Cardiac tamponade electrocardiogram
|
Cardiac tamponade Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Cardiac tamponade electrocardiogram On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cardiac tamponade electrocardiogram |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cardiac tamponade electrocardiogram |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editors-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]; Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S.
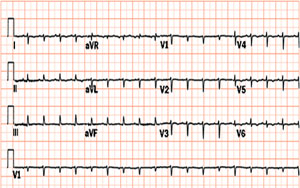
Electrocardiogram
Tamponade may be associated with ST segment changes on the electrocardiogram [1]. Given the insulating properties of the fluid, there may also be low voltage QRS complexes [2]. In some cases, electrical alternans will be present in which case the height of the QRS varies from beat to beat. Tachycardia will likely be present as well.
-
Cardiac Tamponade with low voltage QRS complex and Electrical Alternans
-
12 lead EKG shows Cardiac Tamponade with Electrical Alternans