Candida vulvovaginitis physical examination: Difference between revisions
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | [[Category:Infectious disease]] | ||
| Line 80: | Line 70: | ||
[[Category:Gynecology]] | [[Category:Gynecology]] | ||
[[Category:Microbiology]] | [[Category:Microbiology]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Needs overview]] | ||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
Revision as of 17:18, 5 December 2012
|
Candidiasis Main page |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Candidiasis, commonly called yeast infection or thrush, is a fungal infection (mycosis) of any of the Candida species, of which Candida albicans is the most common.[1][2] Candidiasis thereby encompasses infections that range from superficial, such as oral thrush and vaginitis, to systemic and potentially life-threatening diseases.
Physical Examination
In immunocompetent people, candidiasis can usually only be found in exposed and moist parts of the body[1], such as:
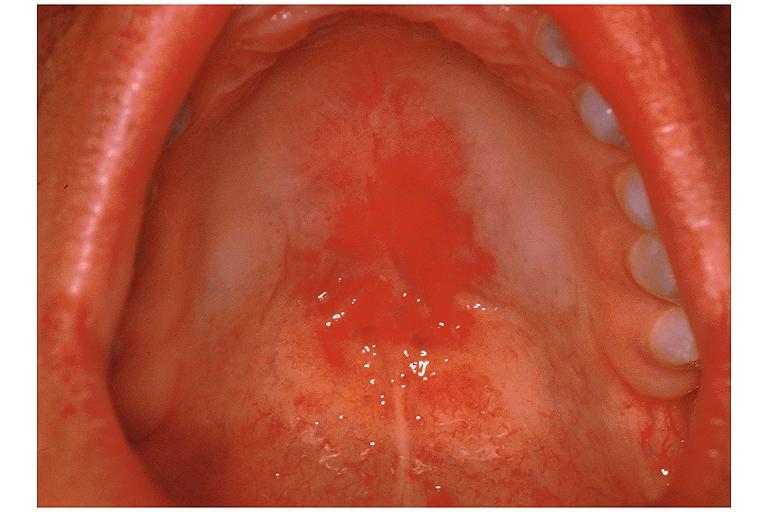
- the oral cavity (oral thrush)
- the vagina and/or vulva (vaginal candidiasis or thrush)
- folds of skin in the diaper area (diaper rash)
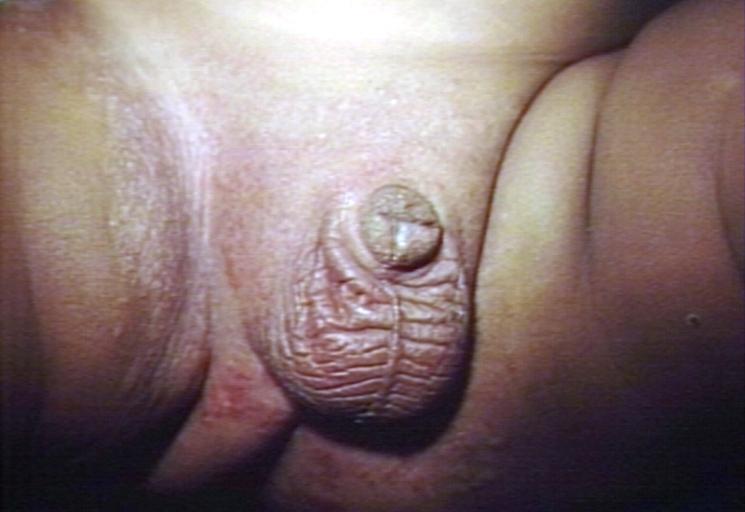
- the nipples while breastfeeding
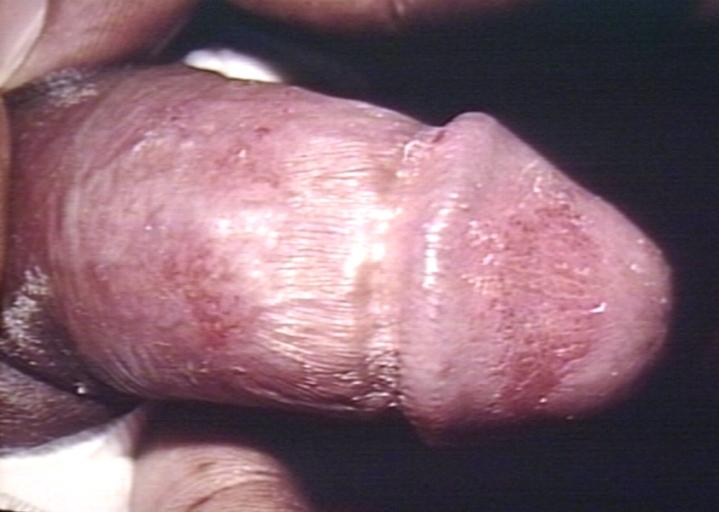
- the penis or foreskin
- the armpit
- the ear
- the skin around the nostrils or in the nostrils
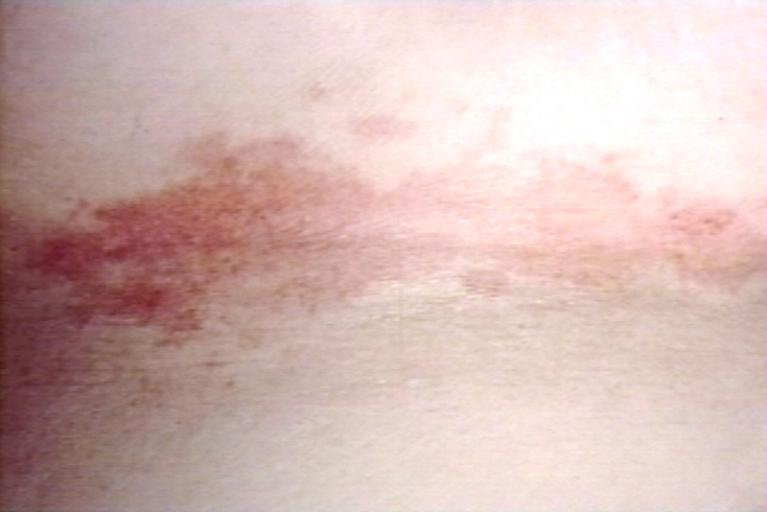
Candidiasis is the second most common cause of vaginal irritation, or vaginitis, and can also occur on the male genitals. In immunocompromised patients, the Candida infection can involve the esophagus and can become systemic, causing a much more serious condition: fungemia.
Children, mostly between the ages of 3 and 9 years, can be affected by chronic mouth yeast infections, normally seen around the mouth as white patches. However, this is not a common condition.
Images
-
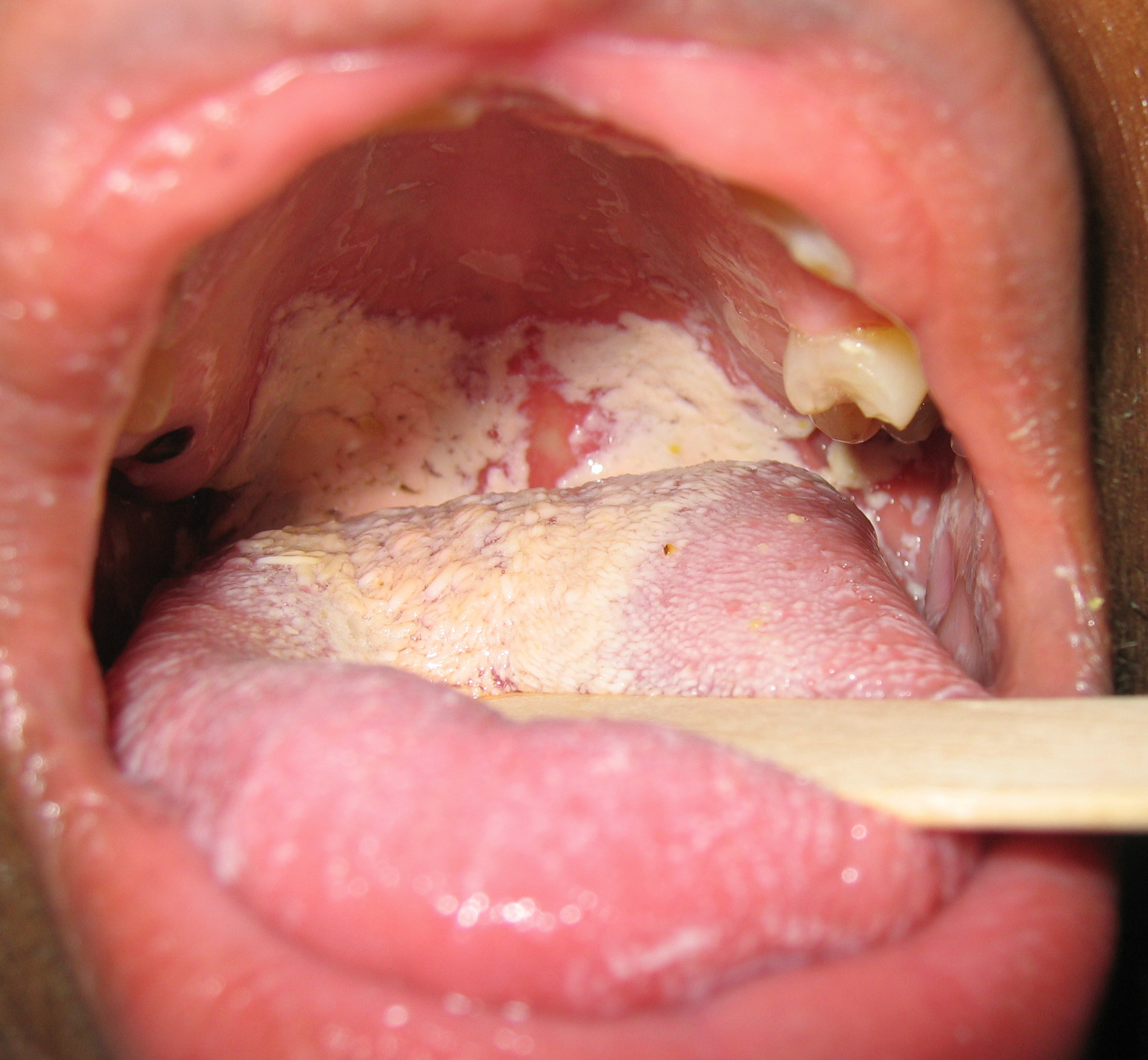
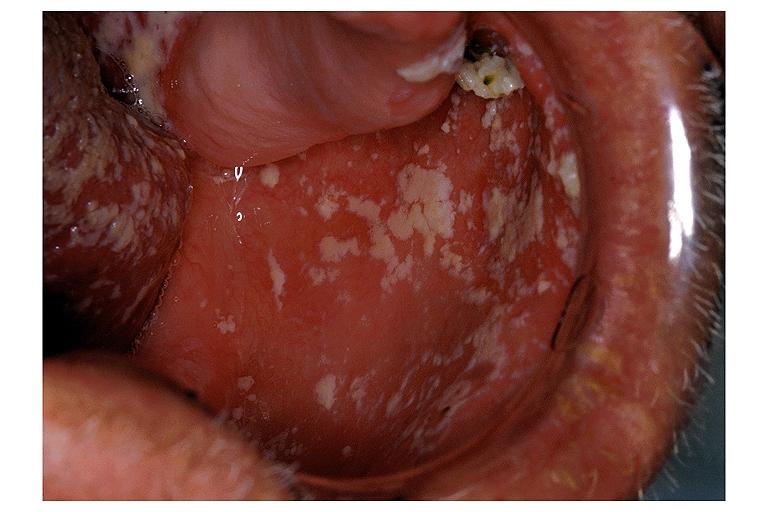
Oral manifestations of HIV infection and AIDS. Chronic oral candidiasis in patient with AIDS. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
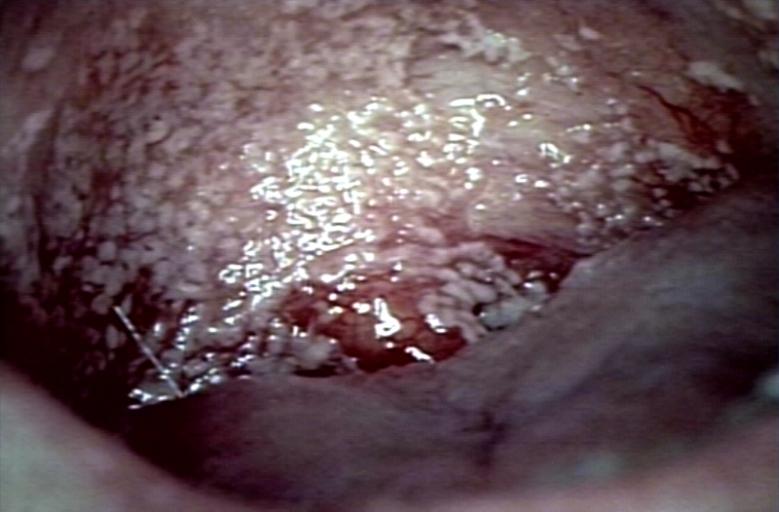
Soft palate showing extensive oral candidiasis in patient with AIDS. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
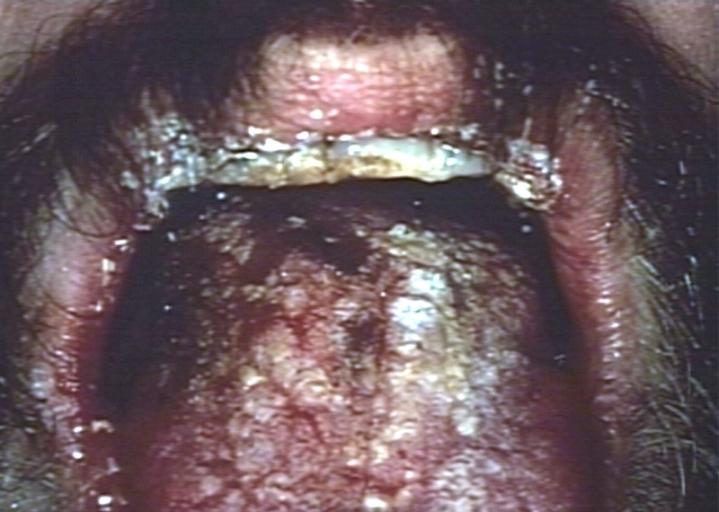
Oral candidiasis Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
Eczema secondary to candidiasis. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
Candidiasis; skinfold. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
Erythematous candidiasis. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
Genital candidiasis. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
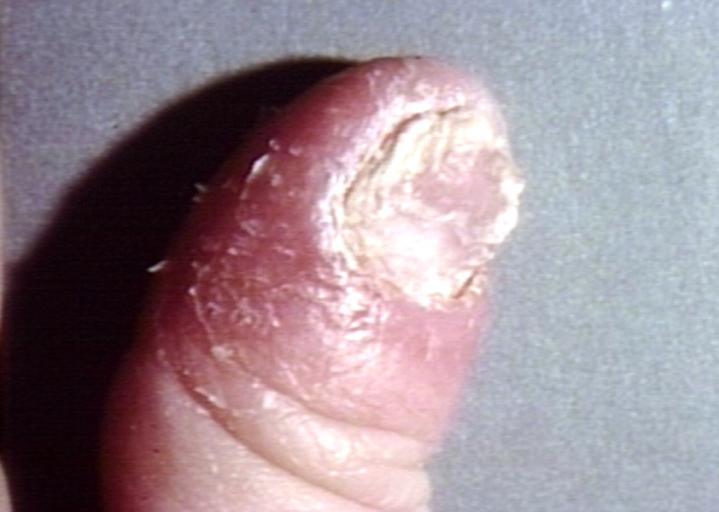
Paronychia: Another manifestation of candidiasis. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
Interdigital candidiasis. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
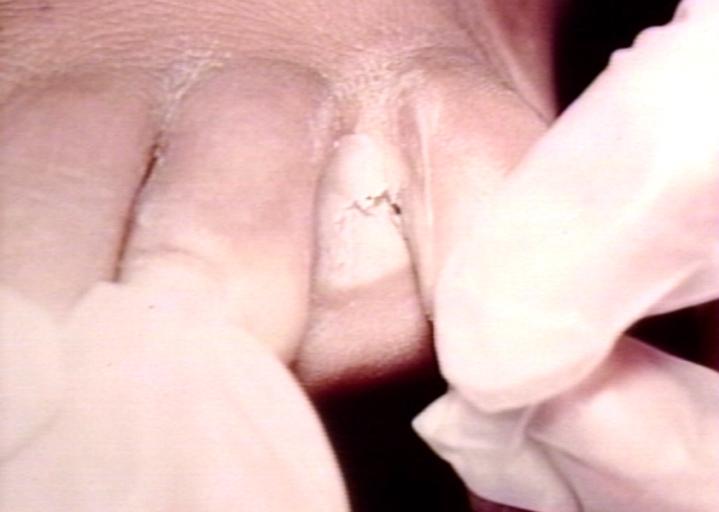
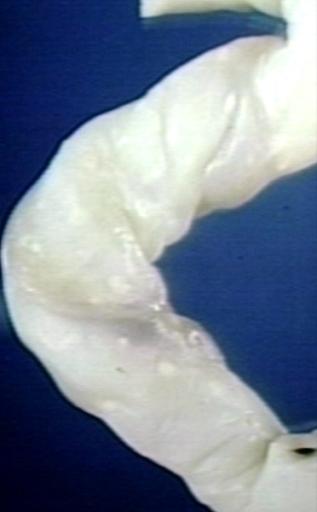
Candidiasis of umblical cord. White spots of colonies are present. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
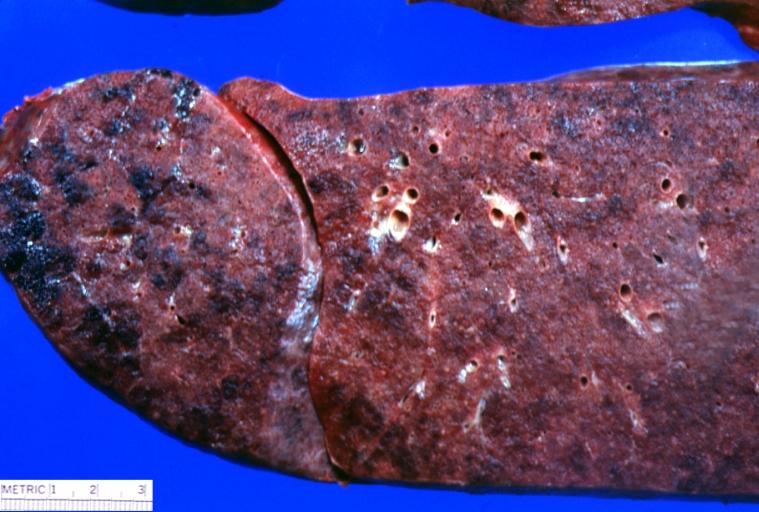
Lung: Candidiasis. Postmortem findings. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Walsh TJ, Dixon DM (1996). "Deep Mycoses". In Baron S et al eds. Baron's Medical Microbiology (via NCBI Bookshelf) (4th ed. ed.). Univ of Texas Medical Branch. ISBN 0-9631172-1-1.
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia Vaginal yeast infection