Clobazam: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 178: | Line 178: | ||
Shake ONFI Oral Suspension well before every administration. When administering the oral suspension, use only the oral dosing syringe provided with the product. Each carton includes two syringes, but only one syringe should be used for dosing. The second oral syringe is reserved as a replacement in case the first syringe is damaged or lost. Insert the provided adapter firmly into the neck of the bottle before first use and keep the adapter in place for the duration of the usage of the bottle. To withdraw the dose, insert the dosing syringe into the adapter and invert the bottle then slowly pull back the plunger to prescribed dose. After removing the syringe from the bottle adapter, slowly squirt ONFI Oral Suspension into the corner of the patient's mouth. Replace the cap after each use. The cap fits over the adapter when the adapter is properly placed. See ONFI Oral Suspension "Instructions for Use" for complete instruction on how to properly dose and administer the ONFI Oral Suspension. | Shake ONFI Oral Suspension well before every administration. When administering the oral suspension, use only the oral dosing syringe provided with the product. Each carton includes two syringes, but only one syringe should be used for dosing. The second oral syringe is reserved as a replacement in case the first syringe is damaged or lost. Insert the provided adapter firmly into the neck of the bottle before first use and keep the adapter in place for the duration of the usage of the bottle. To withdraw the dose, insert the dosing syringe into the adapter and invert the bottle then slowly pull back the plunger to prescribed dose. After removing the syringe from the bottle adapter, slowly squirt ONFI Oral Suspension into the corner of the patient's mouth. Replace the cap after each use. The cap fits over the adapter when the adapter is properly placed. See ONFI Oral Suspension "Instructions for Use" for complete instruction on how to properly dose and administer the ONFI Oral Suspension. | ||
|overdose= | |overdose=====Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage==== | ||
Overdose and intoxication with benzodiazepines, including ONFI, may lead to CNS depression, associated with drowsiness, confusion and lethargy, possibly progressing to ataxia, respiratory depression, hypotension, and, rarely, coma or death. The risk of a fatal outcome is increased in cases of combined poisoning with other CNS depressants, including alcohol. | *Overdose and intoxication with benzodiazepines, including ONFI, may lead to CNS depression, associated with drowsiness, confusion and lethargy, possibly progressing to ataxia, respiratory depression, hypotension, and, rarely, coma or death. | ||
*The risk of a fatal outcome is increased in cases of combined poisoning with other CNS depressants, including alcohol. | |||
====Management of Overdosage==== | |||
The management of ONFI overdose may include gastric lavage and/or administration of activated charcoal, intravenous fluid replenishment, early control of airway and general supportive measures, in addition to monitoring level of consciousness and vital signs. Hypotension can be treated by replenishment with plasma substitutes and, if necessary, with sympathomimetic agents. | *The management of ONFI overdose may include gastric lavage and/or administration of activated charcoal, intravenous fluid replenishment, early control of airway and general supportive measures, in addition to monitoring level of consciousness and vital signs. | ||
*Hypotension can be treated by replenishment with plasma substitutes and, if necessary, with sympathomimetic agents. | |||
The efficacy of supplementary administration of physostigmine (a cholinergic agent) or of flumazenil (a benzodiazepine antagonist) in ONFI overdose has not been assessed. The administration of flumazenil in cases of benzodiazepine overdose can lead to withdrawal and adverse reactions. Its use in patients with epilepsy is typically not recommended. | *The efficacy of supplementary administration of physostigmine (a cholinergic agent) or of flumazenil (a benzodiazepine antagonist) in ONFI overdose has not been assessed. | ||
*The administration of flumazenil in cases of benzodiazepine overdose can lead to withdrawal and adverse reactions. Its use in patients with epilepsy is typically not recommended. | |||
|nonClinToxic=13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility | |nonClinToxic=13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility | ||
Carcinogenesis | Carcinogenesis | ||
| Line 206: | Line 208: | ||
*The oral suspension is packaged with a dispenser set which contains two calibrated oral dosing syringes and a bottle adapter. | *The oral suspension is packaged with a dispenser set which contains two calibrated oral dosing syringes and a bottle adapter. | ||
**NDC 67386-313-21: 2.5 mg/mL supplied in a bottle containing 120 mL of suspension. | **NDC 67386-313-21: 2.5 mg/mL supplied in a bottle containing 120 mL of suspension. | ||
|storage=====Clobazam Tablets==== | |storage=====Clobazam Tablets==== | ||
*Store tablets and oral suspension at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). See USP controlled room temperature. | *Store tablets and oral suspension at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). See USP controlled room temperature. | ||
| Line 243: | Line 243: | ||
Instruct patients to notify their physician if they are breast feeding or intend to breast feed during therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]. | Instruct patients to notify their physician if they are breast feeding or intend to breast feed during therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]. | ||
|alcohol=*Since ONFI has a central nervous system (CNS) depressant effect, patients or their caregivers should be cautioned against simultaneous use with other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol, and cautioned that the effects of other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol may be potentiated. | |alcohol=*Since ONFI has a central nervous system (CNS) depressant effect, patients or their caregivers should be cautioned against simultaneous use with other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol, and cautioned that the effects of other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol may be potentiated. | ||
|brandNames=*Onfi | |brandNames=*Onfi | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 22:04, 13 January 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Stefano Giannoni [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Clobazam is a Benzodiazepine that is FDA approved for the treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) in patients 2 years of age or older. Common adverse reactions include constipation, somnolence or sedation, pyrexia, lethargy, and drooling.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS)
- A daily dose of ONFI greater than 5 mg should be administered in divided doses twice daily
- 5 mg daily dose can be administered as a single dose.
- Dose patients according to body weight.
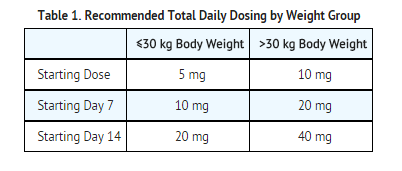
- Do not proceed with dose escalation more rapidly than weekly, because serum concentrations of clobazam and its active metabolite require 5 and 9 days, respectively, to reach steady-state.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Clobazam in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Clobazam in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) (2 years of age or older)
- A daily dose of ONFI greater than 5 mg should be administered in divided doses twice daily
- 5 mg daily dose can be administered as a single dose.
- Dose patients according to body weight.

- Do not proceed with dose escalation more rapidly than weekly, because serum concentrations of clobazam and its active metabolite require 5 and 9 days, respectively, to reach steady-state.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Clobazam in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Clobazam in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- ONFI is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients.
- Hypersensitivity reactions have included serious dermatological reactions.
Warnings
Somnolence or Sedation
- ONFI causes somnolence and sedation.
- In clinical trials, somnolence or sedation was reported at all effective doses and was dose-related.
- In general, somnolence and sedation begin within the first month of treatment and may diminish with continued treatment.
- Prescribers should monitor patients for somnolence and sedation, particularly with concomitant use of other central nervous system depressants.
- Prescribers should caution patients against engaging in hazardous activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating dangerous machinery or motor vehicles, until the effect of ONFI is known.
Potentiation of Sedation from Concomitant Use with Central Nervous System Depressants
- Since ONFI has a central nervous system (CNS) depressant effect, patients or their caregivers should be cautioned against simultaneous use with other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol, and cautioned that the effects of other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol may be potentiated.
Withdrawal Symptoms
- Abrupt discontinuation of ONFI should be avoided.
- ONFI should be tapered by decreasing the dose every week by 5-10 mg/day until discontinuation.
- Withdrawal symptoms occurred following abrupt discontinuation of ONFI; the risk of withdrawal symptoms is greater with higher doses.
- As with all antiepileptic drugs, ONFI should be withdrawn gradually to minimize the risk of precipitating seizures, seizure exacerbation, or status epilepticus.
- Withdrawal symptoms (e.g., convulsions, psychosis, hallucinations, behavioral disorder, tremor, and anxiety) have been reported following abrupt discontinuance of benzodiazepines.
- The more severe withdrawal symptoms have usually been limited to patients who received excessive doses over an extended period of time, followed by an abrupt discontinuation.
- Generally milder withdrawal symptoms (e.g., dysphoria, anxiety, and insomnia) have been reported following abrupt discontinuance of benzodiazepines taken continuously at therapeutic doses for several months.
Serious Dermatological Reactions
- Serious skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have been reported with ONFI in both children and adults during the post-marketing period.
- Patients should be closely monitored for signs or symptoms of SJS/TEN, especially during the first 8 weeks of treatment initiation or when re-introducing therapy.
- ONFI should be discontinued at the first sign of rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related.
- If signs or symptoms suggest SJS/TEN, use of this drug should not be resumed and alternative therapy should be considered.
Physical and Psychological Dependence
- Patients with a history of substance abuse should be under careful surveillance when receiving ONFI or other psychotropic agents because of the predisposition of such patients to habituation and dependence.
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
- Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including ONFI, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. *Patients treated with any AED for any indication should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
- Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted relative risk 1.8, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated.
- There were four suicides in drug treated patients in the trials and none in placebo treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
- The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed.
- Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
- The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed.
- The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5-100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed. Table 2 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
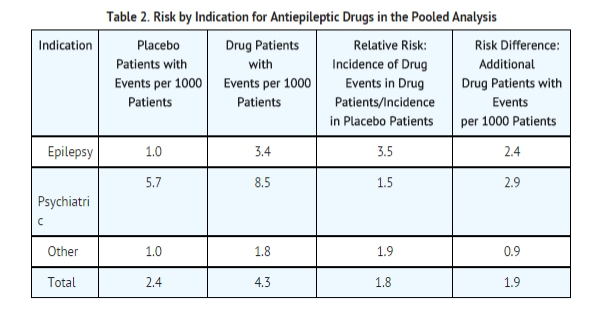
- The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
- Anyone considering prescribing ONFI or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness.
- Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior.
- Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
- Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed that AEDs increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and should be advised of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of the signs and symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm.
- Behaviors of concern should be reported immediately to healthcare providers.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- During its development for the adjunctive treatment of seizures associated with LGS, ONFI was administered to 333 healthy volunteers and 300 patients with a current or prior diagnosis of LGS, including 197 patients treated for 12 months or more.
- The conditions and duration of exposure varied greatly and included single- and multiple-dose clinical pharmacology studies in healthy volunteers and two double-blind studies in patients with LGS (Study 1 and 2). Only Study 1 included a placebo group, allowing comparison of adverse reaction rates on ONFI at several doses to placebo.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation in an LGS Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial (Study 1)
- The adverse reactions associated with ONFI treatment discontinuation in ≥1% of patients in decreasing order of frequency included lethargy, somnolence, ataxia, aggression, fatigue, and insomnia.
Most Common Adverse Reactions in an LGS Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial (Study 1) Table 3 lists the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥5% of ONFI treated patients (at any dose), and at a rate greater than placebo treated patients, in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group clinical study of adjunctive AED therapy for 15 weeks (Study 1).
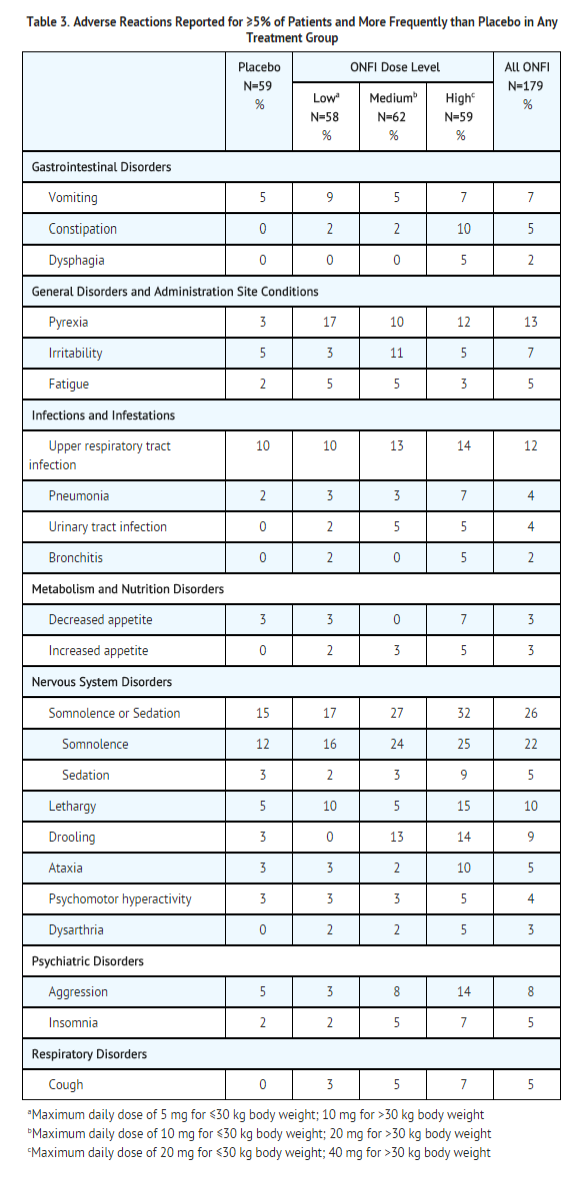
Postmarketing Experience
These reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size; therefore, it is not possible to estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Adverse reactions are categorized by system organ class.
Blood Disorders
- Anemia
- Eosinophilia
- Leukopenia
- Thrombocytopenia
Eye Disorders
- Diplopia
- Vision blurred
Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Abdominal distention
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
- Hypothermia
Investigations
- Hepatic enzyme increased
Musculoskeletal
- Muscle spasms
Psychiatric Disorders
- Agitation
- Anxiety
- Apathy
- Confusional state
- Depression
- Delirium
- Delusion
- Hallucination
Renal and Urinary Disorders
- Urinary retention
Respiratory Disorders
- Aspiration
- Respiratory depression
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
- Rash
- Urticaria
- Angioedema
- Facial and lip edema
Drug Interactions
Effect of ONFI on Other Drugs
Hormonal Contraceptives
- ONFI is a weak CYP3A4 inducer.
- As some hormonal contraceptives are metabolized by CYP3A4, their effectiveness may be diminished when given with ONFI.
- Additional non-hormonal forms of contraception are recommended when using ONFI
Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6
- ONFI inhibits CYP2D6.
- Dose adjustment of drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 may be necessary.
Effect of Other Drugs on ONFI
- Strong and moderate inhibitors of CYP2C19
- Strong and moderate inhibitors of CYP2C19 may result in increased exposure to N-desmethylclobazam, the active metabolite of clobazam.
- This may increase the risk of dose-related adverse reactions.
- Dosage adjustment of ONFI may be necessary when co-administered with strong CYP2C19 inhibitors (e.g., fluconazole, fluvoxamine, ticlopidine) or moderate CYP2C19 inhibitors (e.g., omeprazole).
CNS Depressants and Alcohol
- Concomitant use of ONFI with other CNS depressants may increase the risk of sedation and somnolence.
- Alcohol, as a CNS depressant, will interact with ONFI in a similar way and also increases clobazam's maximum plasma exposure by approximately 50%. Therefore, caution patients or their caregivers against simultaneous use with other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol, and caution that the effects of other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol may be potentiated.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): C
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Clobazam in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS): C
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Clobazam in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Clobazam during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- ONFI is excreted in human milk.
- Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from ONFI, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in patients less than 2 years of age have not been established.
- In a study in which clobazam (4, 36, or 120 mg/kg/day) was orally administered to rats during the juvenile period of development (postnatal days 14 to 48), adverse effects on growth (decreased bone density and bone length) and behavior (altered motor activity and auditory startle response; learning deficit) were observed at the high dose.
- The effect on bone density, but not on behavior, was reversible when drug was discontinued.
- The no-effect level for juvenile toxicity (36 mg/kg/day) was associated with plasma exposures (AUC) to clobazam and its major active metabolite, N-desmethylclobazam, less than those expected at therapeutic doses in pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
Plasma concentrations at any given dose are generally higher in the elderly: proceed slowly with dose escalation. The starting dose should be 5 mg/day for all elderly patients. Then titrate elderly patients according to weight, but to half the dose presented in Table 1, as tolerated. If necessary and based upon clinical response, an additional titration to the maximum dose (20 mg/day or 40 mg/day, depending on weight) may be started on day 21 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Clobazam with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Clobazam with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild and moderate renal impairment. There is no experience with ONFI in patients with severe renal impairment or end stage renal disease (ESRD). It is not known if clobazam or its active metabolite, N-desmethylclobazam, is dialyzable [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Hepatic Impairment
ONFI is hepatically metabolized; however, there are limited data to characterize the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of ONFI. For this reason, proceed slowly with dosing escalations. For patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5-9), the starting dose should be 5 mg/day in both weight groups. Then titrate patients according to weight, but to half the dose presented in Table 1, as tolerated. If necessary and based upon clinical response, start an additional titration on day 21 to the maximum dose (20 mg/day or 40 mg/day, depending on the weight group). There is inadequate information about metabolism of ONFI in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Therefore no dosing recommendation in those patients can be given [see Use in Specific Populations (8.8), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Clobazam in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Clobazam in patients who are immunocompromised.
Dosage Adjustments in CYP2C19 Poor Metabolizers
In CYP2C19 poor metabolizers, levels of N-desmethylclobazam, clobazam's active metabolite, will be increased. Therefore, in patients known to be CYP2C19 poor metabolizers, the starting dose should be 5 mg/day and dose titration should proceed slowly according to weight, but to half the dose presented in Table 1, as tolerated. If necessary and based upon clinical response, an additional titration to the maximum dose (20 mg/day or 40 mg/day, depending on the weight group) may be started on day 21 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)].
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Important Administration Instructions
Instruct patients to read the "Instructions for Use" carefully for complete directions on how to properly dose and administer ONFI oral suspension.
ONFI Tablet Oral Administration ONFI tablets can be taken with or without food. ONFI tablets can be administered whole, broken in half along the score, or crushed and mixed in applesauce.
ONFI Oral Suspension Oral Administration ONFI oral suspension can be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Shake ONFI Oral Suspension well before every administration. When administering the oral suspension, use only the oral dosing syringe provided with the product. Each carton includes two syringes, but only one syringe should be used for dosing. The second oral syringe is reserved as a replacement in case the first syringe is damaged or lost. Insert the provided adapter firmly into the neck of the bottle before first use and keep the adapter in place for the duration of the usage of the bottle. To withdraw the dose, insert the dosing syringe into the adapter and invert the bottle then slowly pull back the plunger to prescribed dose. After removing the syringe from the bottle adapter, slowly squirt ONFI Oral Suspension into the corner of the patient's mouth. Replace the cap after each use. The cap fits over the adapter when the adapter is properly placed. See ONFI Oral Suspension "Instructions for Use" for complete instruction on how to properly dose and administer the ONFI Oral Suspension.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Clobazam Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Clobazam and IV administrations.
Overdosage
Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
- Overdose and intoxication with benzodiazepines, including ONFI, may lead to CNS depression, associated with drowsiness, confusion and lethargy, possibly progressing to ataxia, respiratory depression, hypotension, and, rarely, coma or death.
- The risk of a fatal outcome is increased in cases of combined poisoning with other CNS depressants, including alcohol.
Management of Overdosage
- The management of ONFI overdose may include gastric lavage and/or administration of activated charcoal, intravenous fluid replenishment, early control of airway and general supportive measures, in addition to monitoring level of consciousness and vital signs.
- Hypotension can be treated by replenishment with plasma substitutes and, if necessary, with sympathomimetic agents.
- The efficacy of supplementary administration of physostigmine (a cholinergic agent) or of flumazenil (a benzodiazepine antagonist) in ONFI overdose has not been assessed.
- The administration of flumazenil in cases of benzodiazepine overdose can lead to withdrawal and adverse reactions. Its use in patients with epilepsy is typically not recommended.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Clobazam Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Clobazam Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Clobazam Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Clobazam Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Clobazam Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Carcinogenesis The carcinogenic potential of clobazam has not been adequately assessed.
In a limited study in rats, oral administration of clobazam (4, 20, and 100 mg/kg/day) for 2 years resulted in an increased incidence of thyroid follicular cell adenomas in males at the high dose.
Mutagenesis Clobazam and the major active metabolite, N-desmethylclobazam, were negative for genotoxicity, based on data from a battery of in vitro (bacteria reverse mutation, mammalian clastogenicity) and in vivo (mouse micronucleus) assays.
Impairment of Fertility In a study in which clobazam (50, 350, or 750 mg/kg/day) was orally administered to male and female rats prior to and during mating and continuing in females to gestation day 6, increases in abnormal sperm and pre-implantation loss were observed at the highest dose tested. The no effect level for fertility and early embryonic development in rats was associated with plasma exposures (AUC) for clobazam and its major active metabolite, N-desmethylclobazam, less than those in humans at the maximum recommended human dose of 40 mg/day.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clobazam Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
Clobazam- Tablets
Each clobazam tablet contains 10 mg or 20 mg of clobazam.
- It is a white to off-white, oval tablet with a functional score on one side and either a "1" and "0" or a "2" and "0" debossed on the other side.
- NDC 67386-314-01: 10 mg scored tablet, Bottles of 100
- NDC 67386-315-01: 20 mg scored tablet, Bottles of 100
Clobazam- Oral suspension
- ONFI oral suspension is a berry flavored off-white liquid supplied in a bottle with child-resistant closure.
- The oral suspension is packaged with a dispenser set which contains two calibrated oral dosing syringes and a bottle adapter.
- NDC 67386-313-21: 2.5 mg/mL supplied in a bottle containing 120 mL of suspension.
Storage
Clobazam Tablets
- Store tablets and oral suspension at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). See USP controlled room temperature.
Clobazam Oral suspension
- Store and dispense ONFI oral suspension in its original bottle in an upright position.
- Use within 90 days of first opening the bottle, then discard any remainder
- Store tablets and oral suspension at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). See USP controlled room temperature.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Clobazam |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Clobazam |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Hypersensitivity
Inform patients or caregivers that ONFI is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients [see Warnings and Precautions 5.4)].
Somnolence or Sedation Advise patients or caregivers to check with their healthcare provider before ONFI is taken with other CNS depressants such as other benzodiazepines, opioids, tricyclic antidepressants, sedating antihistamines, or alcohol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
If applicable, caution patients about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that ONFI does not affect them adversely (e.g., impair judgment, thinking or motor skills).
Increasing or Decreasing the ONFI Dose Inform patients or caregivers to consult their healthcare provider before increasing the ONFI dose or abruptly discontinuing ONFI. Advise patients or caregivers that abrupt withdrawal of AEDs may increase their risk of seizure [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Interactions with Hormonal Contraceptives Counsel women to also use non-hormonal methods of contraception when ONFI is used with hormonal contraceptives and to continue these alternative methods for 28 days after discontinuing ONFI to ensure contraceptive reliability [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Serious Dermatological Reactions Advise patients or caregivers that serious skin reactions have been reported in patients taking ONFI. Serious skin reactions, including SJS/TEN, may need to be treated in a hospital and may be life-threatening. If a skin reaction occurs while taking ONFI, patients or caregivers should consult with healthcare providers immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Suicidal Thinking and Behavior Counsel patients, their caregivers, and their families that AEDs, including ONFI, may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and advise them of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts of self-harm. Patients should report behaviors of concern immediately to healthcare providers [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Use in Pregnancy Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during therapy.
Encourage patients to enroll in the NAAED Pregnancy Registry if they become pregnant. This registry is collecting information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. To enroll, patients can call the toll-free number 1-888-233-2334. Information on the registry can also be found at the website http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Use in Nursing Instruct patients to notify their physician if they are breast feeding or intend to breast feed during therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Precautions with Alcohol
- Since ONFI has a central nervous system (CNS) depressant effect, patients or their caregivers should be cautioned against simultaneous use with other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol, and cautioned that the effects of other CNS depressant drugs or alcohol may be potentiated.
Brand Names
- Onfi
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Clobazam Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.