Coagulation factor IX
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Turky Alkathery, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Coagulation factor IX is an antihemophilic factor that is FDA approved for the prevention of bleeding episodes in adult and pediatric patients with hemophilia B and peri-operative management in adult and pediatric patients with hemophilia B. Common adverse reactions include nausea, injection site reaction, injection site pain, headache, dizziness and rash..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
1.1 Control and Prevention of Bleeding Episodes in Hemophilia B BeneFIX®, Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), is indicated for the control and prevention of bleeding episodes in adult and pediatric patients with hemophilia B (congenital factor IX deficiency or Christmas disease).
1.2 Peri-operative Management in Patients with Hemophilia B BeneFIX, Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), is indicated for peri-operative management in adult and pediatric patients with hemophilia B.
BeneFIX, Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), is NOT indicated for:
treatment of other factor deficiencies (e.g., factors II, VII, VIII, and X), treatment of hemophilia A patients with inhibitors to factor VIII, reversal of coumarin-induced anticoagulation, treatment of bleeding due to low levels of liver-dependent coagulation factors.
Dosage
2.1 General Considerations for Administration For Intravenous Use after Reconstitution
Treatment with BeneFIX, Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of hemophilia B. Each vial of BeneFIX has the rFIX potency in the International Units (IU) stated on the vial. Dosage and duration of treatment for all factor IX products depend on the severity of the factor IX deficiency, the location and extent of bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition, age and recovery of factor IX. To ensure that the desired factor IX activity level has been achieved, precise monitoring using the factor IX activity assay is advised. Doses should be titrated using the factor IX activity, pharmacokinetic parameters, such as half-life and recovery, as well as taking the clinical situation into consideration in order to adjust the dose as appropriate.
Dosing of BeneFIX may differ from that of plasma-derived factor IX products [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. Subjects at the low end of the observed factor IX recovery may require upward dosage adjustment of BeneFIX to as much as two times (2X) the initial empirically calculated dose in order to achieve the intended rise in circulating factor IX activity.
The safety and efficacy of BeneFIX administration by continuous infusion have not been established [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2 Method of Calculating Initial Estimated Dose The method of calculating the factor IX dose is shown in TABLE 1.
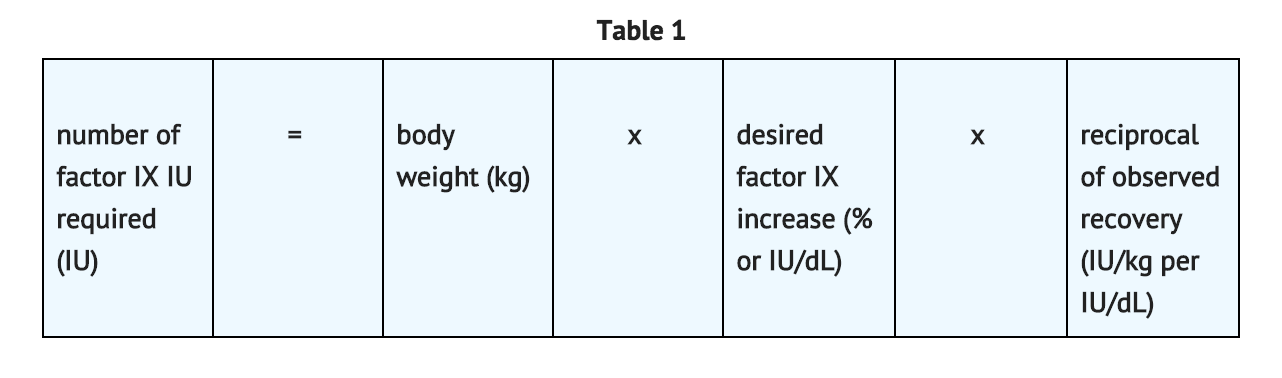
Average Recovery Adult Patients in Clinical Trial
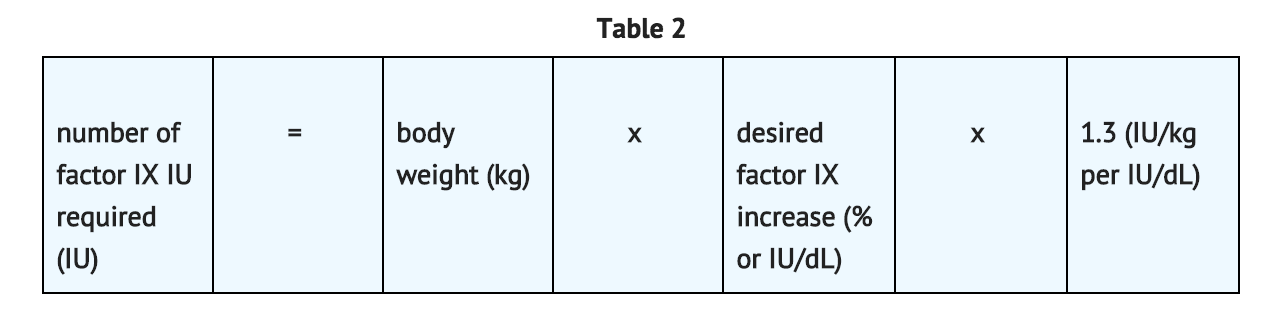
In adult PTPs, on average, one International Unit (IU) of BeneFIX per kilogram of body weight increased the circulating activity of factor IX by 0.8 ® 0.2 IU/dL (range 0.4 to 1.2 IU/dL). The method of dose estimation is illustrated in TABLE 2. If you use 0.8 IU/dL average increase of factor IX per IU/kg body weight administered, then:
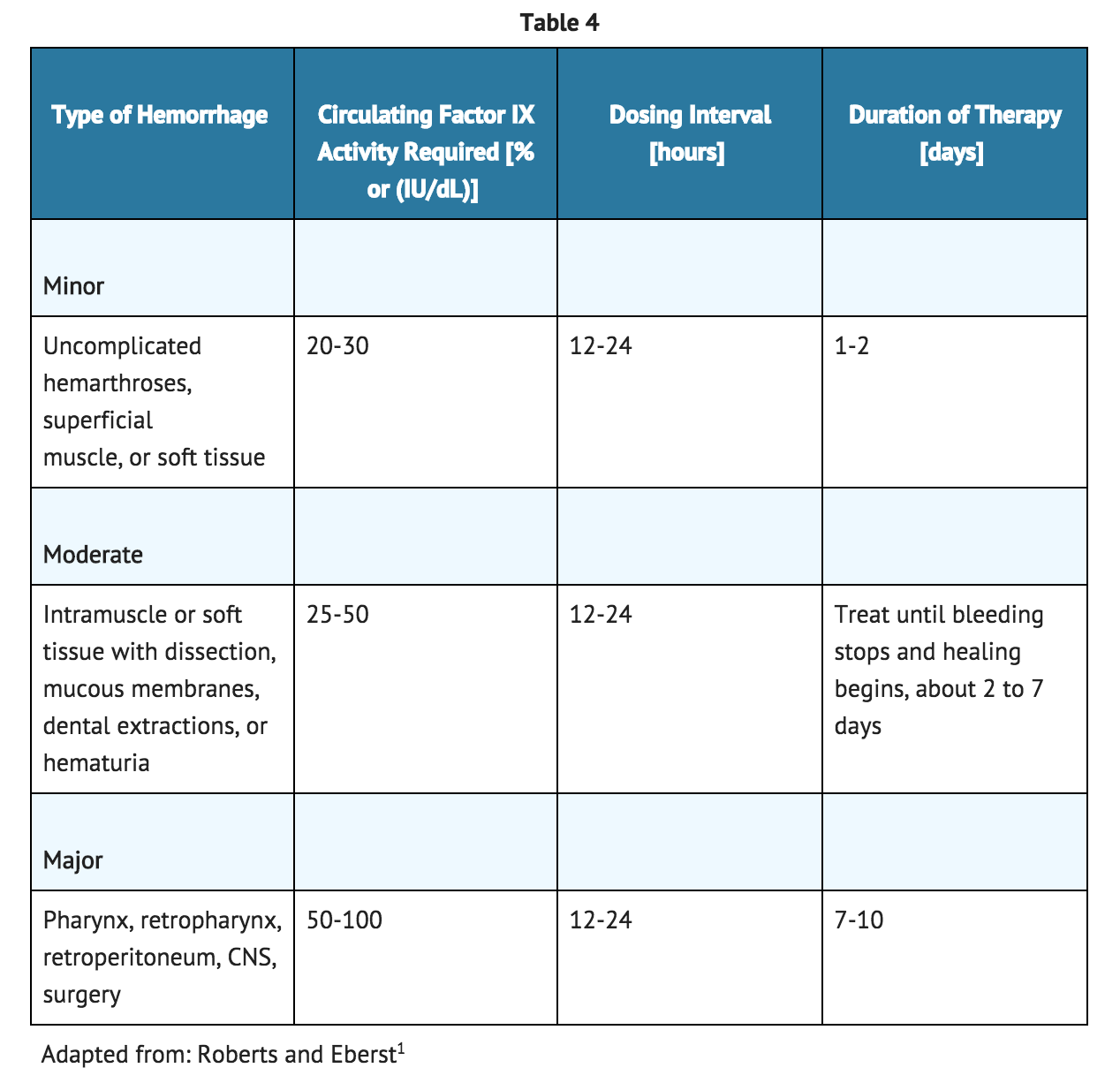
Dosing Guide for Control and Prevention of Bleeding Episodes and Peri-operative Management
2.4 Instructions for Use BeneFIX is administered by intravenous (IV) infusion after reconstitution of the lyophilized powder with the supplied pre-filled diluent (0.234% sodium chloride solution) syringe.
Patients should follow the specific reconstitution and administration procedures provided by their physicians.
For instructions, patients should follow the recommendations in the FDA-Approved Patient Labeling [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Reconstitution, product administration, and handling of the administration set must be done with caution. Discard all equipment, including any reconstituted BeneFIX product, in an appropriate container. Place needles used for venipuncture in a sharps container after single use. Percutaneous puncture with a needle contaminated with blood from an infected patient can transmit infectious viruses including HIV (AIDS) and hepatitis. Obtain immediate medical attention if injury occurs. 2.5 Preparation and Reconstitution

Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Coagulation factor IX in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Coagulation factor IX in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Indication
1.1 Control and Prevention of Bleeding Episodes in Hemophilia B BeneFIX®, Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), is indicated for the control and prevention of bleeding episodes in adult and pediatric patients with hemophilia B (congenital factor IX deficiency or Christmas disease).
1.2 Peri-operative Management in Patients with Hemophilia B BeneFIX, Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), is indicated for peri-operative management in adult and pediatric patients with hemophilia B.
Dosage
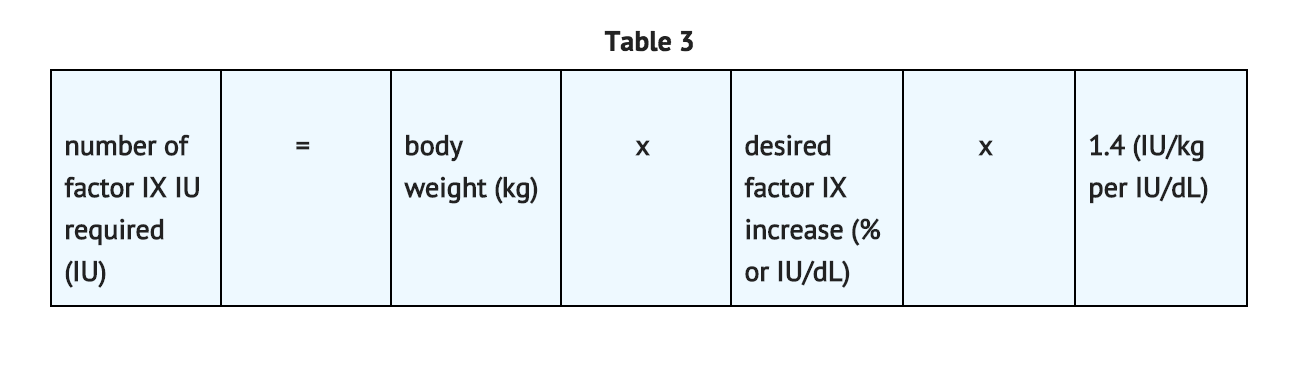
Average Recovery Pediatric Patients (<15 years) in Clinical Trial
In pediatric patients, on average, one international unit of BeneFIX per kilogram of body weight increased the circulating activity of factor IX by 0.7 ® 0.3 IU/dL (range 0.2 to 2.1 IU/dL; median of 0.6 IU/dL per IU/kg). The method of dose estimation is illustrated in TABLE 3. If you use 0.7 IU/dL average increase of factor IX per IU/kg body weight administered, then:
Doses administered should be titrated to the patient's clinical response. Patients may vary in their pharmacokinetic (e.g., half-life, in vivo recovery) and clinical responses to BeneFIX. Although the dose can be estimated by the calculations above, it is highly recommended that, whenever possible, appropriate laboratory tests, including serial factor IX activity assays, be performed.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Coagulation factor IX in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Coagulation factor IX in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
BeneFIX is contraindicated in patients who have manifested life-threatening, immediate hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, to the product or its components, including hamster protein.
Warnings
5.1 General The clinical response to BeneFIX may vary. If bleeding is not controlled with the recommended dose, the plasma level of factor IX should be determined, and a sufficient dose of BeneFIX should be administered to achieve a satisfactory clinical response. If the patient's plasma factor IX level fails to increase as expected or if bleeding is not controlled after the expected dose, the presence of an inhibitor (neutralizing antibodies) should be suspected, and appropriate testing performed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
5.2 Anaphylaxis and Severe Hypersensitivity Reactions Allergic type hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with BeneFIX and have manifested as pruritus, rash, urticaria, hives, facial swelling, dizziness, hypotension, nausea, chest discomfort, cough, dyspnea, wheezing, flushing, discomfort (generalized) and fatigue. Frequently, these events have occurred in close temporal association with the development of factor IX inhibitors. Advise patients to discontinue use of the product and contact their physician and/or seek immediate emergency care.
BeneFIX contains trace amounts of hamster (CHO) proteins. Patients treated with this product may develop hypersensitivity to these non-human mammalian proteins.
5.3 Thromboembolic Complications The safety and efficacy of BeneFIX administration by continuous infusion have not been established [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events in patients receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central venous catheter, including life-threatening superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome in critically ill neonates [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.4 Nephrotic Syndrome Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following immune tolerance induction with factor IX products in hemophilia B patients with factor IX inhibitors and a history of allergic reactions to factor IX. The safety and efficacy of using BeneFIX for immune tolerance induction have not been established.
5.5 Neutralizing Antibodies (Immunogenicity) Patients using BeneFIX should be monitored for the development of factor IX inhibitors by appropriate clinical observations and laboratory tests. Inhibitors have been reported following administration of BeneFIX [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. If expected plasma factor IX activity levels are not attained, or if bleeding is not controlled with an expected dose, an assay that measures factor IX inhibitor concentration should be performed.
Patients with factor IX inhibitors may be at an increased risk of anaphylaxis upon subsequent challenge with factor IX.2 Patients experiencing allergic reactions should be evaluated for the presence of an inhibitor. Patients should be observed closely for signs and symptoms of acute hypersensitivity reactions, particularly during the early phases of initial exposure to product. Because of the potential for allergic reactions with factor IX concentrates, the initial (approximately 10 - 20) administrations of factor IX should be performed under medical supervision where proper medical care for allergic reactions could be provided.
5.6 Monitoring Laboratory Tests Patients should be monitored for factor IX activity levels by the one-stage clotting assay to confirm that adequate factor IX levels have been achieved and maintained, when clinically indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. Patients should be monitored for the development of inhibitors if expected factor IX activity plasma levels are not attained, or if bleeding is not controlled with the recommended dose of BeneFIX. Assays used to determine if factor IX inhibitor is present should be titered in Bethesda Units (BUs).
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Clinical Trials Experience in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
The following post-marketing adverse reactions have been reported for BeneFIX: inadequate factor IX recovery, inadequate therapeutic response, inhibitor development [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)], anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)], angioedema, dyspnea, hypotension, and thrombosis.
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The safety and efficacy of BeneFIX administration by continuous infusion have not been established [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. There have been post-marketing reports of thrombotic events, including life-threatening SVC syndrome in critically ill neonates, while receiving continuous-infusion BeneFIX through a central venous catheter. Cases of peripheral thrombophlebitis and DVT have also been reported. In some, BeneFIX was administered via continuous infusion, which is not an approved method of administration [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Drug Interactions
None known.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): C
Animal reproduction and lactation studies have not been conducted with BeneFIX, Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant). It is not known whether BeneFIX can affect reproductive capacity or cause fetal harm when given to pregnant women. BeneFIX should be administered to pregnant women only if needed.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Coagulation factor IX in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no information available on the effect of factor IX replacement therapy on labor and delivery. Use only if needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted into human milk. Because many drugs are excreted into human milk, caution should be exercised if BeneFIX is administered to nursing mothers.
Use only if needed.
Pediatric Use
Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of BeneFIX have been evaluated in previously treated (PTP) and previously untreated pediatric patients (PUP) [see Dosage and Administration (2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14) and Adverse Reactions (6)]. On average, lower recovery has been observed in pediatric patients (<15 years). A dose adjustment may be needed [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Geriatic Use
Clinical studies of BeneFIX did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Dose selection for an elderly patient should be individualized [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Coagulation factor IX with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Coagulation factor IX with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Coagulation factor IX in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Coagulation factor IX in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Coagulation factor IX in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Coagulation factor IX in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Coagulation factor IX and IV administrations.
Overdosage
No symptoms of overdose have been reported.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
BeneFIX temporarily replaces the missing clotting factor IX that is needed for effective hemostasis.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
The activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) is prolonged in people with hemophilia B. Treatment with factor IX concentrate may normalize the aPTT by temporarily replacing the factor IX. The administration of BeneFIX, Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), increases plasma levels of factor IX, and can temporarily correct the coagulation defect in these patients.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility BeneFIX, Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), has been shown to be nonmutagenic in the Ames assay and non-clastogenic in a chromosomal aberrations assay. No investigations on carcinogenesis or impairment of fertility have been conducted.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Coagulation factor IX |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Coagulation factor IX |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Coagulation factor IX interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Coagulation factor IX Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.