevations >5.5 mEq/L were observed in 10.4% of patients treated with eplerenone tablets with baseline calculated creatinine clearance <70 mL/min, 5.6% of patients with baseline creatinine clearance of 70 to 100 mL/min, and 2.6% of patients with baseline creatinine clearance of >100 mL/min.
- Sodium
- Serum sodium decreased in a dose-related manner. Mean decreases ranged from 0.7 mEq/L at 50 mg daily to 1.7 mEq/L at 400 mg daily. Decreases in sodium (<135 mEq/L) were reported for 2.3% of patients administered eplerenone tablets and 0.6% of placebo-treated patients.
- Triglycerides
- Serum triglycerides increased in a dose-related manner. Mean increases ranged from 7.1 mg/dL at 50 mg daily to 26.6 mg/dL at 400 mg daily. Increases in triglycerides (above 252 mg/dL) were reported for 15% of patients administered eplerenone tablets and 12% of placebo-treated patients.
- Cholesterol
- Serum cholesterol increased in a dose-related manner. Mean changes ranged from a decrease of 0.4 mg/dL at 50 mg daily to an increase of 11.6 mg/dL at 400 mg daily. Increases in serum cholesterol values greater than 200 mg/dL were reported for 0.3% of patients administered eplerenone tablets and 0% of placebo-treated patients.
- Liver Function Tests
- Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) increased in a dose-related manner. Mean increases ranged from 0.8 U/L at 50 mg daily to 4.8 U/L at 400 mg daily for ALT and 3.1 U/L at 50 mg daily to 11.3 U/L at 400 mg daily for GGT. Increases in ALT levels greater than 120 U/L (3 times upper limit of normal) were reported for 15/2259 patients administered eplerenone tablets and 1/351 placebo-treated patients. Increases in ALT levels greater than 200 U/L (5 times upper limit of normal) were reported for 5/2259 of patients administered eplerenone tablets and 1/351 placebo-treated patients. Increases of ALT greater than 120 U/L and bilirubin greater than 1.2 mg/dL were reported 1/2259 patients administered eplerenone tablets and 0/351 placebo-treated patients. Hepatic failure was not reported in patients receiving eplerenone tablets.
BUN/Creatinine: Serum creatinine increased in a dose-related manner. Mean increases ranged from 0.01 mg/dL at 50 mg daily to 0.03 mg/dL at 400 mg daily. Increases in blood urea nitrogen to greater than 30 mg/dL and serum creatinine to greater than 2 mg/dL were reported for 0.5% and 0.2%, respectively, of patients administered eplerenone tablets and 0% of placebo-treated patients.
- Uric Acid
- Increases in uric acid to greater than 9 mg/dL were reported in 0.3% of patients administered eplerenone tablets and 0% of placebo-treated patients.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of eplerenone tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Eplerenone in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Eplerenone during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eplerenone with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eplerenone with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eplerenone with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eplerenone with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eplerenone with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eplerenone in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eplerenone in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eplerenone in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Eplerenone in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Oral
Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Eplerenone in the drug label.
Condition1
Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Eplerenone in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
Description
Management
Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Eplerenone in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Eplerenone Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Eplerenone Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Structure of Eplerenone in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Eplerenone in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Eplerenone in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Eplerenone in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Eplerenone in the drug label.
Condition1
Description
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Eplerenone How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Eplerenone Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Eplerenone |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Eplerenone |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Eplerenone in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Eplerenone interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
Inspra®
Look-Alike Drug Names
- Inspra® — Spiriva®[6]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Pitt, Bertram; Remme, Willem; Zannad, Faiez; Neaton, James; Martinez, Felipe; Roniker, Barbara; Bittman, Richard; Hurley, Steve; Kleiman, Jay; Gatlin, Marjorie (2003). "Eplerenone, a Selective Aldosterone Blocker, in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction after Myocardial Infarction". New England Journal of Medicine. 348 (14): 1309–1321. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030207. ISSN 0028-4793.
- ↑ Epstein, M. (2006). "Selective Aldosterone Blockade with Eplerenone Reduces Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes". Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 1 (5): 940–951. doi:10.2215/CJN.00240106. ISSN 1555-9041.
- ↑ Weinberger, Myron H.; White, William B.; Ruilope, Luis-Miguel; MacDonald, Thomas M.; Davidson, Robert C.; Roniker, Barbara; Patrick, Jeffrey L.; Krause, Scott L. (2005). "Effects of eplerenone versus losartan in patients with low-renin hypertension". American Heart Journal. 150 (3): 426–433. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2004.12.005. ISSN 0002-8703.
- ↑ Zannad, Faiez; McMurray, John J.V.; Krum, Henry; van Veldhuisen, Dirk J.; Swedberg, Karl; Shi, Harry; Vincent, John; Pocock, Stuart J.; Pitt, Bertram (2011). "Eplerenone in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure and Mild Symptoms". New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (1): 11–21. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1009492. ISSN 0028-4793.
- ↑ Swedberg, Karl; Zannad, Faiez; McMurray, John J.V.; Krum, Henry; van Veldhuisen, Dirk J.; Shi, Harry; Vincent, John; Pitt, Bertram (2012). "Eplerenone and Atrial Fibrillation in Mild Systolic Heart Failure". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 59 (18): 1598–1603. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.11.063. ISSN 0735-1097.
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Eplerenone |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Eplerenone |Label Name=No image.jpg
}}