Cimetidine (oral)
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag=Gloria Picoy [1] |genericName=Cimetidine |aOrAn=an |drugClass=histamine H2 receptor antagonist |indicationType=treatment |indication=duodenal ulcer disease, erosive esophagitis, gastric ulcer, systemic mastocytosis, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome |adverseReactions=gynecomastia |blackBoxWarningTitle=TITLE |blackBoxWarningBody=Condition Name: (Content) |fdaLIADAdult=====Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer====
- Dosage: 800 mg at bedtime
- Most patients heal within 4 weeks and there is rarely reason to use cimetidine tablets at full dosage for longer than 6 to 8 weeks.
- Concomitant antacids should be given as needed for relief of pain.
- However, simultaneous administration of cimetidine tablets and antacids is not recommended, since antacids have been reported to interfere with the absorption of cimetidine.
Maintenance therapy for duodenal ulcer patients at reduced dosage after healing of active ulcer
- Patients have been maintained on continued treatment with cimetidine tablets 400 mg at bedtime for periods of up to 5 years.
Short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer
- 800 mg at bedtime
- 300 mg 4 times a day with meals and at bedtime
- There is no information concerning usefulness of treatment periods of longer than 8 weeks.
Erosive gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
- Dosage: 1600 mg daily in divided doses (800 mg twice daily or 400 mg 4 times daily) for 12 weeks
- Erosive esophagitis diagnosed by endoscopy.
- Treatment is indicated for 12 weeks for healing of lesions and control of symptoms
- The use of cimetidine tablets beyond 12 weeks has not been established.
The treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions (i.e., Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, systemic mastocytosis, multiple endocrine adenomas)
- Dosage: 300 mg 4 times a day with meals and at bedtime
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Cimetidine in adult patients. |offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=====Clear cell carcinoma of kidney====
- Dosage: 600 mg PO 4 times daily [1]
Contrast media adverse reaction
- Dosage: 300 mg in 100 mL of D5W over 15 minutes rapidly reversed cutaneous and respiratory phenomenon [2]
Maintenance of Gastric ulcer
- Dosage: 400 mg at bedtime [3]
|fdaLIADPed=Clinical experience in children is limited. Therefore, therapy with cimetidine cannot be recommended for children under 16, unless, in the judgement of the physician, anticipated benefits outweigh the potential risks. In very limited experience, doses of 20 to 40 mg/kg/day have been used. |offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Cimetidine in pediatric patients. |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=====Prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonitis====
- Dosage: 7.5 mg/kg PO 1 to 3 hours before surgery [4]
Molluscum contagiosum infection
- Dosage: 40 mg/kg PO daily [5]
Stress ulcer
- Dosage: 15 to 20 mg/kg PO daily administered IV every 6 hours for 7 days in conjunction with cold saline washes, antacids, and blood transfusions [6]
Verruca vulgaris
- Monotherapy: 30 to 40 mg/kg/day [7] [8] [9]
- Combination therapy: 30 mg/kg orally in 3 divided doses with levamisole [10]
|contraindications=Cimetidine tablets are contraindicated for patients known to have hypersensitivity to the product. |warnings=Rare instances of cardiac arrhythmias and hypotension have been reported following the rapid administration of cimetidine hydrochloride injection by intravenous bolus.
Symptomatic response to treatment with cimetidine does not preclude the presence of a gastric malignancy. There have been rare reports of transient healing of gastric ulcers despite subsequently documented malignancy.
Reversible confusional states have been observed on occasion, predominantly, but not exclusively, in severely ill patients. Advancing age (50 or more years) and preexisting liver and/or renal disease appear to be contributing factors. In some patients these confusional states have been mild and have not required discontinuation of cimetidine. In cases where discontinuation was judged necessary, the condition usually cleared within 3 to 4 days of drug withdrawal. |clinicalTrials=====Gastrointestinal====
- Diarrhea (usually mild) has been reported in approximately 1 in 100 patients.
CNS
- Headaches, ranging from mild to severe, have been reported in 3.5% of 924 patients taking 1600 mg/day, 2.1% of 2,225 patients taking 800 mg/day and 2.3% of 1,897 patients taking placebo.
- Dizziness and somnolence (usually mild) have been reported in approximately 1 in 100 patients on either 1600 mg/day or 800 mg/day.
- Reversible confusional states, e.g., mental confusion, agitation, psychosis, depression, anxiety, hallucinations, disorientation, have been reported predominantly, but not exclusively, in severely ill patients. They have usually developed within 2 to 3 days of initiation of treatment with cimetidine and have cleared within 3 to 4 days of discontinuation of the drug.
Endocrine
- Gynecomastia has been reported in patients treated for one month or longer. In patients being treated for pathological hypersecretory states, this occurred in about 4% of cases while in all others the incidence was 0.3% to 1% in various studies. No evidence of induced endocrine dysfunction was found, and the condition remained unchanged or returned toward normal with continuing treatment with cimetidine.
- Reversible impotence has been reported in patients with pathological hypersecretory disorders, e.g., Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, receiving cimetidine, particularly in high doses, for at least 12 months (range 12 to 79 months, mean 38 months). However, in large-scale surveillance studies at regular dosage, the incidence has not exceeded that commonly reported in the general population.
Hematologic
- Decreased white blood cell counts in patients treated with cimetidine (approximately 1 per 100,000 patients), including agranulocytosis (approximately 3 per million patients), have been reported, including a few reports of recurrence on rechallenge. Most of these reports were in patients who had serious concomitant illnesses and received drugs and/or treatment known to produce neutropenia.
- Thrombocytopenia (approximately 3 per million patients) and, very rarely, cases of pancytopenia or aplastic anemia have also been reported.
- As with some other H2-receptor antagonists, there have been extremely rare reports of immune hemolytic anemia.
Hepatobiliary
- Dose related increases in serum transaminase have been reported. In most cases they did not progress with continued therapy and returned to normal at the end of therapy. There have been rare reports of cholestatic or mixed cholestatic-hepatocellular effects. These were usually reversible. Because of the predominance of cholestatic features, severe parenchymal injury is considered highly unlikely. However, as in the occasional liver injury with other H2-receptor antagonists, in exceedingly rare circumstances fatal outcomes have been reported.
- There has been reported a single case of biopsy-proven periportal hepatic fibrosis in a patient receiving cimetidine.
- Rare cases of pancreatitis, which cleared on withdrawal of the drug, have been reported.
Hypersensitivity
- Rare cases of fever and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis and hypersensitivity vasculitis, which cleared on withdrawal of the drug, have been reported.
Renal
- Small, possibly dose related increases in plasma creatinine, presumably due to competition for renal tubular secretion, are not uncommon and do not signify deteriorating renal function. Rare cases of interstitial nephritis and urinary retention, which cleared on withdrawal of the drug, have been reported.
Cardiovascular
- Rare cases of bradycardia, tachycardia and AV heart block have been reported with H2-receptor antagonists.
Musculoskeletal
- There have been rare reports of reversible arthralgia and myalgia; exacerbation of joint symptoms in patients with preexisting arthritis has also been reported. Such symptoms have usually been alleviated by a reduction in the dosage of cimetidine.
- Rare cases of polymyositis have been reported, but no causal relationship has been established.
Integumental
- Mild rash
- Very rarely, cases of severe generalized skin reactions including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis and generalized exfoliative erythroderma have been reported with H2-receptor antagonists.
- Reversible alopecia has been reported very rarely.
Immune Function
- There have been extremely rare reports of strongyloidiasis hyperinfection in immunocompromised patients.
Respiratory
- A large epidemiological study suggested an increased risk of developing pneumonia in current users of histamine-2-receptor antagonists (H2RAs) compared to patients who had stopped H2RA treatment, with an observed adjusted relative risk of 1.63 (95% CI, 1.07 to 2.48). However, a causal relationship between use of H2RAs and pneumonia has not been established.
|drugInteractions=* Cimetidine, apparently through an effect on certain microsomal enzyme systems, has been reported to reduce the hepatic metabolism of warfarin-type anticoagulants, phenytoin, propranolol, nifedipine, chlordiazepoxide, diazepam, certain tricyclic antidepressants, lidocaine, theophylline and metronidazole, thereby delaying elimination and increasing blood levels of these drugs.
- Clinically significant effects have been reported with the warfarin anticoagulants; therefore, close monitoring of prothrombin time is recommended, and adjustment of the anticoagulant dose may be necessary when cimetidine is administered concomitantly. Interaction with phenytoin, lidocaine and theophylline has also been reported to produce adverse clinical effects.
- However, a crossover study in healthy subjects receiving either 300 mg 4 times daily or 800 mg at bedtime of cimetidine concomitantly with a 300 mg twice daily dose of theophylline extended-release tablets demonstrated less alteration in steady-state theophylline peak serum levels with the 800 mg at bedtime regimen, particularly in subjects aged 54 years and older. Data beyond 10 days are not available.
- Dosage of the drugs mentioned above and other similarly metabolized drugs, particularly those of low therapeutic ratio or in patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment, may require adjustment when starting or stopping the concomitant administration of cimetidine to maintain optimum therapeutic blood levels.
- Alteration of pH may affect absorption of certain drugs (e.g., ketoconazole). If these products are needed, they should be given at least 2 hours before cimetidine administration.
- Additional clinical experience may reveal other drugs affected by the concomitant administration of cimetidine.
|FDAPregCat=B |useInPregnancyFDA=Reproduction studies have been performed in rats, rabbits and mice at doses up to 40 times the normal human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cimetidine. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. |AUSPregCat=B1 |useInNursing=Cimetidine is secreted in human milk and, as a general rule, nursing should not be undertaken while a patient is on a drug. |useInPed=Clinical experience in children is limited. Therefore, therapy with cimetidine cannot be recommended for children under 16, unless, in the judgement of the physician, anticipated benefits outweigh the potential risks. In very limited experience, doses of 20 to 40 mg/kg/day have been used. |useInRenalImpair=Patients with severely impaired renal function have been treated with cimetidine tablets. However, such usage has been very limited. On the basis of this experience the recommended dosage is 300 mg every 12 hours orally. Should the patient’s condition require, the frequency of dosing may be increased to every 8 hours or even further with caution. In severe renal failure, accumulation may occur and the lowest frequency of dosing compatible with an adequate patient response should be used. When liver impairment is also present, further reductions in dosage may be necessary. Hemodialysis reduces the level of circulating cimetidine. Ideally, the dosage schedule should be adjusted so that the timing of a scheduled dose coincides with the end of hemodialysis. |useInReproPotential=Cimetidine has demonstrated a weak antiandrogenic effect. In animal studies this was manifested as reduced prostate and seminal vesicle weights. However, there was no impairment of mating performance or fertility, nor any harm to the fetus in these animals at doses 8 to 48 times the full therapeutic dose of cimetidine, as compared with controls. The cases of gynecomastia seen in patients treated for one month or longer may be related to this effect.
In human studies, cimetidine has been shown to have no effect on spermatogenesis, sperm count, motility, morphology or in vitro fertilizing capacity. |useInImmunocomp=In immunocompromised patients, decreased gastric acidity, including that produced by acid-suppressing agents such as cimetidine, may increase the possibility of a hyperinfection of strongyloidiasis. |administration=Oral |overdose=Studies in animals indicate that toxic doses are associated with respiratory failure and tachycardia that may be controlled by assisted respiration and the administration of a beta-blocker.
Reported acute ingestions orally of up to 20 grams have been associated with transient adverse effects similar to those encountered in normal clinical experience. The usual measures to remove unabsorbed material from the gastrointestinal tract, clinical monitoring, and supportive therapy should be employed.
There have been reports of severe CNS symptoms, including unresponsiveness, following ingestion of between 20 grams and 40 grams of cimetidine, and extremely rare reports following concomitant use of multiple CNS active medications and ingestion of cimetidine at doses less than 20 grams. An elderly, terminally ill dehydrated patient with organic brain syndrome receiving concomitant antipsychotic agents and 4800 mg of cimetidine intravenously over a 24-hour period experienced mental deterioration with reversal on discontinuation of cimetidine.
There have been two deaths in adults who were reported to have ingested over 40 grams orally on a single occasion. |drugBox={{Drugbox2 | Watchedfields = changed | verifiedrevid = 456484490 | IUPAC_name = 1-cyano-2-methyl-3-(2-{[4-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)guanidine | image = Cimetidine structure.png
| tradename = Tagamet | Drugs.com = Monograph | MedlinePlus = a682256 | licence_US = Cimetidine | pregnancy_AU = B1 | pregnancy_US = B | legal_AU = S3 | legal_UK = POM | legal_US = Rx (although 200mg is OTC) | routes_of_administration = Oral, parenteral
| bioavailability = 60–70% | protein_bound = 15–20% | metabolism = Hepatic | elimination_half-life = 2 hours | excretion = Renal
| CASNo_Ref =
| CAS_number_Ref =
| CAS_number = 51481-61-9
| ATC_prefix = A02
| ATC_suffix = BA01
| PubChem = 2756
| IUPHAR_ligand = 1231
| DrugBank_Ref =
| DrugBank = DB00501
| ChemSpiderID_Ref =
| ChemSpiderID = 2654
| UNII_Ref =
| UNII = 80061L1WGD
| KEGG_Ref =
| KEGG = D00295
| ChEBI_Ref =
| ChEBI = 3699
| ChEMBL_Ref =
| ChEMBL = 30
| C=10 | H=16 | N=6 | S=1
| molecular_weight = 252.34 g/mol
| smiles = N#CN\C(=N/C)NCCSCc1ncnc1C
| InChI = 1/C10H16N6S/c1-8-9(16-7-15-8)5-17-4-3-13-10(12-2)14-6-11/h7H,3-5H2,1-2H3,(H,15,16)(H2,12,13,14)
| InChIKey = AQIXAKUUQRKLND-UHFFFAOYAS
| StdInChI_Ref =
| StdInChI = 1S/C10H16N6S/c1-8-9(16-7-15-8)5-17-4-3-13-10(12-2)14-6-11/h7H,3-5H2,1-2H3,(H,15,16)(H2,12,13,14)
| StdInChIKey_Ref =
| StdInChIKey = AQIXAKUUQRKLND-UHFFFAOYSA-N
}}
|mechAction=Cimetidine competitively inhibits the action of histamine at the histamine H2 receptors of the parietal cells and thus is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist.
Cimetidine is not an anticholinergic agent. Studies have shown that cimetidine inhibits both daytime and nocturnal basal gastric acid secretion. Cimetidine also inhibits gastric acid secretion stimulated by food, histamine, pentagastrin, caffeine and insulin. |PD=====Antisecretory Activity====
Acid Secretion
Nocturnal
- An 800 mg oral dose of cimetidine at bedtime reduces mean hourly H+ activity by greater than 85% over an 8-hour period in duodenal ulcer patients, with no effect on daytime acid secretion. A 1600 mg oral dose of cimetidine at bedtime produces 100% inhibition of mean hourly H+ activity over an 8-hour period in duodenal ulcer patients, but also reduces H+ activity by 35% for an additional 5 hours into the following morning. Cimetidine given as 400 mg twice daily and 300 mg 4 times daily decreases nocturnal acid secretion in a dose related manner, i.e., 47% to 83% over a 6 to 8-hour period and 54% over a 9-hour period, respectively.
Food Stimulated
- During the first hour after a standard experimental meal, a 300 mg oral dose of cimetidine inhibited gastric acid secretion in duodenal ulcer patients by at least 50%. During the subsequent 2 hours cimetidine inhibited gastric acid secretion by at least 75%.
- The effect of a 300 mg breakfast dose of cimetidine continued for at least 4 hours and there was partial suppression of the rise in gastric acid secretion following the luncheon meal in duodenal ulcer patients. This suppression of gastric acid output was enhanced and could be maintained by another 300 mg dose of cimetidine given with lunch.
- In another study, a 300 mg dose of cimetidine given with the meal increased gastric pH as compared with placebo.
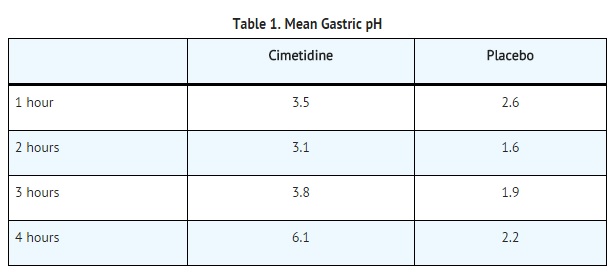
24-Hour Mean H+ Activity
- Cimetidine dosed at 800 mg at bedtime, 400 mg twice daily and 300 mg 4 times daily all provide a similar, moderate (less than 60%) level of 24 hour acid suppression. However, the 800 mg bedtime dose regimen exerts its entire effect on nocturnal acid, and does not affect daytime gastric physiology.
Chemically Stimulated
- Cimetidine administered orally significantly inhibited gastric acid secretion stimulated by betazole (an isomer of histamine), pentagastrin, caffeine and insulin as follows:
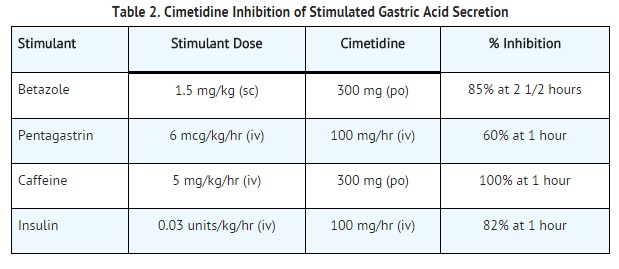
- When food and betazole were used to stimulate secretion, inhibition of hydrogen ion concentration usually ranged from 45% to 75% and the inhibition of volume ranged from 30% to 65%.
Pepsin
- 300 mg of cimetidine taken orally reduced total pepsin output as a result of the decrease in volume of gastric juice.
Intrinsic Factor
- Intrinsic factor secretion was studied with betazole as a stimulant. Cimetidine dosed at 300 mg orally inhibited the rise in intrinsic factor concentration produced by betazole, but some intrinsic factor was secreted at all times.
Lower Esophageal Sphincter Pressure and Gastric Emptying
- Cimetidine has no effect on lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure or the rate of gastric emptying.
|PK=Cimetidine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration and peak levels occur in 45 to 90 minutes. The half-life of cimetidine is approximately 2 hours. Blood concentrations remain above that required to provide 80% inhibition of basal gastric acid secretion for 4 to 5 hours following a dose of 300 mg.
Following parenteral administration, most of the drug is excreted as the parent compound in the urine, the principle route of excretion of cimetidine. After oral administration, the drug is extensively metabolized in which the sulfoxide is the major metabolite. Following a single oral dose, 48% of the drug is recovered from the urine after 24 hours as the parent compound. |clinicalStudies=====Duodenal Ulcer==== Cimetidine has been shown to be effective in the treatment of active duodenal ulcer and, at reduced dosage, in maintenance therapy following healing of active ulcers.
Active Duodenal Ulcer
Cimetidine accelerates the rate of duodenal ulcer healing. Healing rates reported in U.S. and foreign controlled trials with cimetidine are summarized below, beginning with the regimen providing the lowest nocturnal dose.
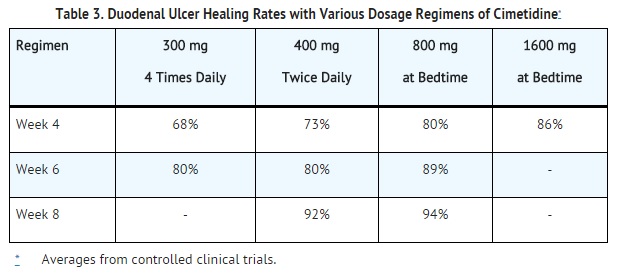
A U.S., double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study demonstrated that all once daily at bedtime regimens of cimetidine were superior to placebo in ulcer healing and that 800 mg of cimetidine at bedtime healed 75% of patients at 4 weeks. The healing rate with 800 mg at bedtime was significantly superior to 400 mg at bedtime (66%) and not significantly different from 1600 mg at bedtime (81%). In the U.S. dose-ranging trial, over 80% of patients receiving 800 mg of cimetidine at bedtime experienced nocturnal pain relief after one day. Relief from daytime pain was reported in approximately 70% of patients after 2 days. As with ulcer healing, the 800 mg dose at bedtime was superior to 400 mg at bedtime and not different from 1600 mg at bedtime. In foreign, double-blind studies with 800 mg of cimetidine at bedtime, 79% to 85% of patients were healed at 4 weeks. While short-term treatment with cimetidine can result in complete healing of the duodenal ulcer, acute therapy will not prevent ulcer recurrence after cimetidine has been discontinued. Some follow-up studies have reported that the rate of recurrence once therapy was discontinued was slightly higher for patients healed on cimetidine than for patients healed on other forms of therapy; however, the patients treated with cimetidine generally had more severe disease.
Maintenance Therapy in Duodenal Ulcer
Treatment with a reduced dose of cimetidine has been proven effective as maintenance therapy following healing of active duodenal ulcers. In numerous placebo-controlled studies conducted worldwide, the percent of patients with observed ulcers at the end of one year’s therapy with 400 mg of cimetidine at bedtime was significantly lower (10% to 45%) than in patients receiving placebo (44% to 70%). Thus, from 55% to 90% of patients were maintained free of observed ulcers at the end of one year with 400 mg of cimetidine at bedtime. Factors such as smoking, duration and severity of disease, gender and genetic traits may contribute to variations in actual percentages. Trials of other anti-ulcer therapy, whether placebo-controlled, positive-controlled or open, have demonstrated a range of results similar to that seen with cimetidine.
Active Benign Gastric Ulcer
Cimetidine has been shown to be effective in the short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer. In a multicenter, double-blind U.S. study, patients with endoscopically confirmed benign gastric ulcer were treated with 300 mg of cimetidine 4 times a day or with placebo for 6 weeks. Patients were limited to those with ulcers ranging from 0.5 to 2.5 cm in size. Endoscopically confirmed healing at 6 weeks was seen in significantly* more patients treated with cimetidine than in patients receiving placebo as shown below:
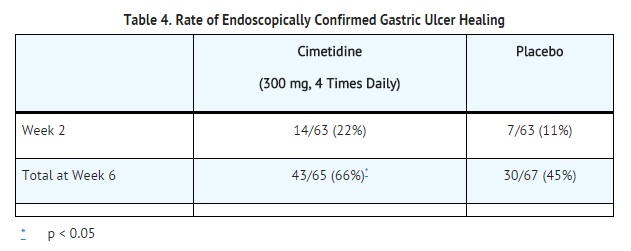
In a similar multicenter U.S. study of the 800 mg bedtime oral regimen, the endoscopically confirmed healing rates were:
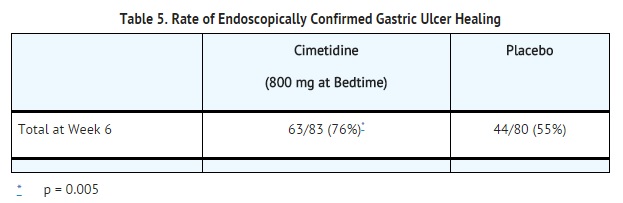
Similarly, in worldwide double-blind clinical studies, endoscopically evaluated benign gastric ulcer healing rates were consistently higher with cimetidine than with placebo.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
In two multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and endoscopically proven erosions and/or ulcers, cimetidine was significantly more effective than placebo in healing lesions. The endoscopically confirmed healing rates were:
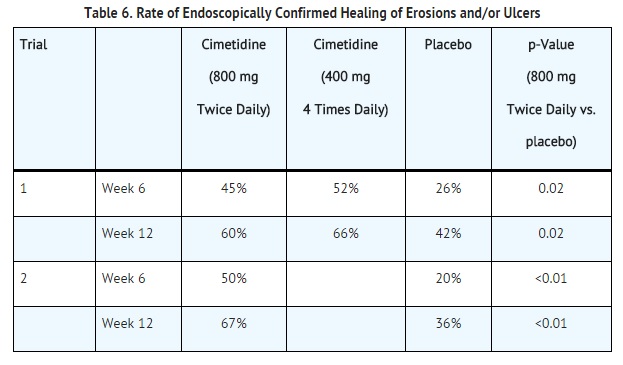
In these trials cimetidine was superior to placebo by most measures in improving symptoms of day- and night-time heartburn, with many of the differences statistically significant. The 4 times daily regimen was generally somewhat better than the twice daily regimen where these were compared.
Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions (such as Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome)
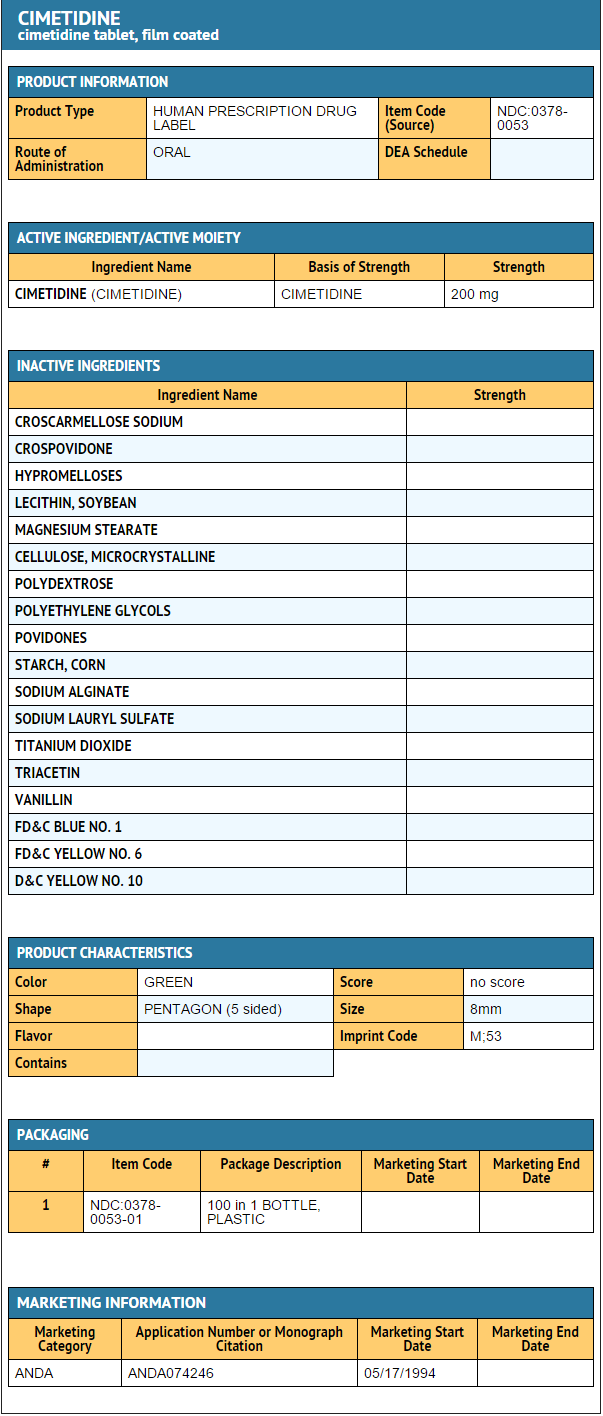
Cimetidine significantly inhibited gastric acid secretion and reduced occurrence of diarrhea, anorexia and pain in patients with pathological hypersecretion associated with Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, systemic mastocytosis and multiple endocrine adenomas. Use of cimetidine was also followed by healing of intractable ulcers. |howSupplied=Cimetidine Tablets, USP are available containing 200 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg and 800 mg of cimetidine.
- The 200 mg tablets are film-coated green, five sided, house shaped, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side and 53 on the other side.
- They are available as follows:
- NDC 0378-0053-01 bottles of 100 tablets
- The 300 mg tablets are film-coated green, five sided, house shaped, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side and 317 on the other side.
- They are available as follows:
- NDC 0378-0317-01 bottles of 100 tablets
- NDC 0378-0317-05 bottles of 500 tablets
- The 400 mg tablets are film-coated green, five sided, house shaped, partially scored tablets debossed with M on one side and 372 on the other side.
- They are available as follows:
- NDC 0378-0372-01 bottles of 100 tablets
- NDC 0378-0372-05 bottles of 500 tablets
- The 800 mg tablets are film-coated green, oval, partially scored tablets debossed with M 541 across the partial score.
- They are available as follows:
- NDC 0378-0541-01 bottles of 100 tablets
|storage=Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F)
|packLabel=
|alcohol=Alcohol-Cimetidine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. |brandNames=* Tagamet [11]
- Tagamet HB
}} {{#subobject:
|Label Page=Cimetidine (oral) |Label Name=Cimetidine package 200 mg.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Cimetidine (oral) |Label Name=Cimetidine package 300 mg.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Cimetidine (oral) |Label Name=Cimetidine package 400 mg.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Cimetidine (oral) |Label Name=Cimetidine package.jpg
}}
- ↑ Inhorn L, Williams SD, Nattam S, Stephens D (1992). "High-dose cimetidine for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. A Hoosier Oncology Group study". Am J Clin Oncol. 15 (2): 157–9. PMID 1553905.
- ↑ Myers GE, Bloom FL (1981). "Cimetidine (Tagamet) combined with steroids and H1 antihistamines for the prevention of serious radiographic contrast material reactions". Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 7 (1): 65–9. PMID 7214521.
- ↑ Kinloch JD, Pearson AJ, Woolf IL, Young PH (1984). "The effect of cimetidine on the maintenance of healing of gastric ulceration". Postgrad Med J. 60 (708): 665–7. PMC 2418023. PMID 6387689.
- ↑ Goudsouzian N, Coté CJ, Liu LM, Dedrick DF (1981). "The dose-response effects of oral cimetidine on gastric pH and volume in children". Anesthesiology. 55 (5): 533–6. PMID 7294407.
- ↑ Dohil M, Prendiville JS (1996). "Treatment of molluscum contagiosum with oral cimetidine: clinical experience in 13 patients". Pediatr Dermatol. 13 (4): 310–2. PMID 8844752.
- ↑ Agarwal AK, Saili A, Pandey KK, Saxena AK, Sarna MS, Dutta AK (1990). "Role of cimetidine in prevention and treatment of stress induced gastric bleeding in neonates". Indian Pediatr. 27 (5): 465–9. PMID 2276774.
- ↑ Ronna T, Lebwohl M (1995). "Cimetidine therapy for plantar warts". J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 85 (11): 717–8. doi:10.7547/87507315-85-11-717. PMID 8537909.
- ↑ Choi YS, Hann SK, Park YK (1993). "The effect of cimetidine on verruca plana juvenilis: clinical trials in six patients". J Dermatol. 20 (8): 497–500. PMID 8245312.
- ↑ Orlow SJ, Paller A (1993). "Cimetidine therapy for multiple viral warts in children". J Am Acad Dermatol. 28 (5 Pt 1): 794–6. PMID 8496433.
- ↑ Parsad D, Pandhi R, Juneja A, Negi KS (2001). "Cimetidine and levamisole versus cimetidine alone for recalcitrant warts in children". Pediatr Dermatol. 18 (4): 349–52. PMID 11576414.
- ↑ "FDA LABEL: CIMETIDINE- cimetidine tablet, film coated".