Propylthiouracil
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Adeel Jamil, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Severe liver injury and acute liver failure, in some cases fatal, have been reported in patients treated with propylthiouracil. These reports of hepatic reactions include cases requiring liver transplantation in adult and pediatric patients.
|
Overview
Propylthiouracil is a thyroid hormone antagonist and anti thyroide drug that is FDA approved for the treatment of Graves' disease with hyperthyroidism or toxic multinodular goiter, and to ameliorate symptoms of [[hyperthyroidism]] in preparation for thyroidectomy. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, loss of taste, arthralgia, paresthesias, myalgia, headache, drowsiness, pruritus, skin rash and urticaria.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Propylthiouracil is indicated:
- in patients with Graves' disease with hyperthyroidism or toxic multinodular goiter who are intolerant of methimazole and for whom surgery or radioactive iodine therapy is not an appropriate treatment option.
- to ameliorate symptoms of hyperthyroidism in preparation for thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy in patients who are intolerant of methimazole.
Dosing Information
- Propylthiouracil is administered orally. The total daily dosage is usually given in 3 equal doses at approximately 8-hour intervals.
Adults
- The initial dose is 300 mg daily. In patients with severe hyperthyroidism, very large goiters, or both, the initial dose may be increased to 400 mg daily; an occasional patient will require 400 to 900 mg daily initially. The usual maintenance dose is 100 to 150 mg daily. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Geriatric Use
- Clinical studies of propylthiouracil did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Propylthiouracil in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Propylthiouracil in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Propylthiouracil is generally not recommended for use in the pediatric patient population except in rare instances in which other alternative therapies are not appropriate options. Studies evaluating appropriate dosing regimen have not been conducted in the pediatric population although general practice would suggest initiation of therapy in patients 6 years or older at a dosage of 50 mg daily with careful upward titration based on clinical response and evaluation of TSH and free T4 levels. Although cases of severe liver injury have been reported with doses as low as 50 mg/day, most cases were associated with doses of 300 mg/day and higher.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Propylthiouracil in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Propylthiouracil in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Propylthiouracil is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug or any of the other product components.
Warnings
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Severe liver injury and acute liver failure, in some cases fatal, have been reported in patients treated with propylthiouracil. These reports of hepatic reactions include cases requiring liver transplantation in adult and pediatric patients.
|
Liver Toxicity
- Liver injury resulting in liver failure, liver transplantation, or death, has been reported with propylthiouracil therapy in adult and pediatric patients. No cases of liver failure have been reported with the use of methimazole in pediatric patients. For this reason, propylthiouracil is not recommended for pediatric patients except when methimazole is not well-tolerated and surgery or radioactive iodine therapy are not appropriate therapies.
- There are cases of Liver injury, including liver faillure and death, in women treated with propylthiouracil during pregnancy. Two reports of in utero exposure with liver failure and death of a newborn have been reported. The use of an alternative antithyroid medication (e.g., methimazole) may be advisable following the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Biochemical monitoring of liver function (bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase) and hepatocellular integrity (ALT, AST) is not expected to attenuate the risk of severe Liver injury due to its rapid and unpredictable onset. Patients should be informed of the risk of liver failure. Patients should be instructed to report any symptoms of hepatic dysfunction (anorexia, pruritus, right upper quadrant pain, etc.) particularly in the first six months of therapy. When these symptoms occur, propylthouracil should be discontinued immediately and liver function tests and ALT and AST levels obtained.
Agranulocytosis
- Agranulocytosis occurs in approximately 0.2% to 0.5% of patients and is a potentially life-threatening side effect of propylthiouracil therapy. Agranulocytosis typically occurs within the first 3 months of therapy. Patients should be instructed to immediately report any symptoms suggestive of agranulocytosis, such as fever or sore throat. Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and aplastic anemia (pancytopenia) may also occur. Propylthiouracil should be discontinued if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia (pancytopenia), ANCA-positive vasculitis, hepatitis, interstitial pneumonitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis is suspected, and the patient's bone marrow indices should be obtained.
Hypothyroidism
- Propylthiouracil can cause hypothyroidism necessitating routine monitoring of TSH and free T4 levels with adjustments in dosing to maintain a euthyroid state. Because the drug readily crosses placental membranes, propylthiouracil can cause fetal goiter and cretinism when administered to a pregnant woman.
PRECAUTIONS
General
- Patients should be instructed to report any symptoms of hepatic dysfunction (anorexia, pruritus, jaundice, light colored stools, dark urine, right upper quadrant pain, etc.), particularly in the first six months of therapy. When these symptoms occur, measurement should be made of liver function (bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase) and hepatocellular integrity (ALT/AST levels).
- Patients who receive propylthiouracil should be under close surveillance and should be counseled regarding the necessity of reporting any evidence of illness, particularly sore throat, skin eruptions, fever, headache, or general malaise. In such cases, white blood cell and differential counts should be obtained to determine whether agranulocytosis has developed. Particular care should be exercised with patients who are receiving concomitant drugs known to be associated with agranulocytosis.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Major adverse reactions (much less common than the minor adverse reactions) include liver injury resulting in hepatitis, liver failure, a need for liver transplantation or death. Inhibition of myelopoiesis (agranulocytosis, granulopenia, and thrombocytopenia), aplastic anemia, drug fever, a lupus-like syndrome (including splenomegaly and vasculitis), hepatitis, periartentis, and hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding have been reported. Nephritis, glomerulonephritis, interstitial pneumonitis, exfoliative dermatitis, and erythema nodosum have been reported. Reports of a vasculitis syndrome associated with the presence of Arteritisanti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) have also been received. Manifestations of ANCA-positive vasculitis may include rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (crescentic and pauci-immune necrotizing glomerulonephritis), sometimes leading to acute renal failure; pulmonary infiltrates or alveolar hemorrhage; skin ulcers; and leucocytoclastic vasculitis. Minor adverse reactions include skin rash, urticaria, nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, arthralgia, paresthesias, loss of taste, taste perversion, abnormal Ioss of hair, myalgia, headache, pruritus, drowsiness, neuritis, edema, vertigo, skin pigmentation, jaundice, sialadenopathy, and lymphadenopathy.
- It should be noted that about 10% of patients with untreated hyperthyroidism have leukopenia (white blood cell count of less than 4,000/mm3), often with relative granulopenia.
- To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact West-ward Pharmaceutical Corp. at 1-877-233-2001 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or WWW.FDA.GOV/MEDWATCH.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Propylthiouracil in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
Anticoagulants (oral)=
- Due to the potential inhibition of vitamin K activity by propylthiouracil, the activity of oral anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin) may be increased; additional monitoring of PT/INR should be considered, especially before surgical procedures.
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents
- Hyperthyroidism may cause an increased clearance of beta blockers with a high extraction ratio. A reduced dose of beta-adrenergic blockers may be needed when a hyperthyroid patient becomes euthyroid.
Digitalis Glycosides
- Serum digitalis levels may be increased when hyperthyroid patients on a stable digitalis glycoside regimen become euthyroid; a reduced dosage of digitalis glycosides may be needed.
Theophylline
- Theophylline clearance may decrease when hyperthyroid patients on a stable theophylline regimen become euthyroid; a reduced dose of theophylline may be needed.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- There are cases of liver injury, including liver faillure and death, in women treated with propylthiouracil during pregnancy. Two reports of in utero exposure with liver failure and death of a newborn have been reported. The use of an alternative antithyroid medication (e.g., methimazole) may be advisable following the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Propylthiouracil in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Propylthiouracil during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Propylthiouracil is transferred to breasdt milk to a small extent and therefore likely results in clinically insignificant doses to the suckling infant. One one study, nine lactating women were administered 400 mg of propylthiouracil by mouth. The mean amount of propylthiouracil excreted during 4 hours after drug administration was 0.025% of the administered dose.
Pediatric Use
- Post-marketing reports of severe liver injury including hepatic failure requiring liver transplantation or resulting in death have been reported in the pediatric population. No such reports have been observed with methimazole. As such, propylthiouracil is not recommended for use in the pediatric population except in rare instances in which methimazole is not well-tolerated and surgery or radioactive iodine therapy are not appropriate.
- When used in children, parents and patients should be informed of the risk of liver failure. If patients taking propylthiouracil develop tiredness, nausea, anorexia, fever, pharyngitis, or malaise, propylthiouracil should be discontinued immediately by the patient, a physician should be contacted, and a white blood cell count, liver function tests, and transaminase levels obtained.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Propylthiouracil with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Propylthiouracil with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Propylthiouracil with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Propylthiouracil in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Propylthiouracil in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Propylthiouracil in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Propylthiouracil in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Monitoring
Laboratory Tests
- Because propylthiouracil may cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding, monitoring of prothrombin time should be considered during therapy with the drug, especially before surgical procedures.
- Thyroid function tests should be monitored periodically during therapy. Once clinical evidence of hyperthyroidism has resolved, the finding of an elevated serum TSH indicates that a lower maintenance dose of propylthiouracil should be employed.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Propylthiouracil in the drug label.
Overdosage
Signs and Symptoms
- Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritus, edema, and pancytopenia. Agranulocytosis is the most serious effect. Rarely, exfoliative dermatitis, hepatitis, neuropathies, or CNS stimulation or depression may occur.
- No information is available on the following: LD50: concentration of propylthiouracil in biologic fluids associated with toxicity and/or death; the amount of drug in a single dose usually associated with symptoms of overdosage; or the amount of propylthiouracil in a single dose likely to be life-threatening.
Treatment
- To obtain up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose, a good resource is the certified Regional Poison Control Center. In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug overdoses, interaction among drugs, and unusual drug kinetics in the patient.
- In the event of an overdose, appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated as dictated by the patient's medical status.
Pharmacology
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682465 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80%-95% |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Elimination half-life | 2 hours |
| Excretion | ? |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H10N2OS |
| Molar mass | 170.233 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Mechanism of Action
- Propylthiouracil inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormones. It inhibits the conversation of thyroxine to triiodothyronine to peripheral tissues and may therefore be an effective treatment for thyroid storm.
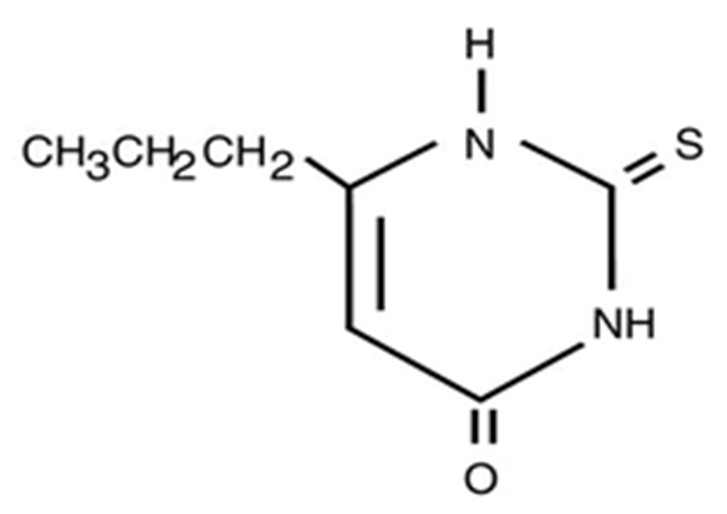
Structure
- Propylthiouracil (6-propyl-2-thiouracil) is one of the thiocarbamide compounds. It is a white, crystalline substance that has a bitter taste and is very slightly soluble in water.
- Propylthiouracil is an antithyroid drug administered orally. The structural formula is:
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Propylthiouracil in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- Propylthiouracil inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormones and thus is effective in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. The drug does not inactivate existing thyroxine and triodothyronine that are stored in the thyroid or circulating in the blood, nor does it interfere with the effectiveness of thyroid hormones given by mouth or by injection. Propylthiouracil inhibits the conversation of thyroxine to triiodothyronine to peripheral tissues and may therefore be an effective treatment for thyroid storm.
- Propylthiouracil is readily absorbed and is extensively metabolized. Approximately 35% of the drug is excreted in the urine, in intact and in conjugated forms, within 24 hours.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Propylthiouracil in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Laboratory animals treated with propylthiouracil for > 1 year have demonstrated thyroid hyperplasia and carcinoma formation1. Such animal findings are seen with continuous suppression of thyroid function by sufficient doses of a variety of antithyroid agents, as well as in dietary iodine deficiency, subtotal thyroidectomy, and implantation of autonomous thyrotropic hormone - secreting pituitary tumors. Pituitary adenomas have also been described.
How Supplied
Propylthiouracil Tablets, USP, 50 mg: White, Round, Scored Tablet, Debossed “West-ward 480”.
Bottles of 100 tablets.
Bottles of 1000 tablets.
Unit Dose Boxes of 100 tablets.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Reference:
International Agency for Research on Cancer, IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Man. 1974; 7:67-76.
Manufactured By: West-ward Pharmaceutical Corp. Eatontown, NJ 07724 Revised August 2011
Storage
- Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light and moisture.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Propylthiouracil |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
Propylthiouracil Tablets, USP
50 mg
100 Tablets
NDC 0143-1480-01 {{#ask: Label Page::Propylthiouracil |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant white taking an antithyroid drug, they should contact their physician immediately about their therapy.
Patients should report immediately any evidence of illness, particularly sore throat, skin eruptions, fever, headache, or general malaise. They also should report symptoms suggestive of hepatic dysfunction (anorexia, pruritis, right upper quadrant pain, etc).
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Propylthiouracil interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Propylthiouracil Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Propylthiouracil Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Propylthiouracil
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Propylthiouracil |Label Name=Propylthiouracil drug lable.png
}}