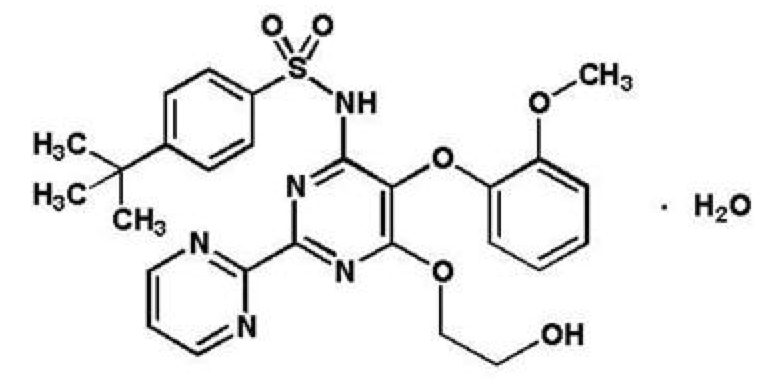
Bosentan
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING: RISKS OF HEPATOTOXICITY and TERATOGENICITY
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Because of the risks of hepatotoxicity and birth defects, Tracleer is available only through a restricted program called the Tracleer Access Program (T.A.P.). T.A.P. is a component of the Tracleer Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS). Under the Tracleer REMS, prescribers, patients, and pharmacies must enroll in the program.
Hepatotoxicity:
Teratogenicity:
|
Overview
Bosentan is an endothelin receptor antagonist that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of pulmonary arterial hypertension. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include edema, hypotension, palpitations, flushing, and headache.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- Tracleer® is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1) to improve exercise ability and to decrease clinical worsening. Studies establishing effectiveness included predominantly patients with NYHA Functional Class II-IV symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (60%), PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (21%), and PAH associated with congenital heart disease with left-to-right shunts (18%).
- Patients with WHO Class II symptoms showed reduction in the rate of clinical deterioration and a trend for improvement in walk distance. Physicians should consider whether these benefits are sufficient to offset the risk of hepatotoxicity in WHO Class II patients, which may preclude future use as their disease progresses.
- Healthcare professionals who prescribe Tracleer must enroll in the Tracleer Access Program (T.A.P.) and must comply with the required monitoring to minimize the risks associated with Tracleer.
- Dosing Information
- Initiate treatment at 62.5 mg twice daily for 4 weeks and then increase to the maintenance dose of 125 mg twice daily. Doses above 125 mg twice daily did not appear to confer additional benefit sufficient to offset the increased risk of hepatotoxicity.
- Tracleer should be administered in the morning and evening with or without food.
Dosage Adjustments for Patients Developing Aminotransferase Elevations
- Measure liver aminotransferase levels prior to initiation of treatment and then monthly. If aminotransferase levels increase, revise the monitoring and treatment plan. The table below summarizes the dosage adjustment and monitoring recommendations for patients who develop aminotransferase elevations >3 × ULN during therapy with Tracleer. Discontinue Tracleer if liver aminotransferase elevations are accompanied by clinical symptoms of hepatotoxicity (such as nausea, vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, jaundice, or unusual lethargy or fatigue) or increases in bilirubin ≥ 2 × ULN. There is no experience with the reintroduction of Tracleer in these circumstances. Information.
Patients with Low Body Weight
- In patients with a body weight below 40 kg but who are over 12 years of age, the recommended initial and maintenance dose is 62.5 mg twice daily. There is limited information about the safety and efficacy of Tracleer in children between the ages of 12 and 18 years.
- Coadministration of Tracleer in Patients on Ritonavir
- In patients who have been receiving ritonavir for at least 10 days, start Tracleer at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability.
- Coadministration of Ritonavir in Patients on Tracleer
- Discontinue use of Tracleer at least 36 hours prior to initiation of ritonavir. After at least 10 days following the initiation of ritonavir, resume Tracleer at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability.
Use in Patients with Pre-existing Hepatic Impairment
- Tracleer should generally be avoided in patients with moderate or severe liver impairment. Initiation of Tracleer should generally be avoided in patients with elevated aminotransferases >3 × ULN. No dose adjustment is required in patients with mildly impaired liver function.
Treatment Discontinuation
- There is limited experience with abrupt discontinuation of Tracleer. No evidence for acute rebound has been observed. Nevertheless, to avoid the potential for clinical deterioration, gradual dose reduction (62.5 mg twice daily for 3 to 7 days) should be considered.
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Bosentan in adult patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH)
- Dosing Information
- 62.5 mg orally twice daily for 4 weeks, followed by 125 mg twice daily or 62.5 mg twice daily in patients weighing less than 40 kilograms.[1]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Bosentan in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Bosentan in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Pregnancy
- Use of Tracleer is contraindicated in females who are or may become pregnant. To prevent pregnancy, females of childbearing potential must use two reliable forms of contraception during treatment and for one month after stopping Tracleer.
- Use with Cyclosporine A
- Coadministration of cyclosporine A and bosentan resulted in markedly increased plasma concentrations of bosentan. Therefore, concomitant use of Tracleer and cyclosporine A is contraindicated.
- Use with Glyburide
- An increased risk of liver enzyme elevations was observed in patients receiving glyburide concomitantly with bosentan. Therefore coadministration of glyburide and Tracleer is contraindicated.
- Hypersensitivity
- Tracleer is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to bosentan or any component of the product. Observed reactions include rash and angioedema
Warnings
|
WARNING: RISKS OF HEPATOTOXICITY and TERATOGENICITY
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Because of the risks of hepatotoxicity and birth defects, Tracleer is available only through a restricted program called the Tracleer Access Program (T.A.P.). T.A.P. is a component of the Tracleer Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS). Under the Tracleer REMS, prescribers, patients, and pharmacies must enroll in the program.
Hepatotoxicity:
Teratogenicity:
|
- Description
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Bosentan in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Bosentan in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Bosentan in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Bosentan during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Bosentan with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Bosentan with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Bosentan with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Bosentan with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Bosentan with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Bosentan in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Bosentan in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Bosentan in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Bosentan in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Bosentan in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Bosentan in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Bosentan in the drug label.
Pharmacology
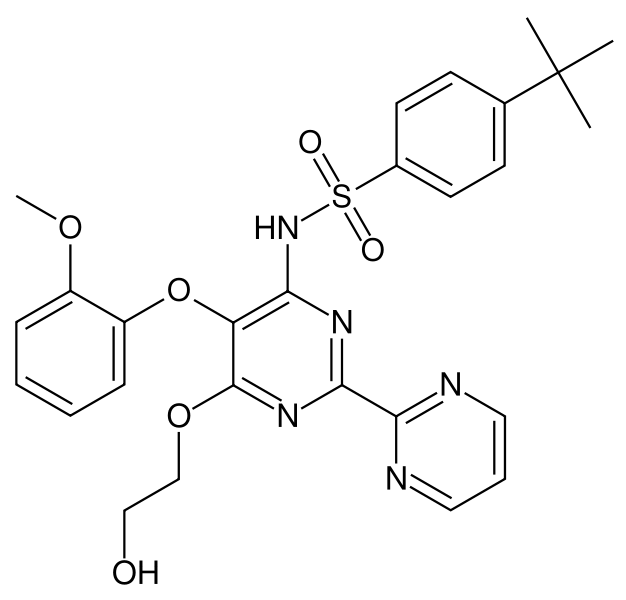
| |
Bosentan
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| N-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5- (2-methoxyphenoxy) -2-pyrimidin-2-yl-pyrimidin-4-yl] -4-tert- butyl-benzenesulfonamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | C02 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 551.615 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% |
| Protein binding | >98% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Half life | 5 hours |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
X |
| Legal status |
Template:Unicode Prescription only |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Bosentan in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Bosentan in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Bosentan in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Bosentan in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Bosentan Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Bosentan |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Bosentan |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Bosentan in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Bosentan interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Tracleer®[2]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- Tracleer® — Tricor®[3]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Jaïs, Xavier (2008-12-16). "Bosentan for treatment of inoperable chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: BENEFiT (Bosentan Effects in iNopErable Forms of chronIc Thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension), a randomized, placebo-controlled trial". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 52 (25): 2127–2134. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.08.059. ISSN 1558-3597. PMID 19095129. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ "TRACLEER (bosentan) tablet, film coated".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Bosentan |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Bosentan |Label Name=Bosentan11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Bosentan |Label Name=Bosentan11.png
}}