Chronic bacterial prostatitis
| Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis | ||
 | ||
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10 | N41.1 | |
| ICD-9 | 601.1 | |
| DiseasesDB | 10801 | |
| MedlinePlus | 000523 | |
| eMedicine | med/1920 | |
| MeSH | D011472 | |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
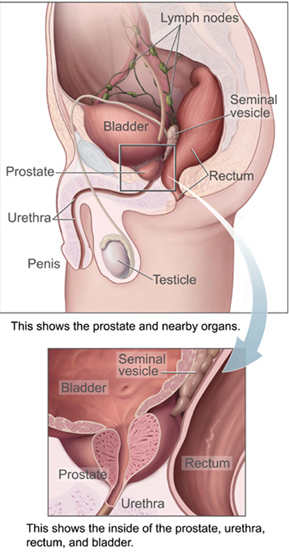
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a bacterial infection of the prostate gland. It should be distinguished from other forms of prostatitis such as acute bacterial prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS).
Signs and symptoms
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a relatively rare condition — occurs in less than 5% of patients with prostate-related non-BPH lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) — that usually presents with an intermittent UTI-type picture and that is defined as recurrent urinary tract infections in men originating from a chronic infection in the prostate. Dr. Weidner, Professor of Medicine, Department of Urology, University of Gießen, has stated: "In studies of 656 men, we seldom found chronic bacterial prostatitis. It is truly a rare disease. Most of those were E-coli."[1] Symptoms may be completely absent until there is also bladder infection, and the most troublesome problem is usually recurrent cystitis.[2]
Diagnosis
In chronic bacterial prostatitis there are bacteria in the prostate but usually no symptoms. The prostate infection is diagnosed by culturing urine as well as prostate fluid (expressed prostatic secretions or EPS) which are obtained by the doctor doing a rectal exam and putting pressure on the prostate. If no fluid is recovered after this prostatic massage, a post massage urine should also contain any prostatic bacteria. Prostate specific antigen levels may be elevated, although there is no malignancy.
Treatment
Treatment requires prolonged courses (4-8 weeks) of antibiotics that penetrate the prostate well (β-lactams and nitrofurantoin are ineffective). These include quinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin), sulfas (Bactrim, Septra) and macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin). Persistent infections may be helped in 80% of patients by the use of alpha blockers (tamsulosin (Flomax), alfuzosin), or long term low dose antibiotic therapy.[3] Recurrent infections may be caused by inefficient urination (benign prostatic hypertrophy, neurogenic bladder), prostatic stones or a structural abnormality that acts as a reservoir for infection.
The addition of prostate massage to courses of antibiotics was previously proposed as being beneficial.[4][5] However, in more recent trials, this was not shown to improve outcome compared to antibiotics alone.[6]
Prognosis
Over time, the relapse rate is high, exceeding 50%. A 2007 study showed that repeated courses of combination antibiotics may eradicate infection in 83.9% of patients with clinical remission extending throughout a follow-up period of 30 months for 94% of these patients.[7]
References
- ↑ Schneider H, Ludwig M, Hossain HM, Diemer T, Weidner W (2003). "The 2001 Gießen Cohort Study on patients with prostatitis syndrome--an evaluation of inflammatory status and search for microorganisms 10 years after a first analysis". Andrologia. 35 (5): 258–62. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0272.2003.00586.x. PMID 14535851.
- ↑ Habermacher GM, Chason JT, Schaeffer AJ (2006). "Prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome". Annu. Rev. Med. 57: 195–206. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.57.011205.135654. PMID 16409145.
- ↑ Shoskes DA, Hakim L, Ghoniem G, Jackson CL (2003). "Long-term results of multimodal therapy for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome". J. Urol. 169 (4): 1406–10. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000055549.95490.3c. PMID 12629373.
- ↑ Nickel JC, Downey J, Feliciano AE, Hennenfent B (1999). "Repetitive prostatic massage therapy for chronic refractory prostatitis: the Philippine experience". Techniques in urology. 5 (3): 146–51. PMID 10527258.
- ↑ Shoskes DA, Zeitlin SI (1999). "Use of prostatic massage in combination with antibiotics in the treatment of chronic prostatitis". Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases. 2 (3): 159–162. doi:10.1038/sj.pcan.4500308. PMID 12496826.
- ↑ Ateya A, Fayez A, Hani R, Zohdy W, Gabbar MA, Shamloul R (2006). "Evaluation of prostatic massage in treatment of chronic prostatitis". Urology. 67 (4): 674–8. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2005.10.021. PMID 16566972.
- ↑ Magri V, Trinchieri A, Pozzi G; et al. (2007). "Efficacy of repeated cycles of combination therapy for the eradication of infecting organisms in chronic bacterial prostatitis". Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 29 (5): 549–56. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2006.09.027. PMID 17336504. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help)
External links
Additional images
-
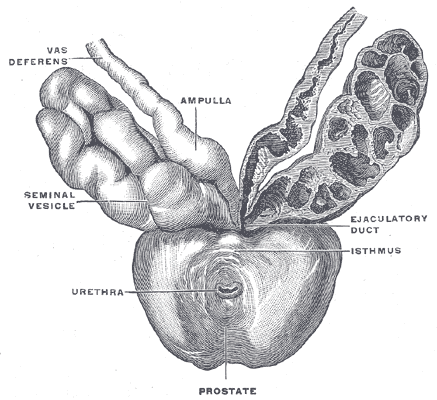
Prostate, urethra, and seminal vesicles.
-
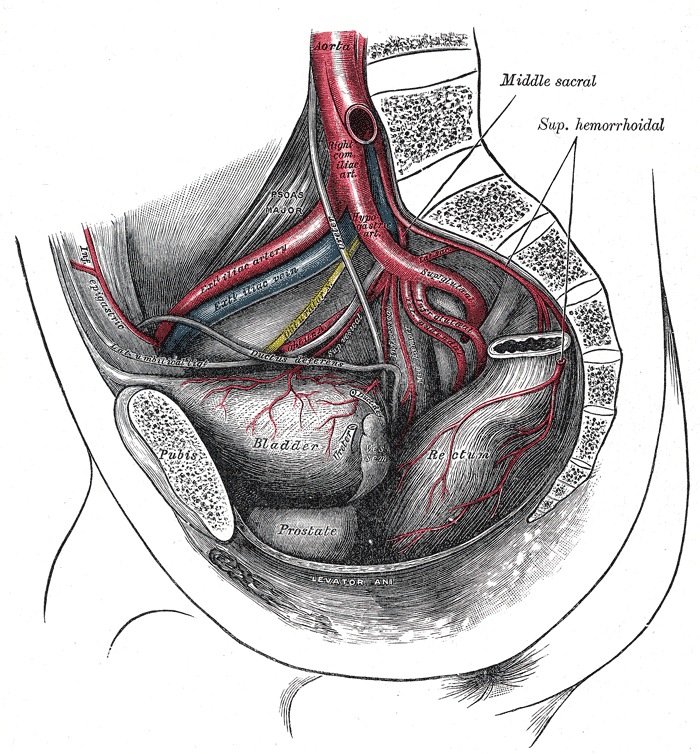
The arteries of the pelvis.
-
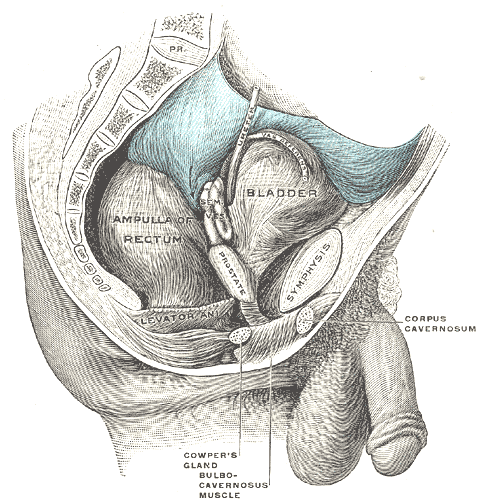
Male pelvic organs seen from right side.
Template:Diseases of the pelvis, genitals and breasts Template:SIB
de:Prostatitis it:Prostatite nl:Prostatitis fi:Eturauhasen tulehdus