ARHGDIA
| Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) alpha | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 1ajw. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | ARHGDIA ; GDIA1; MGC117248; RHOGDI; RHOGDI-1 | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 908 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
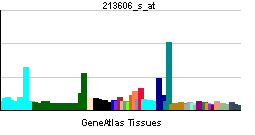 | |||||||||||||
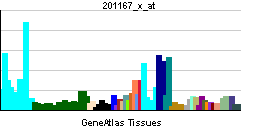 | |||||||||||||
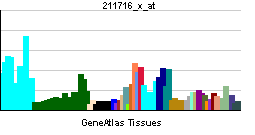 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) alpha, also known as ARHGDIA, is a human gene.[1]
References
Further reading
- Leffers H, Nielsen MS, Andersen AH; et al. (1994). "Identification of two human Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor proteins whose overexpression leads to disruption of the actin cytoskeleton". Exp. Cell Res. 209 (2): 165–74. doi:10.1006/excr.1993.1298. PMID 8262133.
- Wagner T, Tommerup N, Wirth J; et al. (1997). "A somatic cell hybrid panel for distal 17q: GDIA1 maps to 17q25.3". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 76 (3–4): 172–5. PMID 9186513.
- Keep NH, Barnes M, Barsukov I; et al. (1997). "A modulator of rho family G proteins, rhoGDI, binds these G proteins via an immunoglobulin-like domain and a flexible N-terminal arm". Structure. 5 (5): 623–33. PMID 9195882.
- Takahashi K, Sasaki T, Mammoto A; et al. (1997). "Direct interaction of the Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor with ezrin/radixin/moesin initiates the activation of the Rho small G protein". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (37): 23371–5. PMID 9287351.
- Gorvel JP, Chang TC, Boretto J; et al. (1998). "Differential properties of D4/LyGDI versus RhoGDI: phosphorylation and rho GTPase selectivity". FEBS Lett. 422 (2): 269–73. PMID 9490022.
- Takahashi K, Sasaki T, Mammoto A; et al. (1998). "Interaction of radixin with Rho small G protein GDP/GTP exchange protein Dbl". Oncogene. 16 (25): 3279–84. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201874. PMID 9681826.
- Newcombe AR, Stockley RW, Hunter JL, Webb MR (1999). "The interaction between rac1 and its guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI), monitored by a single fluorescent coumarin attached to GDI". Biochemistry. 38 (21): 6879–86. doi:10.1021/bi9829837. PMID 10346909.
- Groysman M, Russek CS, Katzav S (2000). "Vav, a GDP/GTP nucleotide exchange factor, interacts with GDIs, proteins that inhibit GDP/GTP dissociation". FEBS Lett. 467 (1): 75–80. PMID 10664460.
- Lian LY, Barsukov I, Golovanov AP; et al. (2000). "Mapping the binding site for the GTP-binding protein Rac-1 on its inhibitor RhoGDI-1". Structure. 8 (1): 47–55. PMID 10673424.
- Hoffman GR, Nassar N, Cerione RA (2000). "Structure of the Rho family GTP-binding protein Cdc42 in complex with the multifunctional regulator RhoGDI". Cell. 100 (3): 345–56. PMID 10676816.
- Matarrese P, Conti L, Varano B; et al. (2000). "The HIV-1 vpr protein induces anoikis-resistance by modulating cell adhesion process and microfilament system assembly". Cell Death Differ. 7 (1): 25–36. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400616. PMID 10713718.
- Michaelson D, Silletti J, Murphy G; et al. (2001). "Differential localization of Rho GTPases in live cells: regulation by hypervariable regions and RhoGDI binding". J. Cell Biol. 152 (1): 111–26. PMID 11149925.
- Longenecker KL, Garrard SM, Sheffield PJ, Derewenda ZS (2001). "Protein crystallization by rational mutagenesis of surface residues: Lys to Ala mutations promote crystallization of RhoGDI". Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 57 (Pt 5): 679–88. PMID 11320308.
- Grizot S, Fauré J, Fieschi F; et al. (2001). "Crystal structure of the Rac1-RhoGDI complex involved in nadph oxidase activation". Biochemistry. 40 (34): 10007–13. PMID 11513578.
- Di-Poï N, Fauré J, Grizot S; et al. (2001). "Mechanism of NADPH oxidase activation by the Rac/Rho-GDI complex". Biochemistry. 40 (34): 10014–22. PMID 11513579.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
- DerMardirossian C, Schnelzer A, Bokoch GM (2004). "Phosphorylation of RhoGDI by Pak1 mediates dissociation of Rac GTPase". Mol. Cell. 15 (1): 117–27. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.05.019. PMID 15225553.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA; et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMID 15489334.
- Dransart E, Morin A, Cherfils J, Olofsson B (2005). "Uncoupling of inhibitory and shuttling functions of rho GDP dissociation inhibitors". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (6): 4674–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409741200. PMID 15513926.
- Gajate C, Mollinedo F (2005). "Cytoskeleton-mediated death receptor and ligand concentration in lipid rafts forms apoptosis-promoting clusters in cancer chemotherapy". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (12): 11641–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411781200. PMID 15659383.
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |