Cardiac tamponade electrocardiogram: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Electrocardiogram== | ==Electrocardiogram== | ||
EKG findings of cardiac tamponade are: | EKG findings of [[cardiac tamponade]] are: | ||
* Sinus tachycardia | * [[Sinus tachycardia]] | ||
* [[Electrical alternans]] (beat-to-beat alterations in the QRS complex due to swinging of heart in pericardial fluid) | * [[Electrical alternans]] (beat-to-beat alterations in the QRS complex due to swinging of heart in pericardial fluid) | ||
* Low voltage QRS complexes (Low QRS voltage is defined as maximum QRS amplitude in precordial lead < 1 mV and <0.5 mV in the limb leads | * Low voltage QRS complexes (Low QRS voltage is defined as maximum QRS amplitude in precordial lead < 1 mV and <0.5 mV in the limb leads due to insulating properties of fluid) <ref>Longmore, M., Wilkinson, I.B., Rajagopalan, S. (2004) (6th Ed.). Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine. Oxford: Oxford University Press ISBN 9780198568377 </ref>. | ||
* [[ST segment]] <ref>Dolan, B., Holt, L. (2000). Accident & Emergency: Theory into practice. London: Bailliere Tindall ISBN 978-0702022395 </ref>. | * [[ST segment]] <ref>Dolan, B., Holt, L. (2000). Accident & Emergency: Theory into practice. London: Bailliere Tindall ISBN 978-0702022395 </ref>. | ||
* EKG findings of [[pericarditis]], and [[pericardial effusion]] may be seen if these conditions are accompanying tamponade. | * EKG findings of [[pericarditis]], and [[pericardial effusion]] may be seen if these conditions are accompanying tamponade. | ||
Revision as of 17:49, 14 September 2012
Electrocardiogram
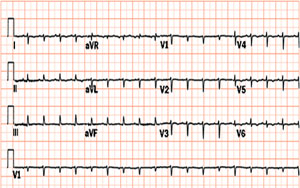
EKG findings of cardiac tamponade are:
- Sinus tachycardia
- Electrical alternans (beat-to-beat alterations in the QRS complex due to swinging of heart in pericardial fluid)
- Low voltage QRS complexes (Low QRS voltage is defined as maximum QRS amplitude in precordial lead < 1 mV and <0.5 mV in the limb leads due to insulating properties of fluid) [1].
- ST segment [2].
- EKG findings of pericarditis, and pericardial effusion may be seen if these conditions are accompanying tamponade.
-
Cardiac Tamponade with low voltage QRS complex and Electrical Alternans
-
12 lead EKG shows Cardiac Tamponade with Electrical Alternans