Aminohippurate: Difference between revisions
Rabin Bista (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (Protected "Aminohippurate": Bot: Protecting all pages from category Drug ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite))) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|genericName=Aminohippurate sodium | |genericName=Aminohippurate sodium | ||
|aOrAn=a | |aOrAn=a | ||
|drugClass=Diagnostic Agent | |drugClass=[[Diagnosis|Diagnostic Agent]] | ||
|indicationType=diagnosis | |indicationType=diagnosis | ||
|indication= | |indication=[[Effective renal plasma flow]] (ERPF) | ||
|adverseReactions=Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria | |adverseReactions=[[Hypersensitivity reactions]] including [[anaphylaxis]], [[angioedema]], [[urticaria]], [[Urinary urgency|Urgent desire to urinate]], | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
|fdaLIADAdult=====Indications==== | |fdaLIADAdult=====Indications==== | ||
* Estimation of | * Estimation of [[Effective renal plasma flow]]. | ||
* Measurement of the functional capacity of the renal tubular secretory mechanism. | * Measurement of the functional capacity of the [[Nephron|renal tubular secretory mechanism]]. | ||
====Dosage==== | ====Dosage==== | ||
For intravenous use only | * For [[intravenous]] use only | ||
Clearance measurements using single injection techniques are generally inaccurate, particularly in the measurement of ERPF. For this reason, intravenous infusions at fixed rates are used to sustain the plasma PAH concentration at the desired level. | * Clearance measurements using single injection techniques are generally inaccurate, particularly in the measurement of ERPF. For this reason, [[intravenous]] infusions at fixed rates are used to sustain the [[plasma]] [[PAH]] concentration at the desired level. | ||
To measure ERPF, the concentration of PAH in the plasma should be maintained at 2 mg per 100 mL, which can be achieved with a priming dose of 6 to 10 mg/kg and an infusion dose of 10 to 24 mg/min. | * To measure ERPF, the concentration of [[PAH]] in the [[plasma]] should be maintained at 2 mg per 100 mL, which can be achieved with a priming dose of 6 to 10 mg/kg and an infusion dose of 10 to 24 mg/min. | ||
As a research procedure for the measurement of TmPAH, the plasma level of PAH must be sufficient to saturate the capacity of the tubular secretory cells. Concentrations from 40 to 60 mg per 100 mL are usually necessary. | * As a research procedure for the measurement of [[TmPAH]], the [[plasma]] level of [[PAH]] must be sufficient to saturate the capacity of the tubular secretory cells. Concentrations from 40 to 60 mg per 100 mL are usually necessary. | ||
Technical details of these tests may be found in Smith {1}; Wesson {2}; Bauer {3}; Pitts{4}; and Schnurr {5}. | * Technical details of these tests may be found in Smith {1}; Wesson {2}; Bauer {3}; Pitts{4}; and Schnurr {5}. | ||
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to use, whenever solution and container permit. NOTE: The normal color range for this product is a colorless to yellow/brown solution. The efficacy is not affected by color changes within this range. | * Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to use, whenever solution and container permit. NOTE: The normal color range for this product is a colorless to yellow/brown solution. The efficacy is not affected by color changes within this range. | ||
Calculations | =====Calculations===== | ||
Effective Renal Plasma Flow (ERPF) | [[Effective Renal Plasma Flow]] (ERPF) | ||
The clearance of PAH, which is extracted almost completely from the plasma during its passage through the renal circulation, constitutes a measure of ERPF. Hence: | * The clearance of [[PAH]], which is extracted almost completely from the plasma during its passage through the renal circulation, constitutes a measure of ERPF. * Hence: | ||
ERPF = UPAHV/PPAH | : ERPF = [[UPAHV]]/[[PPAH]] | ||
Where UPAH = concentration of PAH (mg/mL) in the urine | : Where [[UPAH]] = concentration of [[PAH]] (mg/mL) in the urine | ||
V = rate of urine excretion (mL/min), and | : V = rate of urine excretion (mL/min), and | ||
PPAH = plasma concentration of PAH (mg/mL). | : PPAH = plasma concentration of [[PAH]] (mg/mL). | ||
Example: | * Example: | ||
UPAH = 8.0 mg/mL | : [[UPAH]] = 8.0 mg/mL | ||
V = 1.5 mL/min | : V = 1.5 mL/min | ||
PPAH = 0.02 mg/mL | : [[PPAH]] = 0.02 mg/mL | ||
ERPF = 8.0 x 1.5/0.02 = 600 mL/min | : ERPF = 8.0 x 1.5/0.02 = 600 mL/min | ||
Based on PAH clearance studies, the normal values for ERPF are: | * Based on [[PAH]] clearance studies, the normal values for ERPF are: | ||
men 675 ± 150 mL/min | : men 675 ± 150 mL/min | ||
women 595 ± 125 mL/min | : women 595 ± 125 mL/min | ||
Maximum Tubular Secretory | * Maximum Tubular Secretory | ||
(TmPAH ) Mechanism | : (TmPAH ) Mechanism | ||
The quantity of PAH secreted by the tubules (TmPAH) is given by the difference between the total rate of excretion (UPAHV) and the quantity filtered by the glomeruli (GFR x PPAH). Hence: | * The quantity of [[PAH]] secreted by the tubules (TmPAH) is given by the difference between the total rate of excretion (UPAHV) and the quantity filtered by the glomeruli (GFR x PPAH). Hence: | ||
TmPAH = UPAHV – (GFR x PPAH x 0.83) | : TmPAH = UPAHV – (GFR x PPAH x 0.83) | ||
The factor, 0.83, corrects for that portion of PAH which is bound to plasma protein and hence is unfilterable. | * The factor, 0.83, corrects for that portion of PAH which is bound to plasma protein and hence is unfilterable. | ||
Example: | * Example: | ||
UPAH = 9.55 mg/mL | : [[UPAH]] = 9.55 mg/mL | ||
V = 16.68 mL/min | : V = 16.68 mL/min | ||
GFR = 120 mL/min | : GFR = 120 mL/min | ||
PPAH = 0.60 mg/mL | : [[PPAH]] = 0.60 mg/mL | ||
Then TmPAH = 9.55 x 16.68 – (120 x 0.60 x 0.83) = 100 mg/min. | : Then TmPAH = 9.55 x 16.68 – (120 x 0.60 x 0.83) = 100 mg/min. | ||
Average normal values of TmPAH are 80-90 mg/min. | * Average normal values of TmPAH are 80-90 mg/min. | ||
The value of the expression UPAHV, used in calculations of ERPF and TmPAH, may be found by determining the amount of PAH in a measured volume of urine excreted within a specific period of time. | * The value of the expression [[UPAHV]], used in calculations of ERPF and [[TmPAH]], may be found by determining the amount of PAH in a measured volume of urine excreted within a specific period of time. | ||
These calculations are based on a body surface area of 1.73 m2. Corrections for variations in surface area are made by multiplying the values obtained for ERPF and TmPAH by 1.73/A, where A is the subject surface area. | * These calculations are based on a body surface area of 1.73 m2. Corrections for variations in surface area are made by multiplying the values obtained for ERPF and [[TmPAH]] by 1.73/A, where A is the subject surface area. | ||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | ||
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
<!--Contraindications--> | <!--Contraindications--> | ||
|contraindications=* Hypersensitivity to this product or to its components. | |contraindications=* [[Hypersensitivity]] to this product or to its components. | ||
<!--Warnings--> | <!--Warnings--> | ||
|warnings=====Precautions==== | |warnings=====Precautions==== | ||
General | =====General===== | ||
Intravenous solutions must be given with caution to patients with low cardiac reserve, since a rapid increase in plasma volume can precipitate congestive heart failure. | * [[Intravenous]] solutions must be given with caution to patients with low cardiac reserve, since a rapid increase in [[plasma]] volume can precipitate [[congestive heart failure]]. | ||
For measurement of ERPF, small doses of PAH are used. However, in research procedures to measure TmPAH, high plasma levels are required to saturate the capacity of the tubular cells. During these procedures, the intravenous administration of PAH solutions should be carried out slowly and with caution. The patient should be continuously observed for any adverse reactions. | * For measurement of ERPF, small doses of [[PAH]] are used. However, in research procedures to measure TmPAH, high plasma levels are required to saturate the capacity of the tubular cells. During these procedures, the [[intravenous]] administration of PAH solutions should be carried out slowly and with caution. The patient should be continuously observed for any adverse reactions. | ||
Use caution when injecting this product into latex-sensitive individuals, since the vial stopper contains dry natural latex rubber that may cause allergic reactions. | * Use caution when injecting this product into latex-sensitive individuals, since the vial stopper contains dry natural latex rubber that may cause allergic reactions. | ||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | <!--Adverse Reactions--> | ||
<!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | <!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | ||
|clinicalTrials=Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, vasomotor disturbances, flushing, tingling, nausea, vomiting, and cramps may occur. | |clinicalTrials=* [[Hypersensitivity reactions]] including [[anaphylaxis]], [[angioedema]], [[urticaria]], [[Vasodilator|vasomotor disturbances]], [[flushing]], [[tingling]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], and [[cramps]] may occur. | ||
Patients may have a sensation of warmth or the desire to defecate or urinate during or shortly following initiation of infusion. | * Patients may have a sensation of warmth or the desire to defecate or [[Urinary urgency|urinate]] during or shortly following initiation of infusion. | ||
|postmarketing=There is limited information regarding <i>Postmarketing Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |postmarketing=There is limited information regarding <i>Postmarketing Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | <!--Drug Interactions--> | ||
|drugInteractions=* Renal clearance measurements of PAH cannot be made with any significant accuracy in patients receiving sulfonamides, procaine, or thiazolesulfone. These compounds interfere with chemical color development essential to the analytical procedures. | |drugInteractions=* [[Renal clearance]] measurements of [[PAH]] cannot be made with any significant accuracy in patients receiving [[sulfonamides]], [[procaine]], or [[thiazolesulfone]]. These compounds interfere with chemical color development essential to the analytical procedures. | ||
Probenecid depresses tubular secretion of certain weak acids such as PAH. Therefore, patients receiving probenecid will have erroneously low ERPF and TmPAH values. | * [[Probenecid]] depresses tubular secretion of certain weak acids such as [[PAH]]. Therefore, patients receiving [[probenecid]] will have erroneously low ERPF and TmPAH values. | ||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | <!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
| Line 205: | Line 156: | ||
<!--Administration and Monitoring--> | <!--Administration and Monitoring--> | ||
|administration=* Intravenous | |administration=* [[Intravenous]] | ||
|monitoring=There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |monitoring=There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
| Line 279: | Line 230: | ||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | <!--Mechanism of Action--> | ||
|mechAction= | |mechAction= | ||
<!--Structure--> | <!--Structure--> | ||
|structure=* Aminohippurate sodium1 is an agent to measure effective renal plasma flow (ERPF). It is the sodium salt of para-aminohippuric acid, commonly abbreviated | |structure=* Aminohippurate sodium1 is an agent to measure effective renal plasma flow (ERPF). It is the sodium salt of [[para-aminohippuric acid]], commonly abbreviated “[[PAH]]”. It is water soluble, lipid-insoluble, and has a pKa of 3.83. The empirical formula of the anhydrous salt is C9H9N2NaO3 and its structural formula is: | ||
: [[File:Amminohippurate str.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | : [[File:Amminohippurate str.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
It is provided as a sterile, non-preserved 20 percent aqueous solution for injection, with a pH of 6.7 to 7.6. Each 10 mL contains: Aminohippurate sodium 2 g. Inactive ingredients: Sodium hydroxide to adjust pH, water for injection, q.s. | * It is provided as a sterile, non-preserved 20 percent aqueous solution for injection, with a pH of 6.7 to 7.6. Each 10 mL contains: Aminohippurate sodium 2 g. Inactive ingredients: Sodium hydroxide to adjust pH, water for injection, q.s. | ||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | <!--Pharmacodynamics--> | ||
| Line 292: | Line 243: | ||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | <!--Pharmacokinetics--> | ||
|PK=PAH is filtered by the glomeruli and is actively secreted by the proximal tubules. At low plasma concentrations (1.0 to 2.0 mg/100 mL), an average of 90 percent of PAH is cleared by the kidneys from the renal blood stream in a single circulation. It is ideally suited for measurement of ERPF since it has a high clearance, is essentially nontoxic at the plasma concentrations reached with recommended doses, and its analytical determination is relatively simple and accurate. | |PK=* [[PAH]] is filtered by the [[glomeruli]] and is actively secreted by the [[proximal tubules]]. At low plasma concentrations (1.0 to 2.0 mg/100 mL), an average of 90 percent of PAH is cleared by the kidneys from the renal blood stream in a single circulation. It is ideally suited for measurement of ERPF since it has a high clearance, is essentially nontoxic at the plasma concentrations reached with recommended doses, and its analytical determination is relatively simple and accurate. | ||
PAH is also used to measure the functional capacity of the renal tubular secretory mechanism or transport maximum (TmPAH). This is accomplished by elevating the plasma concentration to levels (40-60 mg/100 mL) sufficient to saturate the maximal capacity of the tubular cells to secrete PAH. | * [[PAH]] is also used to measure the functional capacity of the renal tubular secretory mechanism or transport maximum (TmPAH). This is accomplished by elevating the plasma concentration to levels (40-60 mg/100 mL) sufficient to saturate the maximal capacity of the tubular cells to secrete PAH. | ||
Inulin clearance is generally measured during TmPAH determinations since glomerular filtration rate (GFR) must be known before calculations of secretory Tm measurements can be done | * [[Inulin clearance]] is generally measured during TmPAH determinations since [[glomerular filtration rate]] (GFR) must be known before calculations of secretory Tm measurements can be done | ||
<!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | <!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | ||
|nonClinToxic=Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility | |nonClinToxic======Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility===== | ||
Long-term studies in animals have not been done to evaluate any effects upon fertility or carcinogenic potential of PAH. | * Long-term studies in animals have not been done to evaluate any effects upon fertility or carcinogenic potential of PAH. | ||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | <!--Clinical Studies--> | ||
| Line 308: | Line 259: | ||
|howSupplied=* No. 95 — Aminohippurate Sodium, 20 percent sterile solution for intravenous injection, is supplied as follows: | |howSupplied=* No. 95 — Aminohippurate Sodium, 20 percent sterile solution for intravenous injection, is supplied as follows: | ||
NDC 0006-3395-11 in 10 mL vials. | * NDC 0006-3395-11 in 10 mL vials. | ||
|storage=* Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) | |storage=* Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) | ||
|packLabel=PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - CARTON - 10 ML SINGLE DOSE VIAL | |packLabel=====PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - CARTON - 10 ML SINGLE DOSE VIAL==== | ||
: [[File:Amminohippurate PDP.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | : [[File:Amminohippurate PDP.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
| Line 330: | Line 281: | ||
|drugShortage= | |drugShortage= | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 352: | Line 286: | ||
[[Category:Drug]] | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
[[Category:Amino acid derivatives]] | |||
[[Category:Anilines]] | |||
[[Category:Benzamides]] | |||
[[Category:Acetic acids]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:30, 18 August 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Rabin Bista, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Aminohippurate is a Diagnostic Agent that is FDA approved for the diagnosis of Effective renal plasma flow (ERPF). Common adverse reactions include Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, Urgent desire to urinate,.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- Estimation of Effective renal plasma flow.
- Measurement of the functional capacity of the renal tubular secretory mechanism.
Dosage
- For intravenous use only
- Clearance measurements using single injection techniques are generally inaccurate, particularly in the measurement of ERPF. For this reason, intravenous infusions at fixed rates are used to sustain the plasma PAH concentration at the desired level.
- To measure ERPF, the concentration of PAH in the plasma should be maintained at 2 mg per 100 mL, which can be achieved with a priming dose of 6 to 10 mg/kg and an infusion dose of 10 to 24 mg/min.
- As a research procedure for the measurement of TmPAH, the plasma level of PAH must be sufficient to saturate the capacity of the tubular secretory cells. Concentrations from 40 to 60 mg per 100 mL are usually necessary.
- Technical details of these tests may be found in Smith {1}; Wesson {2}; Bauer {3}; Pitts{4}; and Schnurr {5}.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to use, whenever solution and container permit. NOTE: The normal color range for this product is a colorless to yellow/brown solution. The efficacy is not affected by color changes within this range.
Calculations
Effective Renal Plasma Flow (ERPF)
- The clearance of PAH, which is extracted almost completely from the plasma during its passage through the renal circulation, constitutes a measure of ERPF. * Hence:
- V = rate of urine excretion (mL/min), and
- PPAH = plasma concentration of PAH (mg/mL).
- Example:
- UPAH = 8.0 mg/mL
- V = 1.5 mL/min
- PPAH = 0.02 mg/mL
- ERPF = 8.0 x 1.5/0.02 = 600 mL/min
- Based on PAH clearance studies, the normal values for ERPF are:
- men 675 ± 150 mL/min
- women 595 ± 125 mL/min
- Maximum Tubular Secretory
- (TmPAH ) Mechanism
- The quantity of PAH secreted by the tubules (TmPAH) is given by the difference between the total rate of excretion (UPAHV) and the quantity filtered by the glomeruli (GFR x PPAH). Hence:
- TmPAH = UPAHV – (GFR x PPAH x 0.83)
- The factor, 0.83, corrects for that portion of PAH which is bound to plasma protein and hence is unfilterable.
- Example:
- UPAH = 9.55 mg/mL
- V = 16.68 mL/min
- GFR = 120 mL/min
- PPAH = 0.60 mg/mL
- Then TmPAH = 9.55 x 16.68 – (120 x 0.60 x 0.83) = 100 mg/min.
- Average normal values of TmPAH are 80-90 mg/min.
- The value of the expression UPAHV, used in calculations of ERPF and TmPAH, may be found by determining the amount of PAH in a measured volume of urine excreted within a specific period of time.
- These calculations are based on a body surface area of 1.73 m2. Corrections for variations in surface area are made by multiplying the values obtained for ERPF and TmPAH by 1.73/A, where A is the subject surface area.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Aminohippurate in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Aminohippurate in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Aminohippurate in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Aminohippurate in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to this product or to its components.
Warnings
Precautions
General
- Intravenous solutions must be given with caution to patients with low cardiac reserve, since a rapid increase in plasma volume can precipitate congestive heart failure.
- For measurement of ERPF, small doses of PAH are used. However, in research procedures to measure TmPAH, high plasma levels are required to saturate the capacity of the tubular cells. During these procedures, the intravenous administration of PAH solutions should be carried out slowly and with caution. The patient should be continuously observed for any adverse reactions.
- Use caution when injecting this product into latex-sensitive individuals, since the vial stopper contains dry natural latex rubber that may cause allergic reactions.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, vasomotor disturbances, flushing, tingling, nausea, vomiting, and cramps may occur.
- Patients may have a sensation of warmth or the desire to defecate or urinate during or shortly following initiation of infusion.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Aminohippurate in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- Renal clearance measurements of PAH cannot be made with any significant accuracy in patients receiving sulfonamides, procaine, or thiazolesulfone. These compounds interfere with chemical color development essential to the analytical procedures.
- Probenecid depresses tubular secretion of certain weak acids such as PAH. Therefore, patients receiving probenecid will have erroneously low ERPF and TmPAH values.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Animal reproduction studies have not been done with PAH. It is also not known whether PAH can cause fetal harm when given to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. PAH should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Aminohippurate in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Aminohippurate during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when PAH is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of PAH did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aminohippurate with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aminohippurate with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aminohippurate in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aminohippurate in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aminohippurate in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Aminohippurate in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Aminohippurate in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Aminohippurate in the drug label.
Overdosage
- The intravenous LD50 in female mice is 7.22 g/kg.
Pharmacology
| |
Aminohippurate
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
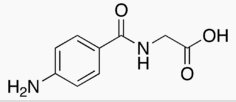
| 2-[(4-Aminobenzoyl)amino]acetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 94-16-6 (sodium salt) |
| ATC code | V04 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 194.19 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Synonyms | PAH, PAHA, Aminohippurate, 4-Aminohippuric acid , N-(4-Aminobenzoyl)glycine, para-Aminohippurate |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Aminohippurate Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
- Aminohippurate sodium1 is an agent to measure effective renal plasma flow (ERPF). It is the sodium salt of para-aminohippuric acid, commonly abbreviated “PAH”. It is water soluble, lipid-insoluble, and has a pKa of 3.83. The empirical formula of the anhydrous salt is C9H9N2NaO3 and its structural formula is:
- It is provided as a sterile, non-preserved 20 percent aqueous solution for injection, with a pH of 6.7 to 7.6. Each 10 mL contains: Aminohippurate sodium 2 g. Inactive ingredients: Sodium hydroxide to adjust pH, water for injection, q.s.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Aminohippurate in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- PAH is filtered by the glomeruli and is actively secreted by the proximal tubules. At low plasma concentrations (1.0 to 2.0 mg/100 mL), an average of 90 percent of PAH is cleared by the kidneys from the renal blood stream in a single circulation. It is ideally suited for measurement of ERPF since it has a high clearance, is essentially nontoxic at the plasma concentrations reached with recommended doses, and its analytical determination is relatively simple and accurate.
- PAH is also used to measure the functional capacity of the renal tubular secretory mechanism or transport maximum (TmPAH). This is accomplished by elevating the plasma concentration to levels (40-60 mg/100 mL) sufficient to saturate the maximal capacity of the tubular cells to secrete PAH.
- Inulin clearance is generally measured during TmPAH determinations since glomerular filtration rate (GFR) must be known before calculations of secretory Tm measurements can be done
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Long-term studies in animals have not been done to evaluate any effects upon fertility or carcinogenic potential of PAH.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Aminohippurate in the drug label.
How Supplied
- No. 95 — Aminohippurate Sodium, 20 percent sterile solution for intravenous injection, is supplied as follows:
- NDC 0006-3395-11 in 10 mL vials.
Storage
- Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F)
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Aminohippurate |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - CARTON - 10 ML SINGLE DOSE VIAL
Ingredients and Appearance
{{#ask: Label Page::Aminohippurate |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Aminohippurate in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Aminohippurate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- AMINOHIPPURATE SODIUM PAH®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Aminohippurate Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.


