Sulfone
|
WikiDoc Resources for Sulfone |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Sulfone |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Sulfone at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Sulfone at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Sulfone
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Sulfone Risk calculators and risk factors for Sulfone
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Sulfone |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
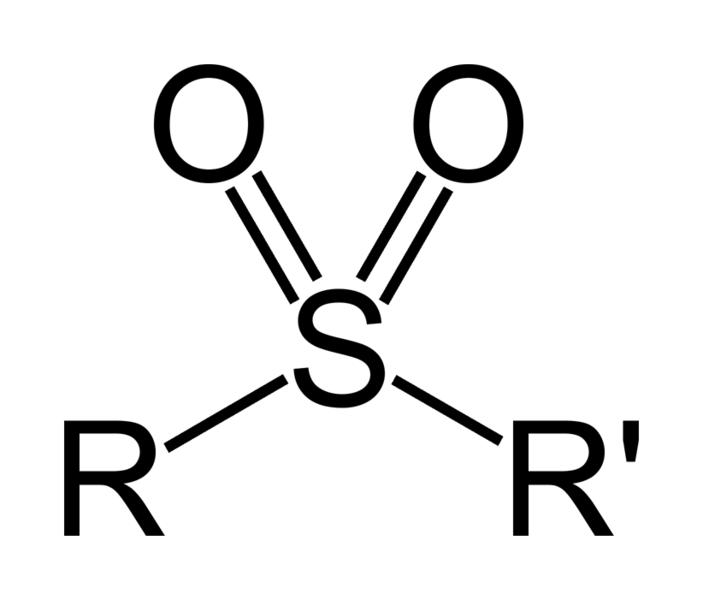
A sulfone is a chemical compound containing a sulfonyl functional group attached to two carbon atoms. The central sulfur atom is twice double bonded to oxygen and has two further hydrocarbon substituents. The general structural formula is R-S(=O)(=O)-R' where R and R' are the organic groups. The use of the alternative name sulphone is discouraged by IUPAC. Sulfides are often the starting materials for sulfones by organic oxidation through the intermediate formation of sulfoxides. For example dimethyl sulfide is oxidized to dimethyl sulfoxide and then to dimethyl sulfone.
In the Ramberg-Bäcklund Reaction and the Julia olefination sulfones are converted to alkenes.
A sulfone can also be any of various organic sulfur compounds having a sulfonyl group attached to two carbon atoms, especially such a compound formerly used as an antibiotic to treat leprosy, dermatitis herpetiformis, tuberculosis, or Pneumocystis pneumonia(PCP).