Dupilumab
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sonya Gelfand
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Dupilumab is a human monoclonal IgG4 antibody that is FDA approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. Common adverse reactions include injection site reactions, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, oral herpes, keratitis, eye pruritus, other herpes simplex virus infection, and dry eye.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Warnings
Conidition 1
(Description)
Conidition 2
(Description)
Conidition 3
(Description)
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Condition 2
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Dupilumab in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)g
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
(Oral/Intravenous/etc)
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Dupilumab and IV administrations.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Chronic Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Pharmacology
Dupilumab
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
- Dupilumab is a human monoclonal IgG4 antibody that inhibits interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13) signaling by specifically binding to the IL-4Rα subunit shared by the IL-4 and IL-13 receptor complexes. Dupilumab inhibits IL-4 signaling via the Type I receptor and both IL-4 and IL-13 signaling through the Type II receptor.
- Blocking IL-4Rα with dupilumab inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 cytokine-induced responses, including the release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and IgE.
Structure
(Description with picture)
Pharmacodynamics
- Consistent with receptor blockade, serum levels of IL-4 and IL-13 were increased following dupilumab treatment. The relationship between the pharmacodynamic activity and the mechanism(s) by which dupilumab exerts its clinical effects is unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
- Following an initial subcutaneous (SC) dose of 600 mg, dupilumab reached peak mean ±SD concentrations (Cmax) of 70.1±24.1 mcg/mL by approximately 1 week post dose.
- Steady-state concentrations were achieved by Week 16 following the administration of 600 mg starting dose and 300 mg dose either weekly (twice the recommended dosing frequency) or every other week. Across clinical trials, the mean ±SD steady-state trough concentrations ranged from 73.3±40.0 mcg/mL to 79.9±41.4 mcg/mL for 300 mg administered every 2 weeks and from 173±75.9 mcg/mL to 193±77.0 mcg/mL for 300 mg administered weekly.
- The bioavailability of dupilumab following a SC dose is estimated to be 64%.
Distribution
- The estimated total volume of distribution was approximately 4.8±1.3 L.
Elimination
- The metabolic pathway of dupilumab has not been characterized. As a human monoclonal IgG4 antibody, dupilumab is expected to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathways in the same manner as endogenous IgG. After the last steady-state dose of 300 mg Q2W or 300 mg QW dupilumab, the median times to non-detectable concentration (<78 ng/mL) are 10 and 13 weeks, respectively.
Dose Linearity
- Dupilumab exhibited nonlinear target-mediated pharmacokinetics with exposures increasing in a greater than dose-proportional manner. The systemic exposure increased by 30-fold when the dose increased 8-fold following a single dose of dupilumab from 75 mg to 600 mg (i.e., 0.25-times to 2-times the recommended dose).
Weight
- Dupilumab trough concentrations were lower in subjects with higher body weight.
Immunogenicity
- Development of antibodies to dupilumab was associated with lower serum dupilumab concentrations. A few subjects who had high antibody titers also had no detectable serum dupilumab concentrations.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
- In subjects who are 65 years and older, the mean ±SD steady-state trough concentrations of dupilumab were 69.4±31.4 mcg/mL and 166±62.3 mcg/mL, respectively, for 300 mg administered every 2 weeks and weekly. No dose adjustment in this population is recommended.
Renal or Hepatic Impairment
- No formal trial of the effect of hepatic or renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of dupilumab was conducted.
Drug Interaction Studies
Cytochrome P450 Substrates
- The effects of dupilumab on the pharmacokinetics of midazolam (metabolized by CYP3A4), warfarin (metabolized by CYP2C9), omeprazole (metabolized by CYP2C19), metoprolol (metabolized by CYP2D6), and caffeine (metabolized by CYP1A2) were evaluated in a study with 12-13 evaluable subjects with atopic dermatitis (a SC loading dose of 600 mg followed by 300 mg SC weekly for six weeks). No clinically significant changes in AUC were observed. The largest effect was observed for metoprolol (CYP2D6) with an increase in AUC of 29%.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Animal studies have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of dupilumab.
- No effects on fertility parameters such as reproductive organs, menstrual cycle length, or sperm analysis were observed in sexually mature mice that were subcutaneously administered a homologous antibody against IL-4Rα at doses up to 200 mg/kg/week.
Clinical Studies
- Three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Trials 1, 2, and 3) enrolled a total of 2119 subjects 18 years of age and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) not adequately controlled by topical medication(s). Disease severity was defined by an Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) score ≥3 in the overall assessment of AD lesions on a severity scale of 0 to 4, an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score ≥16 on a scale of 0 to 72, and a minimum body surface area involvement of ≥10%. At baseline, 59% of subjects were male, 67% were white, 52% of subjects had a baseline IGA score of 3 (moderate AD), and 48% of subjects had a baseline IGA of 4 (severe AD). The baseline mean EASI score was 33 and the baseline weekly averaged peak pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) was 7 on a scale of 0-10.
- In all three trials, subjects in the dupilumab group received subcutaneous injections of dupilumab 600 mg at Week 0, followed by 300 mg every other week (Q2W). In the monotherapy trials (Trials 1 and 2), subjects received dupilumab or placebo for 16 weeks.
- In the concomitant therapy trial (Trial 3), subjects received dupilumab or placebo with concomitant topical corticosteroids (TCS) and as needed topical calcineurin inhibitors for problem areas only, such as the face, neck, intertriginous and genital areas for 52 weeks.
- All three trials assessed the primary endpoint, the change from baseline to Week 16 in the proportion of subjects with an IGA 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) and at least a 2-point improvement. Other endpoints included the proportion of subjects with EASI-75 (improvement of at least 75% in EASI score from baseline), and reduction in itch as defined by at least a 4-point improvement in the peak pruritus NRS from baseline to Week 16.
Clinical Response at Week 16 (Trials 1, 2, and 3)
- The results of the DUPIXENT monotherapy trials (Trials 1 and 2) and the DUPIXENT with concomitant TCS trial (Trial 3) are presented in Table 2.


- In Trial 3, of the 421 subjects, 353 had been on study for 52 weeks at the time of data analysis. Of these 353 subjects, responders at Week 52 represent a mixture of subjects who maintained their efficacy from Week 16 (e.g., 53% of dupilumab IGA 0 or 1 responders at Week 16 remained responders at Week 52) and subjects who were non-responders at Week 16 who later responded to treatment (e.g., 24% of dupilumab IGA 0 or 1 non-responders at Week 16 became responders at Week 52). Results of supportive analyses of the 353 subjects in the dupilumab with concomitant TCS trial (Trial 3) are presented in Table 3.
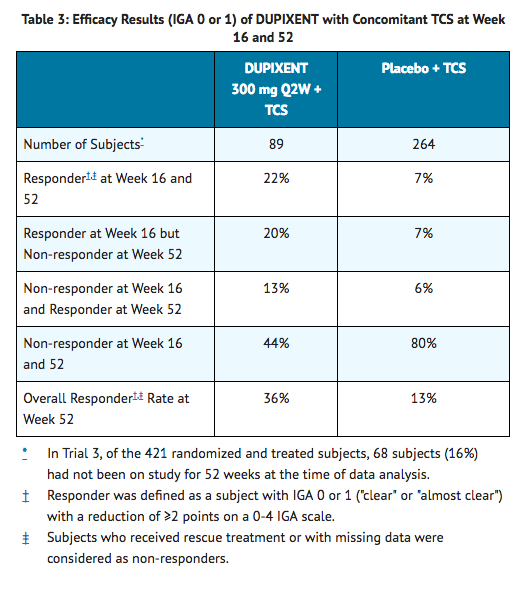
- Treatment effects in subgroups (weight, age, gender, race, and prior treatment, including immunosuppressants) in Trials 1, 2, and 3 were generally consistent with the results in the overall study population.
- In Trials 1, 2, and 3, a third randomized treatment arm of dupilumab 300 mg QW did not demonstrate additional treatment benefit over dupilumab 300 mg Q2W.
- Subjects in Trials 1 and 2 who had an IGA 0 or 1 with a reduction of ≥2 points were re-randomized into Trial 5. Trial 5 evaluated multiple dupilumab monotherapy dose regimens for maintaining treatment response. The study included subjects randomized to continue with dupilumab 300 mg Q2W (62 subjects) or switch to placebo (31 subjects) for 36 weeks. IGA 0 or 1 responses at Week 36 were as follows: 33 (53%) in the Q2W group and 3 (10%) in the placebo group.
How Supplied
- Dupilumab Injection is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution, supplied in single-dose pre-filled syringes with needle shield. Each pre-filled syringe with needle shield is designed to deliver 300 mg of dupilumab in 2 mL solution.
- Dupilumab is available in cartons containing 2 pre-filled syringes with needle shield.

Storage
- Dupilumab is sterile and preservative-free. Discard any unused portion.
- Store refrigerated at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in the original carton to protect from light.
- If necessary, pre-filled syringes may be kept at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) for a maximum of 14 days. Do not store above 77°F (25°C). After removal from the refrigerator, dupilumab must be used within 14 days or discarded.
- Do not expose the syringe to heat or direct sunlight.
- Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
- Do NOT freeze. Do NOT expose to heat. Do NOT shake
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Dupilumab |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel


{{#ask: Label Page::Dupilumab |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Advise the patients and/or caregivers to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use) before the patient starts using dupilumab and each time the prescription is renewed as there may be new information they need to know.
Administration Instructions
- Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on proper subcutaneous injection technique, including aseptic technique, and the preparation and administration of dupilumab prior to use. Advise patients to follow sharps disposal recommendations.
Hypersensitivity
- Advise patients to discontinue dupilumab and to seek immediate medical attention if they experience any symptoms of systemic hypersensitivity reactions.
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis
- Advise patients to consult their healthcare provider if new onset or worsening eye symptoms develop.
Comorbid Asthma
- Advise patients with comorbid asthma not to adjust or stop their asthma treatment without talking to their physicians.

Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Dupilumab interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Dupixent
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Dupilumab Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.