Auricular hematoma
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Related Key Words and Synonyms:
Overview
Diagnosis
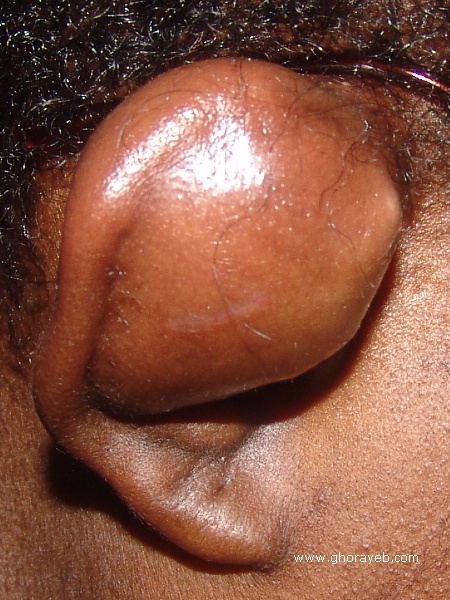
Auricular hematomas are caused by direct trauma to the pinna.The torn perichondrial vessels bleed between the detached perichondrium and underlying cartilage. Interestingly, the presence of a subperichondrial hematoma has been found to stimulate new and often asymmetric cartilage to form. This deformity, which is often referred to as cauliflower ear or wrestler’s ear, is often considered a badge of honor among wrestlers and rugby players.[1]
Physical Examination
Ear Nose and Throat
References
Acknowledgements
The content on this page was first contributed by: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D.