Brucellosis pathophysiology
|
Brucellosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Brucellosis pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Brucellosis pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Brucellosis pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Raviteja Guddeti, M.B.B.S. [2] Danitza Lukac
Overview
Brucella is usually transmitted via the digestive route to the human host. Following transmission, white blood cells phagocyte the pathogen and transports it via the hematologic or lymphatic route to different organs, specially to those of the reticuloendothelial system.[1][2]
Pathophysiology
Transmission[3]
- Brucella spp. are primarily passed among animals, and they cause disease in many different vertebrates.
- Various Brucella species affect sheep, goats, cattle, deer, elk, pigs, dogs, american bishop and several other animals.
- Individuals are generally infected in one of three ways:
- Eating undercooked meat or consuming unpasteurized/raw dairy products
- The most common way to be infected is by eating or drinking unpasteurized/raw dairy products.
- When sheep, goats, cows, or camels are infected, their milk becomes contaminated with the bacteria.
- If the milk from infected animals is not pasteurized, the infection will be transmitted to people who consume dairy products.
- Breathing in the bacteria that cause brucellosis (inhalation)
- This risk is generally greater for people in laboratories that work with the bacteria.
- Slaughterhouse and meat-packing employees have also been known to be exposed to the bacteria and ultimately become infected.
- Bacteria entering the body through skin wounds or mucous membranes through contact with infected animals
- This poses a problem for workers who have close contact with animals or animal excretions (newborn animals, fetuses, and excretions that may result from birth).
- Such workers may include:
- Slaughterhouse workers
- Meat-packing plant employees
- Veterinarians
- Eating undercooked meat or consuming unpasteurized/raw dairy products
- Person-to-person spread of brucellosis is extremely rare.
- Infected mothers who are breast-feeding may transmit the infection to their infants.
- Sexual transmission has been rarely reported.
- While uncommon, transmission may also occur via tissue transplantation or blood transfusions.
Pathogenesis[1][2]
- Virulent Brucella organisms can infect both nonphagocytic and phagocytic cells.
- When Brucella enters the body white blood cells (WBC), particularly neutrophils and macrophages, phagocyte the pathogen.
- WBC transports the pathogen via the hematologic and lymphatic routes to different organs, specially to those from the reticuloendothelial system (RES).
- Brucella multiplies themselves within the vacuoles of the phagocytes without being destructed.
- Different Brucella species are classified as smooth and rough lipopolysaccharide phenotypes.
- Smooth lipopolysaccharides (S-LPS):
- B. abortus, B. melitensis, B. suis and B. neotoma
- S-LPS are more virulent than R-LPS
- S-LPS survive much more effectively than nonsmooth ones
- Rough lipopolysaccharides (R-LPS):
- B. ovis and B. canis
- Smooth lipopolysaccharides (S-LPS):
- In polymorphonuclear or mononuclear phagocytic cells, Brucella spp. uses a number of mechanisms for avoiding or suppressing bactericidal responses:
- Lipopolysaccharide and outer membrane proteins probably play a substantial role in intracellular survival.
- Brucella stays within the cells because it inhibits cellular mechanisms of programmed cell death (apoptosis).
- The survival of Brucella within the cells has been associated with:
- Synthesis of antioxidant enzymes
- Production of guanosine 5 monophosphate (GMP)
- GMP inhibits: phagolysosome fusion, degranulation and activation of the myelo-peroxidase-halide system, and production of tumor necrosis factor.
- Synthesis of proteins of molecular weight 17, 24, 28, 60, and 62 kDa.
- The 24 kDa protein is acid-induced, and its production correlates with bacterial survival under acidic conditions (<pH4).
- The 17 and 28 kDa proteins are apparently specifically induced by macrophages and correlated with intracellular survival.
- The elimination of virulent Brucella depends on activated macrophages and hence requires development of Th1 type cell-mediated responses to protein antigens.
- High iron concentrations promote the killing of Brucella, probably by favoring production of hydroxylamine and hydroxyl radical.
- The mechanisms of pathogenesis of Brucella infection in its natural host species and in humans are still not completely understood, and further studies are needed.
Microscopic Pathology
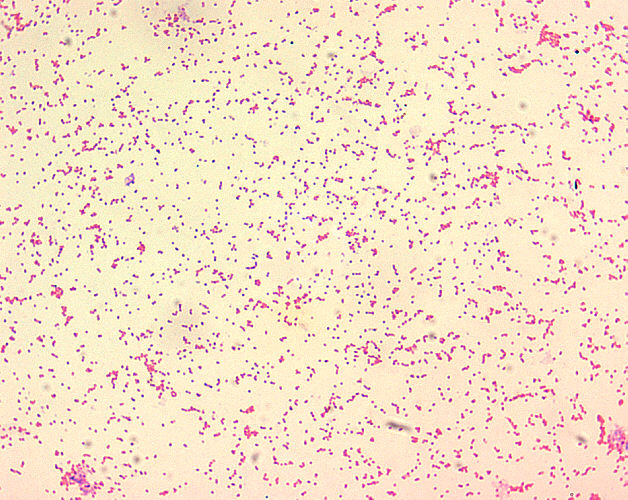
- Brucella spp. are poorly staining, small gram-negative coccobacilli (0.5-0.7 x 0.6-1.5 µm).
- Brucella spp. are seen mostly as single cells and appearing like “fine sand”.[4]
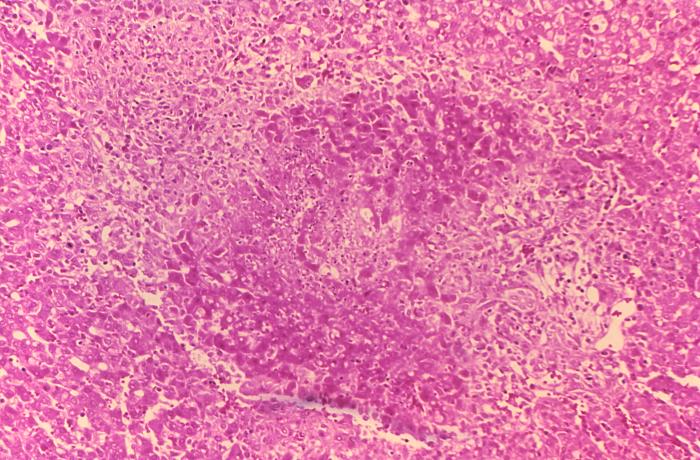
- On microscopic histopathological analysis of the liver, common findings are:
- Granulomas with centrilobular necrosis or focal necrosis and parenchyma destruction.[5]
-
Brucella spp. are poorly staining, small gram-negative coccobacilli (0.5-0.7 x 0.6-1.5 µm), and are seen mostly as single cells and appearing like “fine sand”.
-
Histopathology of guinea pig liver in experimental Brucella suis infection. Granuloma with necrosis.
Reference
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Corbel MJ (1997). "Brucellosis: an overview". Emerg Infect Dis. 3 (2): 213–21. doi:10.3201/eid0302.970219. PMC 2627605. PMID 9204307.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Brucelosis. Wikipedia. https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brucelosis. Accessed on February 2, 2016
- ↑ Brucellosis. CDC. http://www.cdc.gov/brucellosis/transmission/index.html. Accessed on February 1, 2016
- ↑ Brucellosis. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brucellosis. Accessed on January 29, 2016
- ↑ Hunt A, Bothwell P. Histological findings in human brucellosis. J Clin Pathol. 1967; 20: 267-272