Gadoteridol
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ammu Susheela, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Gadoteridol is a non-Ionic contrast media that is FDA approved for the diagnosis of lesions with abnormal vascularity in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine and associated tissues in adults and children over 2 years of age using MRI. Common adverse reactions include taste sense altered.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Central Nervous System
- Gadoteridol injection is indicated for use in MRI in adults and children over 2 years of age to visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine and associated tissues.
Extracranial/Extraspinal Tissues
Central Nervous System
- ADULTS: The recommended dose of Gadoteridol Injection is 0.1 mmol/kg (0.2 mL/kg) administered as a rapid intravenous infusion (10 mL/min-60 mL/min) or bolus (> 60 mL/min). In patients with normal renal function suspected of having poorly enhancing lesions, in the presence of negative or equivocal scans, a supplementary dose of 0.2 mmol/kg (0.4 mL/kg) may be given up to 30 minutes after the first dose.
Extracranial/Extraspinal Tissues
- ADULTS: The recommended dose of gadoteridol is 0.1 mmol/kg (0.2 mL/kg) administered as a rapid intravenous infusion (10 mL/min-60 mL/min) or bolus (> 60 mL/min).
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Gadoteridol in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Gadoteridol in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- CHILDREN (2-18 years): The recommended dose of gadoteridol is 0.1 mmol/kg (0.2 mL/kg) administered as a rapid intravenous infusion (10 mL/min-60 mL/min) or bolus (> 60 mL/min). The safety and efficacy of doses > 0.1 mmol/kg, and sequential and/or repeat procedures has not been studied.
Extracranial/Extraspinal Tissues
- Safety and efficacy for extracranial/extra-spinal tissues has not been established.
- Dose adjustments in renal and liver impairment have not been studied.
- To ensure complete injection of the contrast medium, the injection should be followed by a 5 mL normal saline flush. The imaging procedure should be completed within 1 hour of the first injection of gadoteridol injection.
- Parenteral products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use the solution if it is discolored or particulate matter is present. Any unused portion must be discarded in accordance with regulations dealing with the disposal of such materials.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Gadoteridol in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Gadoteridol in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Gadoteridol is contraindicated in patients with known allergic or hypersensitivity reactions to gadoteridol.
Warnings
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF)
- Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast enhanced MRI or other modalities. The GBCA-associated NSF risk appears highest for patients with chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2) as well as patients with acute kidney injury. The risk appears lower for patients with chronic, moderate kidney disease (GFR 30-59 mL/min/1.73m2) and little, if any, for patients with chronic, mild kidney disease (GFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73m2). NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. Report any diagnosis of NSF following gadoteridol administration to Bracco Diagnostics (1-800-257-8151) or FDA (1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch).
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. Features of acute kidney injury consist of rapid (over hours to days) and usually reversible decrease in kidney function, commonly in the setting of surgery, severe infection, injury or drug-induced kidney toxicity. Serum creatinine levels and estimated GFR may not reliably assess renal function in the setting of acute kidney injury. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g., age > 60 years, diabetes mellitus or chronic hypertension), estimate the GFR through laboratory testing.
- Among the factors that may increase the risk for NSF are repeated or higher than recommended doses of a GBCA and the degree of renal impairment at the time of exposure. Record the specific GBCA and the dose administered to a patient. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended gadoteridol dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug prior to re-administration. For patients receiving hemodialysis, physicians may consider the prompt initiation of hemodialysis following the administration of a GBCA in order to enhance the contrast agent’s elimination. The usefulness of hemodialysis in the prevention of NSF is unknown.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
- In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of [[]acute kidney injury]] may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent; administer the lowest dose necessary for adequate imaging.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Severe and fatal hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have been observed with administration of gadolinium products, including gadoteridol. Patients with a history of allergy, drug reactions or other hypersensitivity-like disorders should be closely observed during the procedure and for several hours after drug administration. If a reaction occurs, stop gadoteridol and immediately begin appropriate therapy including resuscitation.
- Deoxygenated sickle erythrocytes have been shown in in vitro studies to align perpendicular to a magnetic field which may result in vaso-occlusive complications in vivo. The enhancement of magnetic moment by gadoteridol may possibly potentiate sickle erythrocyte alignment. Gadoteridol in patients with sickle cell anemia and other hemoglobinopathies has not been studied.
- Patients with other hemolytic anemias have not been adequately evaluated following administration of gadoteridol to exclude the possibility of increased hemolysis.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The adverse events described in this section were observed in clinical trials involving 1251 patients (670 males and 581 females). Adult patients ranged in age from 18-91 yrs. Pediatric patients ranged from 2-17 years. The racial breakdown was 83% Caucasian, 8% Black, 3% Hispanic, 2% Asian, and 1% other. In 2% of the patients, race was not reported.
- The most commonly noted adverse experiences were nausea and taste perversion with an incidence of 1.4%. These events were mild to moderate in severity. Seizure is also found in patients taking gadoteridol.
- The following additional adverse events occurred in fewer than 1% of the patients:
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Gadoteridol in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Gadoteridol Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Gadoteridol administered to rats at 10 mmol/kg/day (33 times the maximum recommended human dose of 0.3 mmol/kg or 6 times the human dose based on a mmol/m2 comparison) for 12 days during gestation doubled the incidence of postimplantation loss. When rats were administered 6.0 or 10.0 mmol/ kg/day for 12 days, an increase in spontaneous locomotor activity was observed in the offspring. Gadoteridol increased the incidence of spontaneous abortion and early delivery in rabbits administered 6 mmol/kg/day (20 times the maximum recommended human dose or 7 times the human dose based on a mmol/m2 comparison) for 13 days during gestation.
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Gadoteridol) injection should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Gadoteridol in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Gadoteridol during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when gadoteridol is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and efficacy in children under the age of 2 years have not been established. The safety and efficacy of doses > 0.1 mmol/kg; and sequential and/or repeat procedures has not been studied in children.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gadoteridol with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gadoteridol with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gadoteridol with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gadoteridol in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gadoteridol in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Gadoteridol in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Gadoteridol in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Gadoteridol in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Gadoteridol in the drug label.
Overdosage
Clinical consequences of overdose with gadoteridol have not been reported.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Gadoteridol Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
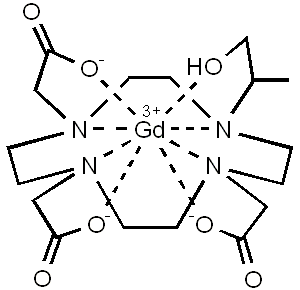
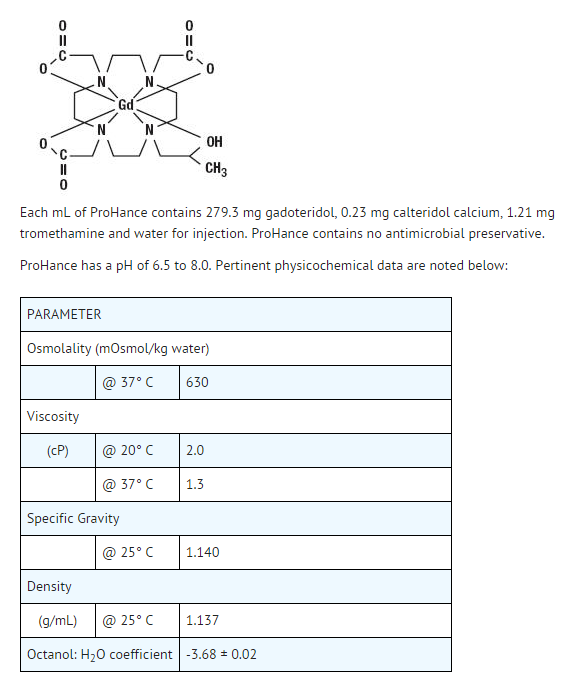
- Gadoteridol injection is a nonionic contrast medium for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), available as a 0.5M sterile clear colorless to slightly yellow aqueous solution in vials and syringes for intravenous injection.
- Gadoteridol is the gadolinium complex of 10-(2-hydroxy-propyl)-1,4,7,10- tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-triacetic acid with a molecular weight of 558.7, an empirical formula of C17H29N4O7Gd and has the following structural formula:
- Gadoteridol has an osmolality 2.2 times that of plasma (285 mOsmol/kg water) and is hypertonic under conditions of use.
Pharmacodynamics
- Gadoteridol is a paramagnetic agent and, as such, develops a magnetic moment when placed in a magnetic field. The relatively large magnetic moment produced by the paramagnetic agent results in a relatively large local magnetic field, which can enhance the relaxation rates of water protons in the vicinity of the paramagnetic agent.
- In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), visualization of normal and pathologic brain tissue depends in part on variations in the radiofrequency signal intensity that occur with 1) differences in proton density; 2) differences of the spin-lattice or longitudinal relaxation times (T1); and 3) differences in the spin-spin or transverse relaxation time (T2). When placed in a magnetic field, gadoteridol decreases T1 relaxation times in the target tissues. At recommended doses, the effect is observed with greatest sensitivity in the T1-weighted sequences.
- Gadoteridol does not cross the intact blood-brain barrier and, therefore, does not accumulate in normal brain or in lesions that have a normal blood-brain barrier, e.g., cysts, mature post-operative scars, etc. However, disruption of the blood-brain barrier or abnormal vascularity allows accumulation of gadoteridol in lesions such as neoplasms, abscesses, and subacute infarcts. The pharmacokinetics of gadoteridol in various lesions is not known.
Pharmacokinetics
- The pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered gadoteridol in normal subjects conforms to a two-compartment open model with mean distribution and elimination half-lives (reported as mean ± SD) of about 0.20 ± 0.04 hours and 1.57 ± 0.08 hours, respectively.
- Gadoteridol is eliminated in the urine with 94.4 ± 4.8% (mean ± SD) of the dose excreted within 24 hours post-injection. It is unknown if biotransformation or decomposition of gadoteridol occur in vivo.
- The renal and plasma clearance rates (1.41 ± 0.33 mL/ min/kg and 1.50 ± 0.35 mL/ min/kg, respectively) of gadoteridol are essentially identical, indicating no alteration in elimination kinetics on passage through the kidneys and that the drug is essentially cleared through the kidney. The volume of distribution (204 ± 58 mL/kg) is equal to that of extracellular water, and clearance is similar to that of substances which are subject to glomerular filtration.
- It is unknown if protein binding of gadoteridol occurs in vivo.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Gadoteridol in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
- Gadoteridol was evaluated in two blinded read trials in a total of 133 adults who had an indication for head and neck extracranial or extraspinal magnetic resonance imaging. These 133 adults (74 men, 59 women) had a mean age of 53 with a range of 19 to 76 years. Of these patients, 85% were Caucasian, 13% Black, 2% Asian, and < 1% other. The results of the non-contrast and gadoteridol MRI scans were compared. In this database, approximately 75-82% of the scans were enhanced. 45-48% of the scans provided additional diagnostic information, and 8-25% of the diagnoses were changed. The relevance of the findings to disease sensitivity and specificity has not been fully evaluated.
- Gadoteridol was evaluated in a multicenter clinical trial of 103 children who had an indication for a brain or spine MRI. These 103 children, (54 boys and 49 girls) had a mean age of 8.7 years with an age range of 2 to 20 years. Of these 103 children, 54 were between 2 and 12 years of age. Also, of these 103 children, 74% were Caucasian, 11% Black, 12% Hispanic, 2% Asian, and 2% other. The results of the non-contrast and gadoteridol MRI scans were compared. Gadoteridol was given in one single 0.1 mmol/kg dose. Repeat dosing was not studied. In this database, MRI enhancement was noted in approximately 60% of the scans and additional diagnostic information in 30-95% of the scans.
How Supplied
- Gadoteridol injection is a clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution containing 279.3 mg/mL of gadoteridol in rubber stoppered vials. Gadoteridol is available in boxes of:
Storage
- Gadoteridol Injection should be stored at 25° C (77° F) excursions permitted to 15-30° C (59-86° F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light. DO NOT FREEZE. Should freezing occur in the vial, gadoteridol should be brought to room temperature before use. If allowed to stand at room temperature for a minimum of 60 minutes, Gadoteridol Injection should return to a clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution. Before use, examine the product to assure that all solids are redissolved and that the container and closure have not been damaged. Should solids persist, discard vial. Frozen syringes should be discarded.
- Directions for Use of the Gadoteridol Injection single dose syringe*
- Screw the threaded tip of the plunger rod clockwise into the cartridge plunger and push forward a few millimeters to break any friction between the cartridge plunger and syringe barrel.
- Holding syringe erect, unscrew the plastic tip cap from the tip of the syringe and attach either a sterile, disposable needle or tubing with a compatible luer lock using a push-twist action.
- Hold the syringe erect and push plunger forward until all of the air is evacuated and fluid either appears at the tip of the needle or the tubing is filled. Following the usual aspiration procedure, complete the injection. To ensure complete delivery of the contrast medium, the injection should be followed by a normal saline flush.
- Properly dispose of the syringe and any other materials used.
- The syringe assembly is a HYPAK SCF® single dose syringe supplied by Becton Dickinson.
- Holding syringe erect, unscrew the plastic tip cap from the tip of the syringe and attach either a sterile, disposable needle or tubing with a compatible luer lock using a push-twist action.
- Hold the syringe erect and push plunger forward until all of the air is evacuated and fluid either appears at the tip of the needle or the tubing is filled. Following the usual aspiration procedure, complete the injection. To ensure complete delivery of the contrast medium, the injection should be followed by a normal saline flush.
- Properly dispose of the syringe and any other materials used.
- The syringe assembly is a HYPAK SCF® single dose syringe supplied by Becton Dickinson.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Gadoteridol |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Gadoteridol |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Gadoteridol in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Gadoteridol interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ProHance®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Gadoteridol Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Gadoteridol |Label Name=Galdi 04.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Gadoteridol |Label Name=Galti 05.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Gadoteridol |Label Name=DailyMed - PROHANCE- gadoteridol injection, solution .png
}}