Adrenocortical carcinoma: Difference between revisions
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
Revision as of 20:21, 23 January 2012
| Adrenocortical carcinoma | |
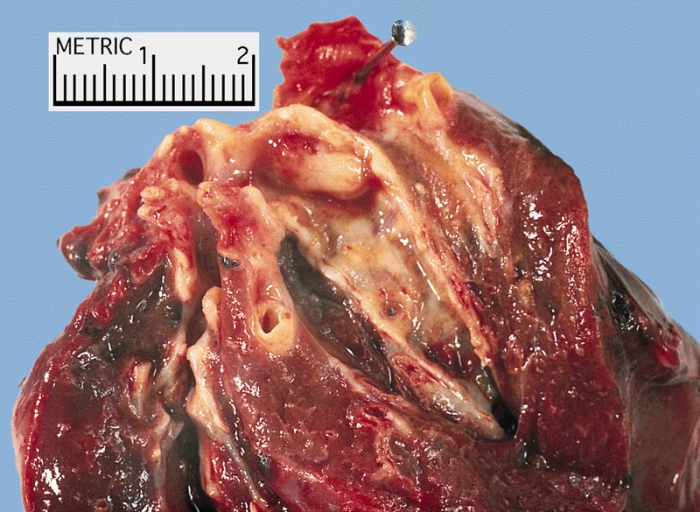 | |
|---|---|
| Metastasis of an adrenocortical carcinoma to the lung | |
| ICD-10 | C74.0 |
| ICD-9 | 194 |
|
Adrenocortical carcinoma Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Adrenocortical carcinoma from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Study |
|
Adrenocortical carcinoma On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Adrenocortical carcinoma |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Adrenocortical carcinoma |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Signs and Symptoms
Diagnosis
Radiology
Differential Diagnosis
- Adrenocortical adenoma
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Adrenal medullary tumors
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
Treatment
Prognosis
ACC, generally, carries a poor prognosis[1] and is unlike most tumours of the adrenal cortex, which are benign (adenomas) and only occasionally cause Cushing's syndrome. Five-year disease-free survival for a complete resection of a stage I-III ACC is approximately 30%.[1] The most important prognostic factors are age of the patient and stage of the tumor. Poor prognostic factors: mitotic activity, venous invasion, weight of 50g+; diameter of 6.5 cm+, Ki-67/MIB1 labeling index of 4%+, p53+.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Allolio B, Fassnacht M (2006). "Clinical review: Adrenocortical carcinoma: clinical update". J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 91 (6): 2027–37. PMID 16551738. Free Full Text.