Hirschsprung's disease other imaging findings: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Tarek Nafee (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
A [[barium enema]] is the mainstay of diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s disease. | A [[barium enema]] is the mainstay of diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s disease. | ||
==Other Imaging Findings== | ==Other Imaging Findings== | ||
===Barium Enema=== | ===Barium Enema=== | ||
Revision as of 22:07, 15 June 2017
|
Hirschsprung's disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hirschsprung's disease other imaging findings On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hirschsprung's disease other imaging findings |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Hirschsprung's disease other imaging findings |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
A barium enema is the mainstay of diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s disease.
Other Imaging Findings
Barium Enema
Imaging findings are:
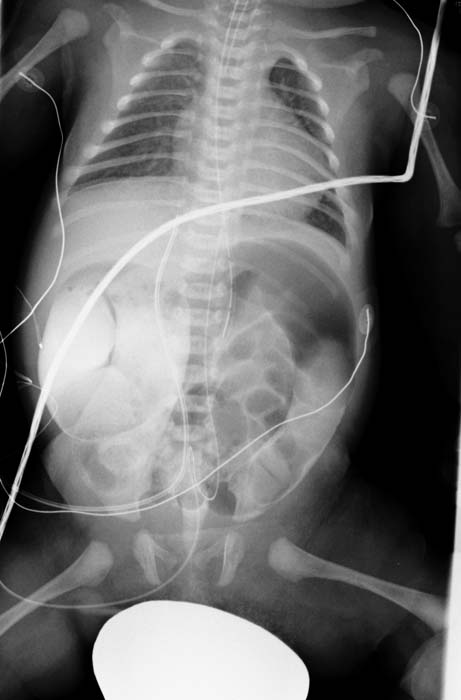
- Radiography performed in children with Hirschsprung disease yields findings similar to those in other forms of low small bowel obstruction: variable gaseous distention of the colon and small bowel, often with air-fluid levels.
- The colon is usually difficult to identify accurately, and gas is usually absent in the rectum.
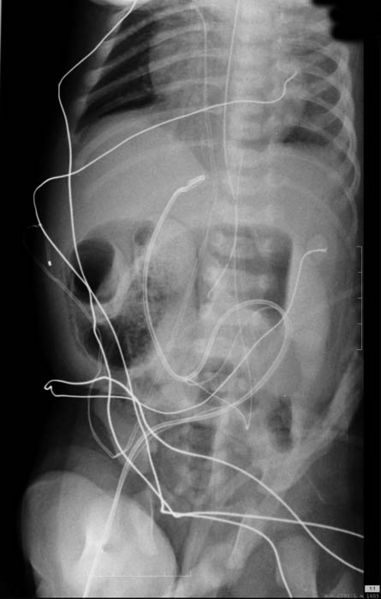
- Barium enema studies demonstrate patency of the colon, which is short but usually normal in caliber.
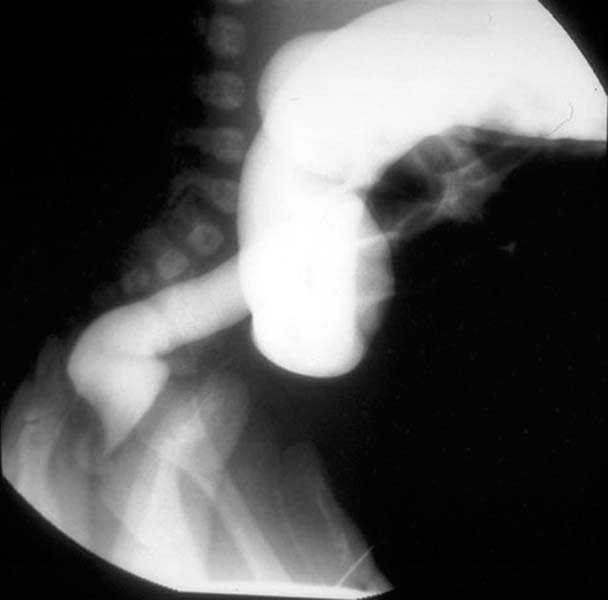
- A transition zone between the narrow and dilated portions of the colon in the shape of an inverted cone is the most characteristic radiologic finding.
- When this transition zone is observed, the examination should be discontinued because filling of the more proximal dilated bowel beyond the transition zone may lead to impaction.
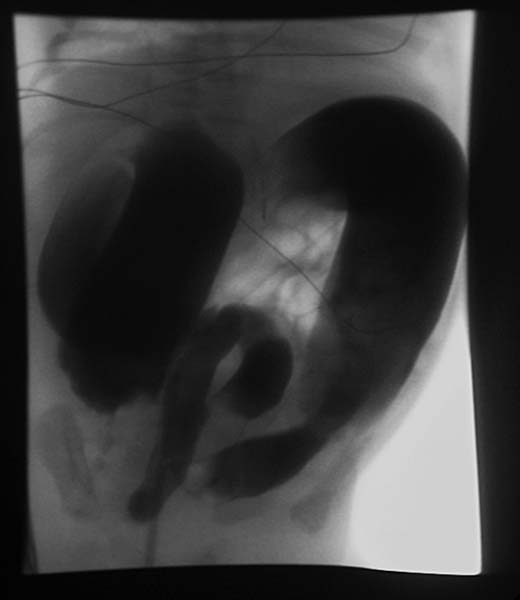
- The radiologic diagnosis of total colonic aganglionosis is difficult. Findings at barium enema examination may be normal or may include a short colon of normal caliber, microcolon, or a transition zone in the ileum.