Band 3
| Solute carrier family 4, anion exchanger, member 1 (erythrocyte membrane protein band 3, Diego blood group) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Atomic microscope image of Band 3 | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbols | SLC4A1 ; WD; AE1; BND3; CD233; DI; EMPB3; EPB3; FR; MGC116750; MGC116753; MGC126619; MGC126623; RTA1A; SW; WD1; WR | ||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 37290 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
| solute carrier family 4 (anion exchanger), member 1, adaptor protein | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SLC4A1AP |
| Entrez | 22950 |
| HUGO | 13813 |
| OMIM | 602655 |
| RefSeq | NM_018158 |
| UniProt | Q9BWU0 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 2 p23.3 |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Band 3 |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Band 3 at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Band 3 at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Band 3
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Band 3 Risk calculators and risk factors for Band 3
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Anion Exchanger 1 (AE1) or Band 3 is a phylogenetically preserved transport protein responsible for catalysing the electroneutral exchange of chloride (Cl-) for bicarbonate (HCO3-) across a plasma membrane.
It is ubiquitous throughout the vertebrates. In humans it is present in two specific sites:
- the erythrocyte (red blood cell) cell membrane and
- the basolateral surface of the alpha-intercalated cell (the acid secreting cell type) in the collecting duct of the kidney.
The erythrocyte and kidney forms are different isoforms of the same protein.
Discovery
AE1 was discovered following SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis of erythrocyte cell membrane. The large 'third' band on the electrophoresis gel represented AE1, which was thus initially termed 'Band 3'. The chloride-bicarbonate exchanger in the red cell membrane is not a pump, which would use metabolic energy. Nor is it strictly an enzyme. It is protein counter-transporter, known as band III. [1]
AE1 in Red Cells
AE1 is an important structural component of the erythrocyte cell membrane, making up to 25% of the cell membrane surface, indeed each red cell contains approximately one million copies of AE1.
Function
Here it performs two functions:
- Electroneutral chloride and bicarbonate exchange across the plasma membrane on a one-for-one basis.This is crucial for CO2 uptake by the red cell and conversion (by hydration catalysed by carbonic anhydrase) into a proton and a bicarbonate ion. The bicarbonate is then extruded from the cell by the band 3 molecule.
- Physical linkage of the plasma membrane to the underlying membrane skeleton (via binding with ankyrin and protein 4.2). This appears to be to prevent membrane surface loss, rather than being to do with membrane skeleton assembly.
Pathology
Mutations of erythroid AE1 affecting the extracellular domains of the molecule may cause alterations in the individual's blood group, as band 3 determines the Diego blood group.
More importantly erythroid AE1 mutations cause between 15-25% of cases of Hereditary spherocytosis (a disorder associated with progressive red cell membrane loss), and also cause the hereditary conditions of Hereditary stomatocytosis [2] and Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis [3]
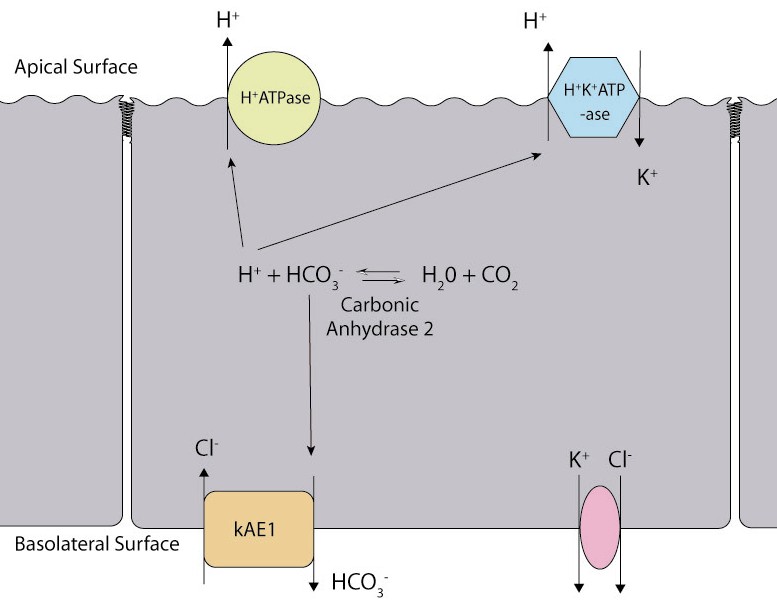
AE1 in Alpha-Intercalated cells
A different isoform of AE1, known as kAE1 (which is 65 amino acids shorter than erythroid AE1) is found in the basolateral surface of the alpha-intercalated cell in the cortical collecting duct of the kidney.
Function
This is the principal acid secreting cell of the kidney, which generates hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions from carbon dioxide and water-a reaction catalysed by Carbonic anhydrase.
The hydrogen ions are pumped into the collecting duct tubule by vacuolar H+ATPase, the apical proton pump,which thus excretes acid into the urine.
kAE1 exchanges bicarbonate for chloride on the basolateral surface, essentially returning bicarbonate to the blood.
Pathology
Mutations of kidney AE1 cause distal (type1) renal tubular acidosis, which is an inability to acidify the urine, even if the blood is too acid. These mutations are disease causing as they cause mistargetting of the mutant band 3 proteins so that they are retained within the cell or occasionally addressed to the wrong (ie apical) surface.
See also
References
- ↑ Hunter M (1977). "Human erythrocyte anion permeabilities measured under conditions of net charge transfer". J Physiol. 268 (1): 35–49. PMID 874904.
- ↑ LJ Bruce (2005). "Monovalent cation leaks in human red cells caused by single amino-acid substitutions in the transport domain of the band 3 chloride-bicarbonate exchanger, AE1". Nature Genetics. 37 (11): 1258–63. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Jarolim p (1991). "Deletion in Erythrocyte Band 3 Gene in Malaria-Resistant Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis". PNAS. 88: 11022–11026..
External links
- Diego blood group system at BGMUT Blood Group Antigen Gene Mutation Database at NCBI, NIH
- Band+3+Protein at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Chloride-Bicarbonate+Antiporters at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
Further reading
- Tanner MJ (1993). "Molecular and cellular biology of the erythrocyte anion exchanger (AE1)". Semin. Hematol. 30 (1): 34–57. PMID 8434259.
- Chambers EJ, Askin D, Bloomberg GB; et al. (1998). "Studies on the structure of a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic loop of the human red cell anion exchanger (band 3, AE1)". Biochem. Soc. Trans. 26 (3): 516–20. PMID 9765907.
- Inaba M (2002). "[Band 3: expanding knowledge on its functions]". Seikagaku. 73 (12): 1431–5. PMID 11831035.
- Tanner MJ (2002). "Band 3 anion exchanger and its involvement in erythrocyte and kidney disorders". Curr. Opin. Hematol. 9 (2): 133–9. PMID 11844997.
- Shayakul C, Alper SL (2004). "Defects in processing and trafficking of the AE1 Cl-/HCO3- exchanger associated with inherited distal renal tubular acidosis". Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 8 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1007/s10157-003-0271-x. PMID 15067510.