|
|
| (68 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| {{Infobox_Disease | | {{Infobox_Disease |
| | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} |
| | Image = Abdominal mass 1.jpg | | | Image = Abdominal mass 1.jpg |
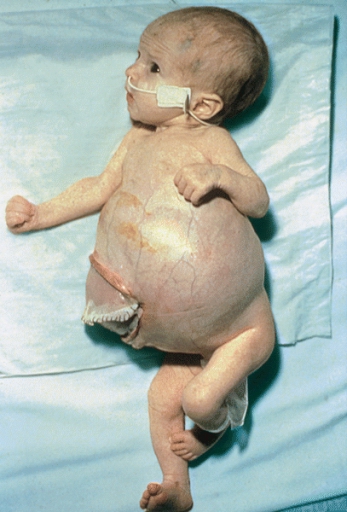
| | Caption = This infant has massive hepatomegaly due to metastatic neuroblastoma. Intra-abdominal pressure is partially relieved by a silastic pouch. <br> <small> [http://www.peir.net Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology] </small> | | | Caption = This infant has massive hepatomegaly due to metastatic neuroblastoma. Intra-abdominal pressure is partially relieved by a silastic pouch. <br> <small> [http://www.peir.net Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology] </small> |
| | DiseasesDB =
| |
| | DasesDB_mult =
| |
| | ICD10 =
| |
| | ICD9 =
| |
| | ICDO =
| |
| | OMIM =
| |
| | MedlinePlus =
| |
| | eMedicineSubj =
| |
| | eMedicineTopic =
| |
| | eMedicine_mult =
| |
| | MeshID =
| |
| }} | | }} |
| {{SI}}
| | '''For patient information page on this topic, click [[Abdominal mass (patient information)|here]].''' |
| {{CMG}}
| |
|
| |
|
| {{Editor Join}} | | {{Abdominal mass}} |
| | {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief:''' [[User:Johnfanisrour|John Fani Srour, M.D.]] |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview== | | ==[[Abdominal mass overview|Overview]]== |
|
| |
|
| An '''abdominal mass''' is any localized enlargement or [[swelling]] in the [[human abdomen]]. Depending on its location, the abdominal mass may be caused by an enlarged [[liver]] ([[hepatomegaly]]), enlarged [[spleen]] ([[splenomegaly]]), protruding [[kidney]], a [[Pancreas|pancreatic mass]], a [[Retroperitoneum|retroperitoneal mass]] (a mass in the [[posterior ]] of the [[peritoneum]]), an [[abdominal aortic aneurysm]], or various [[tumour]]s, such as those caused by abdominal [[carcinomatosis]] and [[omental]] [[metastasis]]. The [[treatment]]s depend on the cause, and may range from [[watchful waiting]] to radical [[surgery]].
| | ==[[Abdominal mass pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== |
|
| |
|
| ==Features== | | ==[[Abdominal mass causes|Causes]]== |
| Many '''abdominal mass'''es are discovered incidentally during routine [[physical examination]]. When they present [[symptom]]atically, '''abdominal mass'''es are most frequently associated with [[Pain and nociception|pain]] or digestive problems. However, depending on the cause, masses may be associated with other [[sign (medical)|sign]]s and symptoms, such as [[jaundice]] or [[bowel obstruction]].
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Diagnosis== | | ==[[Abdominal mass differential diagnosis|Differentiating Abdominal Mass from other Diseases]]== |
| The first steps in diagnosis are a [[medical history]] and physical examination. Important clues during history include [[weight loss]], [[diarrhea]] and [[abdominal pain]].
| |
|
| |
|
| During physical examination, the clinician must identify the location of the mass, as well as characterize its location (usually specified in terms of quadrants). The mass should be assessed for whether it is rigid or mobile. It should also be characterized for pulse or [[peristalsis]], as these would help in further identifying the mass.
| | ==[[Abdominal mass epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== |
|
| |
|
| Routine [[blood test]]s are usually the next step in diagnosis after a thorough medical history and physical examination. They should include a [[full blood count]], [[blood urea nitrogen]] ([[BUN]]), [[creatinine]], and [[liver function tests]] such as [[Liver function tests#Albumin (Alb)|albumin]], [[international normalized ratio]] ([[INR]]), [[partial thromboplastin time]] ([[PTT]]), [[serum amylase]] and [[Liver function tests#Total bilirubin (TBIL)|total bilirubin]] ([[TBIL]]). If late-stage [[liver disease]] is suspected, then a [[Liver function tests#Serum glucose (BG, Glu)|serum glucose]] may be appropriate.
| | ==[[Abdominal mass risk factors|Risk Factors]]== |
|
| |
|
| ===Physical Examination=== | | ==[[Abdominal mass natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== |
| * Associated symptoms:
| |
| *:* [[Rectal bleeding]]
| |
| *:* [[Weight change]]
| |
| *:* [[Urinary symptoms]]
| |
| *:* [[Fever]]
| |
| *:* [[Changes in bowel habits]]
| |
|
| |
|
| ====Abdomen==== | | ==Diagnosis== |
| * Examine [[abdomen]] for areas of [[tenderness]]
| |
| | |
| ====Other====
| |
| * Examine [[pelvis]] for areas of [[tenderness]]
| |
| | |
| ===Laboratory Findings===
| |
| * [[Blood urea nitrogen]] ([[BUN]])/[[creatinine]]
| |
| * [[Complete blood count]] ([[CBC]])
| |
| * [[LFTs]] ([[liver function tests]])
| |
| * [[Urinalysis]]
| |
| * [[Beta-human chorionic gonadotrophin]]
| |
|
| |
| ====Electrolyte and Biomarker Studies====
| |
| * [[Electrolytes]]
| |
| * [[Tumor markers]] (if concern is [[malignancy]])
| |
| * [[Toxicology]] screen
| |
| * [[Blood culture]] (if concern is [[infection]])
| |
| | |
| ====X Ray====
| |
| * [[KUB]] ([[kidneys, ureters, bladder]]) [[x-rays]] could possibly reveal free [[intraperitoneal]] air, [[constipation]] or obstruction.
| |
| | |
| ====MRI and CT====
| |
| * Abdominal [[CT]] with oral [[IV]] contrast will evaluate for bowel [[pathology]], [[abscess]], and [[hepatosplenomegaly]]
| |
| | |
| ====Other Diagnostic Studies====
| |
| * [[Laparoscopy]] of the intra-abdominal cavity allows for direct visualization
| |
| * [[Colonoscopy]] helps in the diagnosis of bowel [[pathology]]
| |
| * [[Paracentesis]] with fluid evaluation.
| |
| | |
| ==Complete Differential Diagnosis of Causes of abdominal mass==
| |
| | |
| In alphabetical order. <ref>Sailer, Christian, Wasner, Susanne. Differential Diagnosis Pocket. Hermosa Beach, CA: Borm Bruckmeir Publishing LLC, 2002:77 ISBN 1591032016</ref> <ref>Kahan, Scott, Smith, Ellen G. In A Page: Signs and Symptoms. Malden, Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishing, 2004:68 ISBN 140510368X</ref>
| |
| | |
| Col2
| |
| *[[Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm]]
| |
| *[[Abscess]]
| |
| *[[Actinomyces]]
| |
| *[[Acute pancreatitis]]
| |
| *[[Adrenal tumor]]
| |
| *[[Alveolar hydatid disease]] (parasite mass, most commonly involving the liver)
| |
| *[[Amyloidosis]] (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Aneurysms]]
| |
| *[[Aortic aneurysm]]
| |
| *[[Ascites]] (localized ascites)
| |
| *[[Autoimmune pancreatitis]] (inflammatory mass)
| |
| *[[Bartonellosis]] (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Bezoar]]
| |
| *[[Biliary atresia]]
| |
| *[[Bladder distention]]
| |
| *[[Blind loop syndrome]] ( the mass is the loop of the bowel)
| |
| *[[Bowel obstruction]] (the mass is a loop of the obstructed bowel)
| |
| *[[Brenner tumor]] (ovarian tumor)
| |
| *[[Brucellosis]] (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Burkitt's lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Carcinoid tumours]]
| |
| *[[Castleman disease]] (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Cat scratch fever]] (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Cholangiocarcinoma]]
| |
| *[[Cholecystitis]] ( inflammatory mass, or abscess)
| |
| *[[Choledochal cyst]]
| |
| *[[Cholelithiasis]] ( a stone filled gallbladder can produces a painless right-upper-quadrant mass)
| |
| *[[Choriocarcinoma]]
| |
| *[[Chronic myelogenous leukemia]] (splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Cirrhosis]] ( the liver itself or one significantly enlarged nodule) C66
| |
| *[[Colonic diverticulitis]] (inflammatory mass or peridiverticular abscess)
| |
| *[[Colorectal cancer]]
| |
| *[[Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis]]
| |
| *[[Congenital megacolon]] (Hirschsprung's disease)
| |
| *[[Constipation]] (fecal mass or dilated colon)
| |
| *[[Crohn's disease]] ( abscess, loop of obstructed bowel, or inflammatory mass with or with out fistula)
| |
| *[[Cryptorchidism]]
| |
| *[[Dermoid cyst]]
| |
| *[[Desmoplastic small round cell tumor]] ( soft tissue sarcoma, usually multiple abdominal masses)
| |
| *[[Distal intestinal obstruction syndrome]] ( in patients with cystic fibrosis or pancreatic enzymes insufficiency)
| |
| *[[Ectopic pregnancy]]
| |
| *[[Endodermal sinus tumor]]
| |
| *[[Endometriosis]]
| |
| *[[Entamoeba histolytica]] (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Eosinophilic gastroenteritis]] ( rare presentation as an obstructing caecal mass)
| |
| *[[Extramedullary haemopoiesis]]
| |
| *[[Gallbladder benign tumor]]
| |
| *[[Gallbladder cancer]]
| |
| *[[Gallbladder empyema]]
| |
| *[[Gastrointestinal stromal tumor]]
| |
| *[[Gastroschisis]] ( other names paraomphalocele, laparoschisis, or abdominoschisis)
| |
| *[[Gaucher disease]] (splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Germ cell tumor]]
| |
| *[[Hairy cell leukaemia]] (splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Hamartoma]]
| |
| *[[Hemangioendothelioma]]
| |
| *[[Hemangiopericytoma]]
| |
| *[[Hepatic adenoma]]
| |
| *[[Hepatoblastoma]]
| |
| *[[Hepatomegaly]]
| |
| *[[Hernia]]
| |
| *[[Hirschsprung's disease]] (congenital megacolon)
| |
| *[[Histiocytosis X]] (splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Hodgkin's lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Hydatid cyst]]
| |
| *[[Hydronephrosis]]
| |
| *[[Intususception of intestine]]
| |
| *[[kala-azar]] or [[Leishmaniasis]] (splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Kaposi sarcoma]]
| |
| *[[Kidney cancer]] (including renal cell carcinoma)
| |
| *[[Krukenberg tumor]] (secondary ovarian malignancy whose primary site arose in the gastrointestinal tract)
| |
| *[[Large bowel obstruction]]
| |
| *[[Leiomyoma]]
| |
| *[[Liposarcoma (retroperitoneal)]]
| |
| *[[Liver abscess]]
| |
| *[[Liver cancer, metastatic]]
| |
| *[[Liver cancer, primary]] ( hepatocellular carcinoma)
| |
| *[[Liver granuloma]]
| |
| *[[Lymphogranuloma venereum]]
| |
| *[[Malaria]] (splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Meigs' syndrome]] (ovarian tumor)
| |
| *[[Mesenteric cyst]]
| |
| *[[Mesothelioma]] ( abdominal )
| |
| *[[Mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Mycobacterium tuberculosis]](hepatomegaly and splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Myelofibrosis]] (splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Nephroblastoma]]
| |
| *[[Neurilemmoma]]
| |
| *[[Neuroblastoma]]
| |
| *[[Neuroendocrine tumor]]
| |
| *[[Neurofibromatosis]]
| |
| *[[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Obesity]] ( subcutaneous fat mass)
| |
| *[[Oesophagostomiasis]] ( a parasitic intestinal helminth that develops in the colonic wall, causing pus-filled granulomas)
| |
| *[[Ogilvie's Syndrome]] (dilated loop of bowels)
| |
| *[[Oncocytoma]] (of the kidney)
| |
| *[[Ovarian cancer]]
| |
| *[[Ovarian cyst]]
| |
| *[[Palpable gallbladder (Courvoisier's sign)]]
| |
| *[[Pancreatic abscess]]
| |
| *[[Pancreatic cancer]]
| |
| *[[Pancreatic islet cell tumors ]]
| |
| *[[Pancreatic pseudocyst]]
| |
| *[[Pelvic inflammatory disease[[ (abscess)
| |
| *[[Pelvic kidney]]
| |
| *[[Peritoneal adhesions]]
| |
| *[[Phaeochromocytoma]]
| |
| *[[Plexosarcoma]]
| |
| *[[POEMS syndrome ]]
| |
| *[[Polycystic kidney disease]]
| |
| *[[Pregnancy]]
| |
| *[[Prune belly syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Pseudomyxoma peritonei]]
| |
| *[[Psittacosis]] (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Pyloric stenosis]]
| |
| *[[Rectus sheath hematoma]]
| |
| *[[Relapsing fever ]]
| |
| *[[Renal cell carcinoma]]
| |
| *[[Renal oncocytoma]]
| |
| *[[Renal transplantation]] (the mass is the transplanted kidney)
| |
| *[[Rhabdoid tumor]]
| |
| *[[Riedel lobe of liver]] (sessile accessory lobe of the liver, a normal variant)
| |
| *[[Sacrococcygeal teratoma]]
| |
| *[[Sarcoidosis]] ( granulomatus mass, hepatomegal, or splenomegaly
| |
| *[[Sickle cell crisis]] (abdominal / sequestration)
| |
| *[[Sister Mary Joseph nodule]]
| |
| *[[Small bowel lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Small bowel obstruction]]
| |
| *[[Small intestine cancer]]
| |
| *[[Spleen lymphoma]]
| |
| *[[Splenomegaly]]
| |
| *[[Splenosis]] (autotransplantation of splenic tissues, usually after splenic rupture)
| |
| *[[Stomach cancer]]
| |
| *[[Syphilis, congenital]]
| |
| *[[Tertiary syphilis]] (hepatomegaly and splenomegaly)
| |
| *[[Toxic megacolon]]
| |
| *[[Toxoplasma, congenital]]
| |
| *[[Transitional cell carcinoma]] (bladder)
| |
| *[[Urachal cyst]] (a sinus remaining from the allantosis during embryogenesis)
| |
| *[[Ureteropelvic junction obstruction]] (pediatric hydronephrosis and palpable kidneys)
| |
| *[[Urine retention]] (distended bladder)
| |
| *[[Uterine enlargement]]
| |
| *[[Uterine leiomyoma (fibroids)]]
| |
| *[[Varicocele]]
| |
| *[[Vermiform appendix]]
| |
| *[[Visceral larva migrans]]
| |
| *[[Volvulus]] (twisted piece of the gastrointestinal tract)
| |
| *[[Wandering spleen]]
| |
| *[[Wilm's tumor]](pediatric renal tumor)
| |
| *[[Yersinia enterocolitica]] (inflammatory mass, lymphoid mass, or Intususception of intestine)
| |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| ==Complete Differential Diagnosis of Causes of abdominal mass==
| |
| {|style="width:90%; height:100px" border="1"
| |
| |style="height:100px"; style="width:25%" border="1" bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | '''Cardiovascular'''
| |
| |style="height:100px"; style="width:75%" border="1" bgcolor="Beige" | No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Chemical / poisoning'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Dermatologic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Drug Side Effect'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Ear Nose Throat'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Endocrine'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Environmental'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Gastroenterologic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Genetic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Hematologic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Iatrogenic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Infectious Disease'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Musculoskeletal / Ortho'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Neurologic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Nutritional / Metabolic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Obstetric/Gynecologic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Oncologic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Opthalmologic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Overdose / Toxicity'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Psychiatric'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Pulmonary'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Renal / Electrolyte'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Rheum / Immune / Allergy'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Sexual'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Trauma'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Urologic'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue"
| |
| | '''Miscellaneous'''
| |
| |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
| | [[Abdominal mass history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Abdominal mass physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Abdominal mass laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Abdominal mass x ray|X Ray]] | [[Abdominal mass CT|CT]] | [[Abdominal mass MRI|MRI]] | [[Abdominal mass ultrasound|Ultrasound]] | [[Abdominal mass other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Abdominal mass other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] |
|
| |
|
| ==Treatment== | | ==Treatment== |
| * Immediately treat life-threatening causes (such as abdominal aortic aneurysms).
| |
| * Organomegaly typically resolves once the underlying etiology is treated.
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Acute Pharmacotherapies===
| | [[Abdominal mass medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Abdominal mass surgery|Surgery]] | [[Abdominal mass primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Abdominal mass secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Abdominal mass cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Abdominal mass future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] |
| * [[Ogilvie's syndrome]] responds to decompression by IV [[neostigmine]] or by a rectal tube
| |
| * [[Constipation]] is usually treated with [[laxative]]s, increased dietary fiber and fluids, enemas.
| |
| *:* Manual disimpaction is reserved for fecal impaction.
| |
| *:* Stop use of offending medications.
| |
| * Masses caused by infections require [[antibiotic]]s (and possible surgery)
| |
| | |
| ===Surgery and Device Based Therapy===
| |
| * Several benign and malignant masses require surgical intervention
| |
| * [[Hirschsprung's disease]] often requires surgery.
| |
| | |
| ==References==
| |
| {{Reflist|2}}
| |
| | |
| ==Additional Resources==
| |
| * [http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency MedlinePlus medical encyclopedia]: [http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003274.htm Abdominal mass] - An informative primer on abdominal masses and their common causes.
| |
| * [http://gastroresource.com/GITextbook/en/Default.htm First Principles of Gastroenterology]: [http://gastroresource.com/GITextbook/En/chapter1/1-18.htm Abdominal Mass] - This chapter discusses the basic approach to abdominal masses.
| |
| | |
| ==Acknowledgements==
| |
| The content on this page was first contributed by {{CMG}}
| |
| | |
| {{SIB}}
| |
|
| |
|
| | == Case Studies == |
| | [[Abdominal mass case study one|Case #1]] |
|
| |
|
| | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} |
| | {{WikiDoc Sources}} |
|
| |
|
| | [[Category:Medical signs]] |
| [[Category:Signs and symptoms]] | | [[Category:Signs and symptoms]] |
| [[Category:Oncology]] | | [[Category:Oncology]] |
| Line 376: |
Line 44: |
| [[Category:Hematology]] | | [[Category:Hematology]] |
| [[Category:Gynecology]] | | [[Category:Gynecology]] |
| | | [[Category:Up-To-Date]] |
| {{WikiDoc Help Menu}}
| | [[Category:Medicine]] |
| {{WikiDoc Sources}}
| | [[Category:Nephrology]] |
| | [[Category:Surgery]] |