Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alonso Alvarado, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS/SEVERE HEPATOMEGALY WITH STEATOSIS and POST TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
LACTIC ACIDOSIS/SEVERE HEPATOMEGALY WITH STEATOSIS and POST TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B: Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, a component of STRIBILD, in combination with other antiretrovirals.
STRIBILD is not approved for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and the safety and efficacy of STRIBILD have not been established in patients coinfected with HBV and HIV-1. Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HBV and human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) and have discontinued EMTRIVA or VIREAD, which are components of STRIBILD. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and discontinue STRIBILD. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted
|
Overview
Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate is a atiretroviral that is FDA approved for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults who are antiretroviral treatment-naïve. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include a list of adverse reactions, separated by commas..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Dosage Information
The recommended dosage of STRIBILD is one tablet taken orally once daily with food.
Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment
Initiation of STRIBILD in patients with estimated creatinine clearance below 70 mL per minute is not recommended. Because STRIBILD is a fixed-dose combination tablet, STRIBILD should be discontinued if estimated creatinine clearance declines below 50 mL per min during treatment with STRIBILD as dose interval adjustment required for emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DF) cannot be achieved.
Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of STRIBILD is required in patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. No pharmacokinetic or safety data are available regarding the use of STRIBILD in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). Therefore, STRIBILD is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Testing Prior to Initiation of STRIBILD
Prior to initiation of STRIBILD, patients should be tested for hepatitis B infection and estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose and urine protein should be documented in all patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
Coadministration of STRIBILD is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events. These drugs and other contraindicated drugs (which may lead to reduced efficacy of STRIBILD and possible resistance) are listed in Table 1
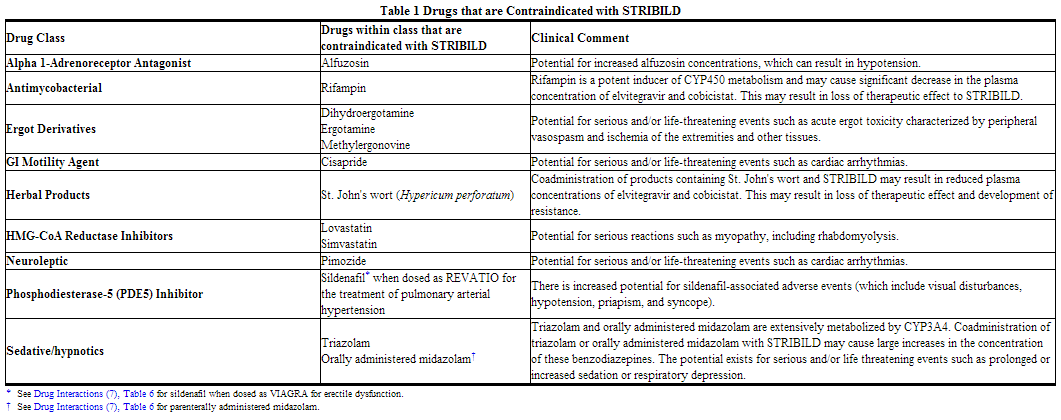
Warnings
|
WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS/SEVERE HEPATOMEGALY WITH STEATOSIS and POST TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
LACTIC ACIDOSIS/SEVERE HEPATOMEGALY WITH STEATOSIS and POST TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B: Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, a component of STRIBILD, in combination with other antiretrovirals.
STRIBILD is not approved for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and the safety and efficacy of STRIBILD have not been established in patients coinfected with HBV and HIV-1. Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HBV and human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) and have discontinued EMTRIVA or VIREAD, which are components of STRIBILD. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and discontinue STRIBILD. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted
|
Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including tenofovir DF, a component of STRIBILD, in combination with other antiretrovirals. A majority of these cases have been in women. Obesity and prolonged nucleoside exposure may be risk factors. Particular caution should be exercised when administering nucleoside analogs to any patient with known risk factors for liver disease; however, cases have also been reported in patients with no known risk factors. Treatment with STRIBILD should be suspended in any patient who develops clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity (which may include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked transaminase elevations).
Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV
It is recommended that all patients with HIV-1 be tested for the presence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) before initiating antiretroviral therapy. STRIBILD is not approved for the treatment of chronic HBV infection and the safety and efficacy of STRIBILD have not been established in patients coinfected with HBV and HIV-1. Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HBV and HIV-1 and have discontinued emtricitabine or tenofovir DF, two of the components of STRIBILD. In some patients infected with HBV and treated with EMTRIVA, the exacerbations of hepatitis B were associated with liver decompensation and liver failure. Patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV should be closely monitored with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months after stopping treatment with STRIBILD. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted.
New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Renal impairment, including cases of acute renal failure and Fanconi syndrome (renal tubular injury with severe hypophosphatemia), has been reported with the use of tenofovir DF, a component of STRIBILD, and with the use of STRIBILD.
In the clinical trials of STRIBILD over 96 weeks, 10 (1.4%) subjects in the STRIBILD group (N=701) and 2 (0.3%) subjects in the combined comparator groups (N = 707) discontinued study drug due to a renal adverse reaction. Of these discontinuations, 8 in the STRIBILD group and 1 in the combined comparator groups occurred during the first 48 week. Four (0.6%) of the subjects who received STRIBILD developed laboratory findings consistent with proximal renal tubular dysfunction leading to discontinuation of STRIBILD compared to none in the comparator groups. Two of these four subjects had renal impairment (i.e. estimated creatinine clearance less than 70 mL per minute) at baseline. The laboratory findings in these 4 subjects with evidence of proximal tubulopathy improved but did not completely resolve in all subjects upon discontinuation of STRIBILD. Renal replacement therapy was not required for these subjects. Estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose and urine protein should be documented in all patients prior to initiating therapy. Initiation of STRIBILD in patients with estimated creatinine clearance below 70 mL per minute is not recommended.
STRIBILD should be avoided with concurrent or recent use of a nephrotoxic agent (e.g., high-dose or multiple non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)). Cases of acute renal failure after initiation of high dose or multiple NSAIDs have been reported in HIV-infected patients with risk factors for renal dysfunction who appeared stable on tenofovir DF. Some patients required hospitalization and renal replacement therapy. Alternatives to NSAIDs should be considered, if needed, in patients at risk for renal dysfunction.
Persistent or worsening bone pain, pain in extremities, fractures and/or muscular pain or weakness may be manifestations of proximal renal tubulopathy and should prompt an evaluation of renal function in at-risk patients.
Routine monitoring of estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein should be performed during STRIBILD therapy in all patients. Additionally, serum phosphorus should be measured in patients at risk for renal impairment. Although cobicistat (a component of STRIBILD) may cause modest increases in serum creatinine and modest declines in estimated creatinine clearance without affecting renal glomerular function, patients who experience a confirmed increase in serum creatinine of greater than 0.4 mg per dL from baseline should be closely monitored for renal safety.
The emtricitabine and tenofovir DF components of STRIBILD are primarily excreted by the kidney. STRIBILD should be discontinued if estimated creatinine clearance declines below 50 mL per minute as dose interval adjustment required for emtricitabine and tenofovir DF cannot be achieved with the fixed-dose combination tablet.
Avoid Use with Other Antiretroviral Products
STRIBILD is indicated for use as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection and coadministration with other antiretroviral products is not recommended.
STRIBILD is not recommended for coadministration with the following: emtricitabine or tenofovir DF (ATRIPLA, COMPLERA, EMTRIVA, TRUVADA, VIREAD); products containing lamivudine (COMBIVIR, EPIVIR, EPIVIR-HBV, EPZICOM, TRIZIVIR) or adefovir dipivoxil (HEPSERA); ritonavir (NORVIR, KALETRA).
Bone Effects of Tenofovir DF
Bone Mineral Density
In clinical trials in HIV-1 infected adults, tenofovir DF (a component of STRIBILD) was associated with slightly greater decreases in bone mineral density (BMD) and increases in biochemical markers of bone metabolism, suggesting increased bone turnover relative to comparators. Serum parathyroid hormone levels and 1.25 Vitamin D levels were also higher in subjects receiving tenofovir DF. For additional information, see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and consult the VIREAD prescribing information.
The effects of tenofovir DF-associated changes in BMD and biochemical markers on long-term bone health and future fracture risk are unknown. Assessment of BMD should be considered for HIV-1 infected patients who have a history of pathologic bone fracture or other risk factors for osteoporosis or bone loss. Although the effect of supplementation with calcium and vitamin D was not studied, such supplementation may be beneficial in all patients. If bone abnormalities are suspected, then appropriate consultation should be obtained.
Mineralization Defects
Cases of osteomalacia associated with proximal renal tubulopathy, manifested as bone pain or pain in extremities and which may contribute to fractures, have been reported in association with the use of tenofovir DF. Arthralgias and muscle pain or weakness have also been reported in cases of proximal renal tubulopathy. Hypophosphatemia and osteomalacia secondary to proximal renal tubulopathy should be considered in patients at risk of renal dysfunction who present with persistent or worsening bone or muscle symptoms while receiving products containing tenofovir DF.
Fat Redistribution
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and "cushingoid appearance" have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including STRIBILD. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections [such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP), or tuberculosis], which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution, however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Condition 2
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
(Description)
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
(Oral/Intravenous/etc)
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
Solution
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Y-Site
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Admixture
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Syringe
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
TPN/TNA
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Chronic Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Pharmacology
Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
(Description)
Structure
(Description with picture)
Pharmacodynamics
(Description)
Pharmacokinetics
(Description)
Nonclinical Toxicology
(Description)
Clinical Studies
Condition 1
(Description)
Condition 2
(Description)
Condition 3
(Description)
How Supplied
(Description)
Storage
There is limited information regarding Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
(Patient Counseling Information)
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Elvitegravir, Cobicistat, Emtricitabine, And Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
- (Paired Confused Name 1a) — (Paired Confused Name 1b)
- (Paired Confused Name 2a) — (Paired Confused Name 2b)
- (Paired Confused Name 3a) — (Paired Confused Name 3b)
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.