Glycogen storage disease type II physical examination: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Glycogen storage disease type II}} | {{Glycogen storage disease type II}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Anmol}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Physical examination of patients with glycogen storage disease type 2 (GSD type 2) is usually remarkable for [[muscular weakness]], [[hypotonia]], absent [[deep tendon reflex]] and paucity of movements. Patients with infantile GSD type 2 usually appear [[dyspneic]], pale, and/or [[cyanotic]]. | |||
==Physical Examination== | ==Physical Examination== | ||
* Physical examination of patients with | *Physical examination of patients with glycogen storage disease type 2 (GSD type 2) is usually remarkable for muscular weakness, hypotonia, absent deep tendon reflexes and paucity of movements.<ref name="pmid12897283">{{cite journal| author=van den Hout HM, Hop W, van Diggelen OP, Smeitink JA, Smit GP, Poll-The BT et al.| title=The natural course of infantile Pompe's disease: 20 original cases compared with 133 cases from the literature. | journal=Pediatrics | year= 2003 | volume= 112 | issue= 2 | pages= 332-40 | pmid=12897283 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12897283 }}</ref><ref name="pmid16133732">{{cite journal| author=Winkel LP, Hagemans ML, van Doorn PA, Loonen MC, Hop WJ, Reuser AJ et al.| title=The natural course of non-classic Pompe's disease; a review of 225 published cases. | journal=J Neurol | year= 2005 | volume= 252 | issue= 8 | pages= 875-84 | pmid=16133732 | doi=10.1007/s00415-005-0922-9 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16133732 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15126982">{{cite journal| author=Kishnani PS, Howell RR| title=Pompe disease in infants and children. | journal=J Pediatr | year= 2004 | volume= 144 | issue= 5 Suppl | pages= S35-43 | pmid=15126982 | doi=10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.01.053 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15126982 }} </ref> | ||
===Appearance of the Patient=== | ===Appearance of the Patient=== | ||
*Patients with [ | *Patients with infantile GSD type 2 usually appear [[dyspneic]], pale, and/or [[cyanotic]] | ||
*Sometimes the appearance is also called as "Floppy baby appearance" | |||
===Vital Signs=== | ===Vital Signs=== | ||
*[[Tachypnea]] | |||
*[[ | |||
===Skin=== | ===Skin=== | ||
*[[Cyanosis]] | *[[Cyanosis]] | ||
* [[Pallor]] | * [[Pallor]] | ||
===HEENT=== | ===HEENT=== | ||
* | * Head lag | ||
*Laxity of facial muscles | |||
* [[Enlarged tongue]] may be present. | |||
* | * Tougue fibrillation and/or absent tongue movements may be present | ||
* [[ | |||
* | |||
===Neck=== | ===Neck=== | ||
* Neck examination of patients with | * Neck examination of patients with GSD type 2 is usually normal. | ||
===Lungs=== | ===Lungs=== | ||
* | * [[Dyspnea]] | ||
===Heart=== | ===Heart=== | ||
*[[Heart sounds#Summation Gallop|Gallops]] may be present | |||
*[[Murmur]] may be present | |||
*[[Heart sounds#Summation Gallop|Gallops]] | |||
* | |||
===Abdomen=== | ===Abdomen=== | ||
*[[Hepatomegaly]] may be present | |||
*[[Splenomegaly]] may be present | |||
*[[ | |||
*[[ | |||
===Back=== | ===Back=== | ||
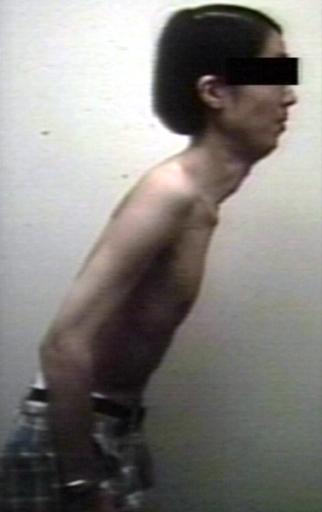
* | * [[Scoliosis]] may be present | ||
===Genitourinary=== | ===Genitourinary=== | ||
* Genitourinary examination of patients with | * Genitourinary examination of patients with GSD type 2 is usually normal. | ||
===Neuromuscular=== | |||
* | *Positive [[Gower's sign]] | ||
* | * [[Hypotonia]] | ||
* Absent [[deep tendon reflex]] | |||
===Extremities=== | |||
*[[Calf muscle|Calf muscles]] feel firm on [[palpation]] | |||
*Decreased [[Deep tendon reflex|deep tendon reflexes]] | |||
* [[Tremors]] may be present | |||
* [[Spasm]] of legs may be rarely present | |||
==Image gallery== | |||
Images shown below are courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. [http://www.peir.net © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology] | |||
<div align="left"> | |||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
Image:218243.jpg|Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II. Child in crib | |||
Image:227286.jpg|Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II | |||
Image:227289.jpg|Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
=== | <div align="left"> | ||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
Image:227292.jpg|Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II, 9 years old patient | |||
Image:227295.jpg|Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II, 9 years old patient | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
=== | <div align="left"> | ||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
Image:227298.jpg|Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II | |||
Image:227313.jpg|Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 173: | Line 84: | ||
[[Category:Endocrinology]] | [[Category:Endocrinology]] | ||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | [[Category:Hepatology]] | ||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:Pediatrics]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Genetic disorders]] | |||
[[Category:Metabolic disorders]] | |||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:55, 30 January 2018
|
Glycogen storage disease type II Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Glycogen storage disease type II from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Glycogen storage disease type II physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Glycogen storage disease type II physical examination |
|
FDA on Glycogen storage disease type II physical examination |
|
CDC on Glycogen storage disease type II physical examination |
|
Glycogen storage disease type II physical examination in the news |
|
Blogs on Glycogen storage disease type II physical examination |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Glycogen storage disease type II |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Glycogen storage disease type II physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Anmol Pitliya, M.B.B.S. M.D.[2]
Overview
Physical examination of patients with glycogen storage disease type 2 (GSD type 2) is usually remarkable for muscular weakness, hypotonia, absent deep tendon reflex and paucity of movements. Patients with infantile GSD type 2 usually appear dyspneic, pale, and/or cyanotic.
Physical Examination
- Physical examination of patients with glycogen storage disease type 2 (GSD type 2) is usually remarkable for muscular weakness, hypotonia, absent deep tendon reflexes and paucity of movements.[1][2][3]
Appearance of the Patient
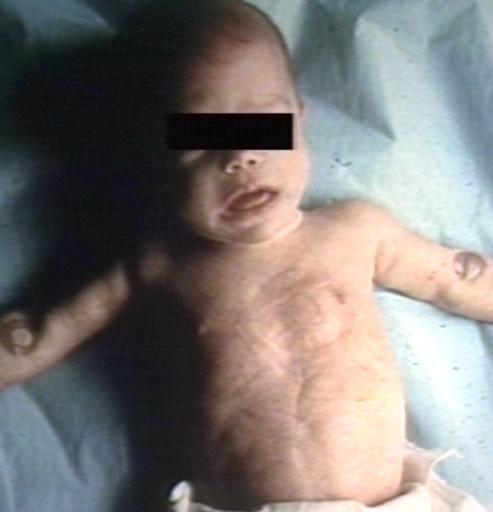
- Patients with infantile GSD type 2 usually appear dyspneic, pale, and/or cyanotic
- Sometimes the appearance is also called as "Floppy baby appearance"
Vital Signs
Skin
HEENT
- Head lag
- Laxity of facial muscles
- Enlarged tongue may be present.
- Tougue fibrillation and/or absent tongue movements may be present
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with GSD type 2 is usually normal.
Lungs
Heart
Abdomen
- Hepatomegaly may be present
- Splenomegaly may be present
Back
- Scoliosis may be present
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with GSD type 2 is usually normal.
Neuromuscular
- Positive Gower's sign
- Hypotonia
- Absent deep tendon reflex
Extremities
- Calf muscles feel firm on palpation
- Decreased deep tendon reflexes
- Tremors may be present
- Spasm of legs may be rarely present
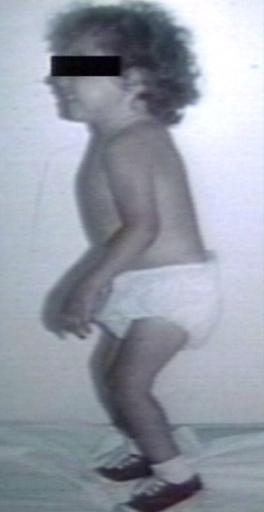
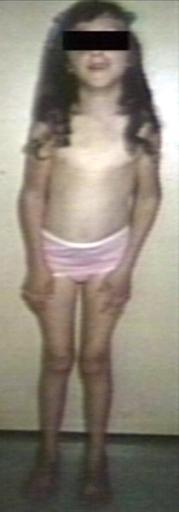
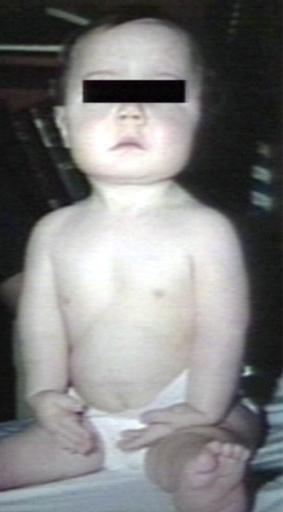
Image gallery
Images shown below are courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II. Child in crib
-
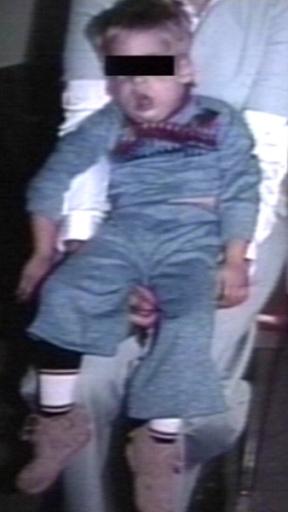
Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II
-
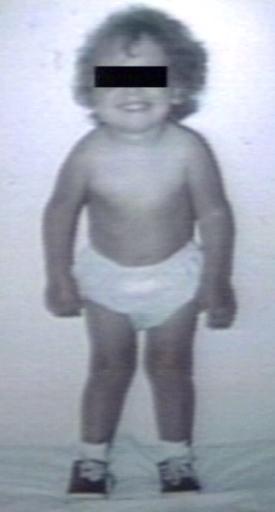
Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II
-
Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II, 9 years old patient
-
Pompe's Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease Type II, 9 years old patient
References
- ↑ van den Hout HM, Hop W, van Diggelen OP, Smeitink JA, Smit GP, Poll-The BT; et al. (2003). "The natural course of infantile Pompe's disease: 20 original cases compared with 133 cases from the literature". Pediatrics. 112 (2): 332–40. PMID 12897283.
- ↑ Winkel LP, Hagemans ML, van Doorn PA, Loonen MC, Hop WJ, Reuser AJ; et al. (2005). "The natural course of non-classic Pompe's disease; a review of 225 published cases". J Neurol. 252 (8): 875–84. doi:10.1007/s00415-005-0922-9. PMID 16133732.
- ↑ Kishnani PS, Howell RR (2004). "Pompe disease in infants and children". J Pediatr. 144 (5 Suppl): S35–43. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.01.053. PMID 15126982.