Botulism pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images) |
(→Images) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Images== | ==Images== | ||
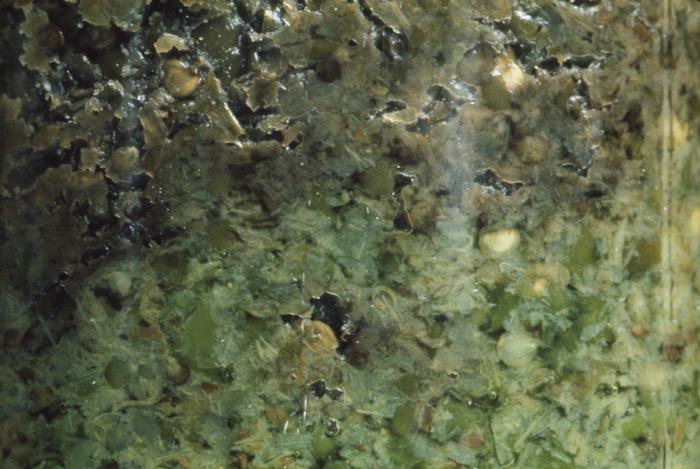
[[Image:Botulism outbreak.jpg|500px|This is a close up of contaminated Jalapeño peppers involved in an outbreak of botulism in Pontiac, Michigan, April, 1977. Ingestion of botulinal toxin results in an illness of variable severity. Common symptoms are diplopia, blurred vision, and bulbar weakness. Symmetric paralysis may progress rapidly.]] | [[Image:Botulism outbreak.jpg|500px|This is a close up of contaminated Jalapeño peppers involved in an outbreak of botulism in Pontiac, Michigan, April, 1977. Ingestion of botulinal toxin results in an illness of variable severity. Common symptoms are diplopia, blurred vision, and bulbar weakness. Symmetric paralysis may progress rapidly.]] | ||
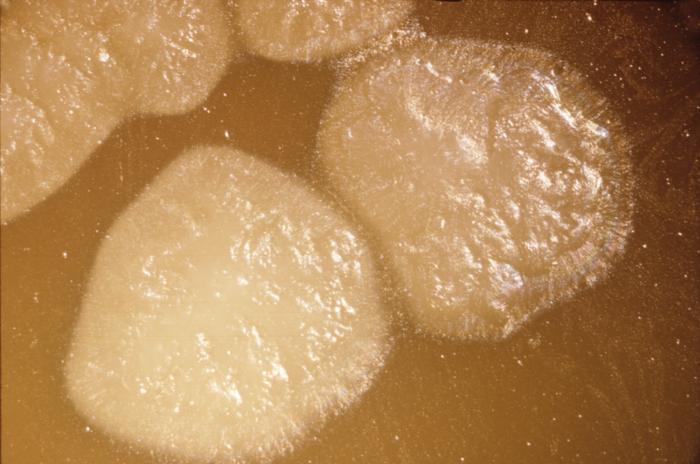
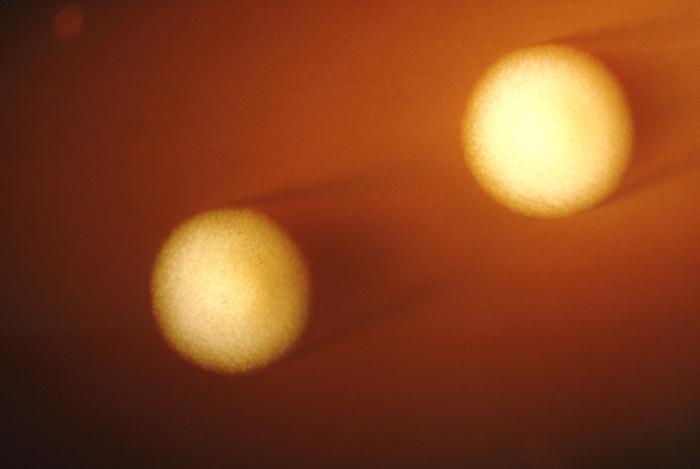
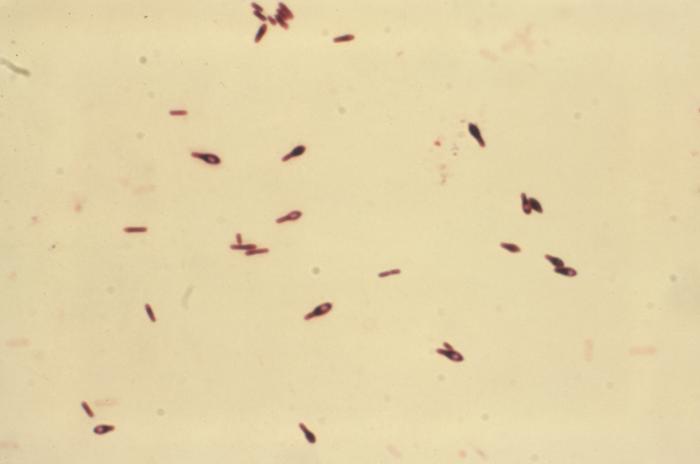
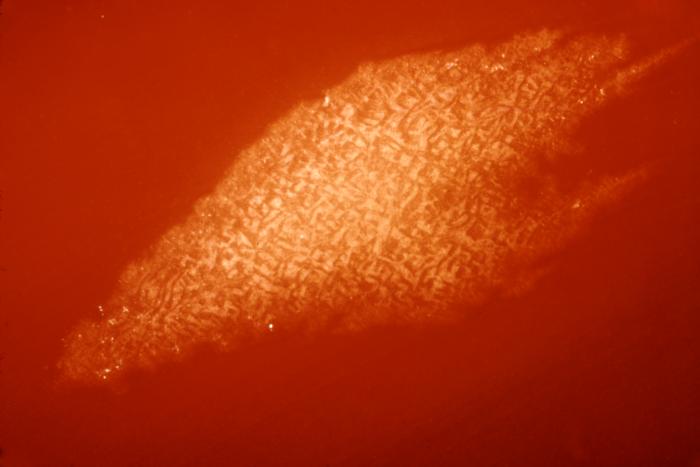
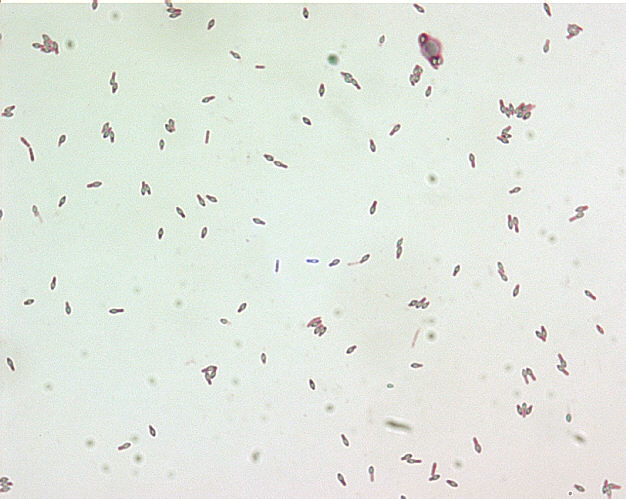
[[Image:Botulism type E.jpg| | [[Image:Botulism type E.jpg|500pc|These are Clostridium botulinum Type E colonies displaying an opaque zone grown on a 48hr egg yolk agar plate; Mag. 1.9 | ||
C. botulinum Type E is an indigenous organism in the aquatic environment, and is the type mainly associated with botulism from seafood products. It is a Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore-forming food borne pathogen.]] | C. botulinum Type E is an indigenous organism in the aquatic environment, and is the type mainly associated with botulism from seafood products. It is a Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore-forming food borne pathogen.]] | ||
Revision as of 15:47, 16 February 2012
|
Botulism Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Botulism pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Botulism pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Botulism pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Michael Maddaleni, B.S.