WBR0334: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} | |QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|SubCategory=Neurology | |||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|SubCategory=Neurology | |||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|SubCategory=Neurology | |||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|SubCategory=Neurology | |||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|SubCategory=Neurology | |||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|SubCategory=Neurology | |||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|SubCategory=Neurology | |||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|MainCategory=Embryology | |||
|SubCategory=Neurology | |||
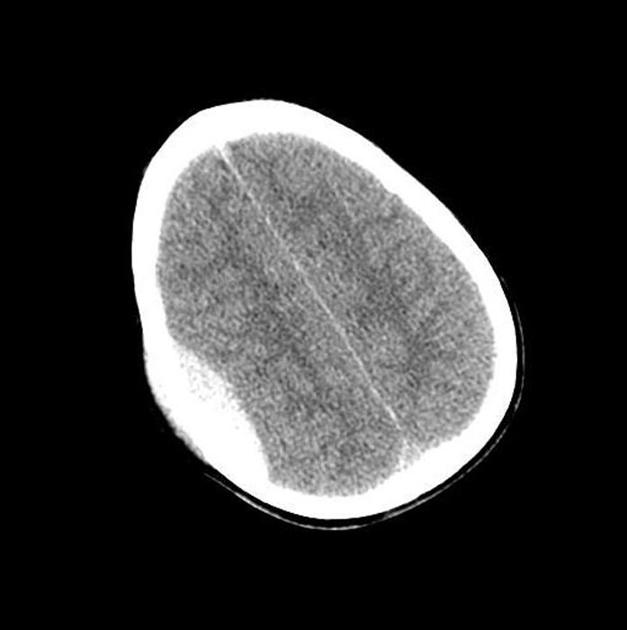
|Prompt=A 45 year old man sustains a motor vehicle collision and is brought by the EMS to the emergency department. He complains of headache, severe nausea, and weakness of his upper extremity. Immediate CT-scan is performed and shows the findings in the image below. The injured artery in this patient is derived from which aortic arch? | |Prompt=A 45 year old man sustains a motor vehicle collision and is brought by the EMS to the emergency department. He complains of headache, severe nausea, and weakness of his upper extremity. Immediate CT-scan is performed and shows the findings in the image below. The injured artery in this patient is derived from which aortic arch? | ||
[[Image:WBR0334.jpg|400px]] | [[Image:WBR0334.jpg|400px]] | ||
Image courtesy of Radswiki. [http://www.radiopaedia.org Radiopaedia] (original file [http://radiopaedia.org/cases/epidural-hematoma-2 here]). [http://radiopaedia.org/licence Creative Commons BY-SA-NC] | |||
|Explanation=The patient is most likely presenting with epidural hematoma following the motor vehicle collision due to a fracture of the temporal bone that leads to rupture of the middle meningeal artery, a branch of the maxillary artery. Based on the CT scan findings, there is a biconvex blood collection that appears hyperdense. It does not cross the suture lines, but may cross the falx and the tentorium. Embryologically, the maxillary artery is derived from the 1st aortic arch. | |Explanation=The patient is most likely presenting with epidural hematoma following the motor vehicle collision due to a fracture of the temporal bone that leads to rupture of the middle meningeal artery, a branch of the maxillary artery. Based on the CT scan findings, there is a biconvex blood collection that appears hyperdense. It does not cross the suture lines, but may cross the falx and the tentorium. Embryologically, the maxillary artery is derived from the 1st aortic arch. | ||
Revision as of 02:46, 21 November 2013
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Embryology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Neurology |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 45 year old man sustains a motor vehicle collision and is brought by the EMS to the emergency department. He complains of headache, severe nausea, and weakness of his upper extremity. Immediate CT-scan is performed and shows the findings in the image below. The injured artery in this patient is derived from which aortic arch?
|
| Answer A | AnswerA::1st |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::The maxillary artery is derived from the 1st aortic arch. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::2nd |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::The stapedial and hyoid arteries are derived from the 2nd aortic arch. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::3rd |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::The common carotid artery and the proximal segment of the internal carotid artery are derived from the 3rd aortic arch. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::4th |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::The aortic arch and the proximal part of the right subclavian artery are derived from the 4th aortic arch. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::6th |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::The proximal segments of the pulmonary arteries and the ductus arteriosus are derived from the 6th aortic arch. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::A |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::The patient is most likely presenting with epidural hematoma following the motor vehicle collision due to a fracture of the temporal bone that leads to rupture of the middle meningeal artery, a branch of the maxillary artery. Based on the CT scan findings, there is a biconvex blood collection that appears hyperdense. It does not cross the suture lines, but may cross the falx and the tentorium. Embryologically, the maxillary artery is derived from the 1st aortic arch.
Educational Objective:
The middle meningeal artery, ruptured in epidural hematomas, is a branch of the maxillary artery. The maxillary artery is derived from the first 1st aortic arch. |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::first, WBRKeyword::1st, WBRKeyword::aortic, WBRKeyword::arch, WBRKeyword::maxilary, WBRKeyword::artery, WBRKeyword::branch, WBRKeyword::derive, WBRKeyword::derived, WBRKeyword::derivative, WBRKeyword::epidural, WBRKeyword::hematoma, WBRKeyword::stroke, WBRKeyword::motor, WBRKeyword::vehicle, WBRKeyword::collision, WBRKeyword::lucid, WBRKeyword::interval, WBRKeyword::headache, WBRKeyword::nausea, WBRKeyword::CT, WBRKeyword::scan, WBRKeyword::weakness |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |