Arnold-Chiari malformation history and symptoms: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
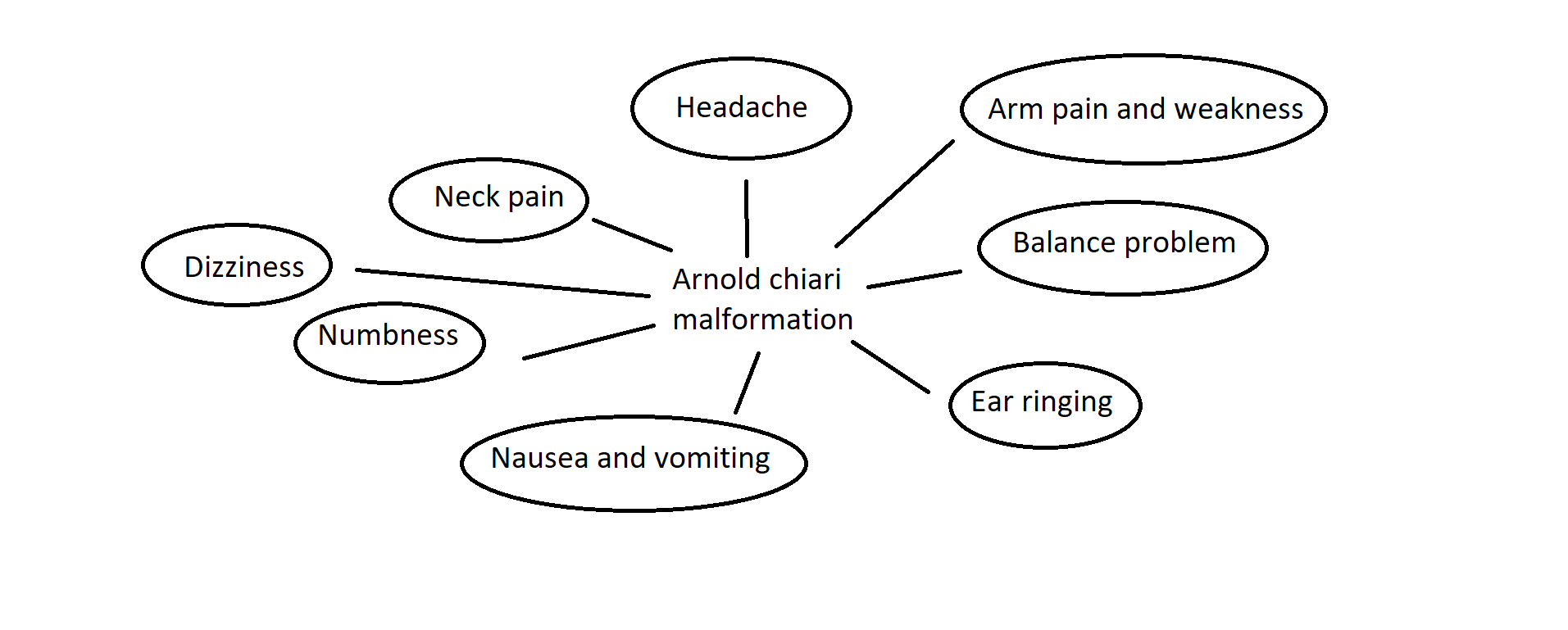
The | The most common [[symptoms]] of Arnold-Chiari malformation is [[headache]], [[arm pain]] and [[weakness]], [[neck pain]], [[nausea and vomiting]], [[Balance disorder|balance problem]], [[dizziness]] and [[ear ringing]]. | ||
==History and Symptoms== | ==History and Symptoms== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
=== Common Symptoms === | === Common Symptoms === | ||
* Common symptoms of Arnold-Chiari malformation type 1 and 2 include:<ref name="DysteMenezes1989">{{cite journal|last1=Dyste|first1=Gregg N.|last2=Menezes|first2=Arnold H.|last3=VanGilder|first3=John C.|title=Symptomatic Chiari malformations|journal=Journal of Neurosurgery|volume=71|issue=2|year=1989|pages=159–168|issn=0022-3085|doi=10.3171/jns.1989.71.2.0159}}</ref><ref name="BellCharney1987">{{cite journal|last1=Bell|first1=William O.|last2=Charney|first2=Edward B.|last3=Bruce|first3=Derek A.|last4=Sutton|first4=Leslie N.|last5=Schut|first5=Luis|title=Symptomatic Arnold-Chiari malformation: review of experience with 22 cases|journal=Journal of Neurosurgery|volume=66|issue=6|year=1987|pages=812–816|issn=0022-3085|doi=10.3171/jns.1987.66.6.0812}}</ref><ref name="PapasozomenosRoessmann1981">{{cite journal|last1=Papasozomenos|first1=S.|last2=Roessmann|first2=U.|title=Respiratory distress and Arnold-Chiari malformation|journal=Neurology|volume=31|issue=1|year=1981|pages=97–97|issn=0028-3878|doi=10.1212/WNL.31.1.97}}</ref> | * Common [[Symptom|symptoms]] of Arnold-Chiari malformation type 1 and 2 include:<ref name="DysteMenezes1989">{{cite journal|last1=Dyste|first1=Gregg N.|last2=Menezes|first2=Arnold H.|last3=VanGilder|first3=John C.|title=Symptomatic Chiari malformations|journal=Journal of Neurosurgery|volume=71|issue=2|year=1989|pages=159–168|issn=0022-3085|doi=10.3171/jns.1989.71.2.0159}}</ref><ref name="BellCharney1987">{{cite journal|last1=Bell|first1=William O.|last2=Charney|first2=Edward B.|last3=Bruce|first3=Derek A.|last4=Sutton|first4=Leslie N.|last5=Schut|first5=Luis|title=Symptomatic Arnold-Chiari malformation: review of experience with 22 cases|journal=Journal of Neurosurgery|volume=66|issue=6|year=1987|pages=812–816|issn=0022-3085|doi=10.3171/jns.1987.66.6.0812}}</ref><ref name="PapasozomenosRoessmann1981">{{cite journal|last1=Papasozomenos|first1=S.|last2=Roessmann|first2=U.|title=Respiratory distress and Arnold-Chiari malformation|journal=Neurology|volume=31|issue=1|year=1981|pages=97–97|issn=0028-3878|doi=10.1212/WNL.31.1.97}}</ref> | ||
** In [[infant]]s | ** In [[infant]]s | ||
***[[Stridor]] | ***[[Stridor]] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
***[[Sleep apnea]] | ***[[Sleep apnea]] | ||
*** Impaired [[fine motor]] skills | *** Impaired [[fine motor]] skills | ||
*** Muscle weakness | ***[[Muscle weakness]] | ||
***[[Palpitations]] | ***[[Palpitations]] | ||
*** Excessive clearing of the throat with no obstructions | *** Excessive clearing of the throat with no obstructions | ||
NOTE: Patients may experience no symptoms or remain asymptomatic until early adulthood at which point they will often experience severe headaches and neck pain. | NOTE: Patients may experience no [[Symptom|symptoms]] or remain asymptomatic until early adulthood at which point they will often experience severe [[headaches]] and [[neck pain]]. | ||
NOTE: Some patients may go an entire lifetime without having noticeable symptoms. Or, symptoms can be minimal, then turn severe suddenly due to head trauma which alters the condition of the spine, brain, or cerebellar tonsils and begins to cause more difficulties. | NOTE: Some [[Patient|patients]] may go an entire lifetime without having noticeable [[Symptom|symptoms]]. Or, [[Symptom|symptoms]] can be minimal, then turn severe suddenly due to [[head trauma]] which alters the condition of the [[spine]], [[brain]], or [[cerebellar tonsils]] and begins to cause more difficulties. | ||
* Common symptoms of Arnold-Chiari malformation type 3 and 4 include: | * Common [[symptoms]] of Arnold-Chiari malformation type 3 and 4 include: | ||
** Respiratory failure in infancy | **[[Respiratory failure]] in [[infancy]] | ||
** Seizure (epilepsy) | **[[Seizure]] ([[epilepsy]]) | ||
** Mental retardation | **[[Mental retardation]] | ||
** Flaccid or spastic paralysis | **[[Flaccid]] or [[spastic paralysis]] | ||
** Sever neurological problems[[File:Untitleddd.png|700px|none|thumb|Source: {{Fs}}]] | ** Sever [[neurological]] problems[[File:Untitleddd.png|700px|none|thumb|Source: {{Fs}}]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 00:41, 19 September 2019
|
Arnold-Chiari malformation Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Arnold-Chiari malformation from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Arnold-Chiari malformation history and symptoms On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Arnold-Chiari malformation history and symptoms |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Arnold-Chiari malformation history and symptoms |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Template:Ae Fahimeh Shojaei, M.D.
Overview
The most common symptoms of Arnold-Chiari malformation is headache, arm pain and weakness, neck pain, nausea and vomiting, balance problem, dizziness and ear ringing.
History and Symptoms
History
Common Symptoms
- Common symptoms of Arnold-Chiari malformation type 1 and 2 include:[1][2][3]
- In infants
- Stridor
- Swallowing difficulties
- In older children
- Limb weakness
- Dizziness
- Vertigo
- Neuropathic pain
- Pain at the point of tethering
- Visual disturbances
- Difficulty swallowing
- Ringing in the ears
- Sleep apnea
- Impaired fine motor skills
- Muscle weakness
- Palpitations
- Excessive clearing of the throat with no obstructions
- In infants
NOTE: Patients may experience no symptoms or remain asymptomatic until early adulthood at which point they will often experience severe headaches and neck pain.
NOTE: Some patients may go an entire lifetime without having noticeable symptoms. Or, symptoms can be minimal, then turn severe suddenly due to head trauma which alters the condition of the spine, brain, or cerebellar tonsils and begins to cause more difficulties.
- Common symptoms of Arnold-Chiari malformation type 3 and 4 include:
- Respiratory failure in infancy
- Seizure (epilepsy)
- Mental retardation
- Flaccid or spastic paralysis
- Sever neurological problems
Source: Fahimeh Shojaei, M.D.
Less Common Symptoms
Less common symptoms of Arnold-Chiari malformation include:
References
- ↑ Dyste, Gregg N.; Menezes, Arnold H.; VanGilder, John C. (1989). "Symptomatic Chiari malformations". Journal of Neurosurgery. 71 (2): 159–168. doi:10.3171/jns.1989.71.2.0159. ISSN 0022-3085.
- ↑ Bell, William O.; Charney, Edward B.; Bruce, Derek A.; Sutton, Leslie N.; Schut, Luis (1987). "Symptomatic Arnold-Chiari malformation: review of experience with 22 cases". Journal of Neurosurgery. 66 (6): 812–816. doi:10.3171/jns.1987.66.6.0812. ISSN 0022-3085.
- ↑ Papasozomenos, S.; Roessmann, U. (1981). "Respiratory distress and Arnold-Chiari malformation". Neurology. 31 (1): 97–97. doi:10.1212/WNL.31.1.97. ISSN 0028-3878.