Fludrocortisone Acetate
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Kiran Singh, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Fludrocortisone Acetate is a corticosteroid that is FDA approved for the treatment of primary and secondary adrenocortical insufficiency in Addison's disease and for the treatment of salt-losing adrenogenital syndrome.. Common adverse reactions include edema,rash,urticaria,muscle weakness,headache,vertigo,glycosuria and peptic ulcer.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- Fludrocortisone acetate tablets USP, 0.1 mg are indicated as partial replacement therapy for primary and secondary adrenocortical insufficiency in Addison's disease and for the treatment of salt-losing adrenogenital syndrome.
Dosage
- Dosage depends on the severity of the disease and the response of the patient. Patients should be continually monitored for signs that indicate dosage adjustment is necessary, such as remission or exacerbations of the disease and stress (surgery, infection, trauma)
Addison's Disease
- In Addison's disease, the combination of fludrocortisone acetate tablets with a glucocorticoid such as hydrocortisone or cortisone provides substitution therapy approximating normal adrenal activity with minimal risks of unwanted effects.
- The usual dose is 0.1 mg of fludrocortisone acetate tablets daily, although dosage ranging from 0.1 mg three times a week to 0.2 mg daily has been employed. In the event transient hypertension develops as a consequence of therapy, the dose should be reduced to 0.05 mg daily. Fludrocortisone acetate tablets are preferably administered in conjunction with cortisone (10 mg to 37.5 mg daily in divided doses) or hydrocortisone (10 mg to 30 mg daily in divided doses).
Salt-Losing Adrenogenital Syndrome
- The recommended dosage for treating the salt-losing adrenogenital syndrome is 0.1 mg to 0.2 mg of fludrocortisone acetate tablets daily.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
- There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Fludrocortisone Acetate in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
- There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Fludrocortisone Acetate in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Fludrocortisone Acetate in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
- There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Fludrocortisone Acetate in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
- There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Fludrocortisone Acetate in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Corticosteroids are contraindicated in patients with systemic fungal infections and in those with a history of possible or known hypersensitivity to these agents.
Warnings
BECAUSE OF ITS MARKED EFFECT ON SODIUM RETENTION THE USE OF FLUDROCORTISONE ACETATE IN THE TREATMENT OF CONDITIONS OTHER THAN THOSE INDICATED HEREIN IS NOT ADVISED.
- Corticosteroids may mask some signs of infection, and new infections may appear during their use. There may be decreased resistance and inability to localize infection when corticosteroids are used. If an infection occurs during fludrocortisone acetate therapy, it should be promptly controlled by suitable antimicrobial therapy.
- Prolonged use of corticosteroids may produce posterior subcapsular cataracts, glaucoma with possible damage to the optic nerves, and may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to fungi or viruses.
- Average and large doses of hydrocortisone or cortisone can cause elevation of blood pressure, salt and water retention, and increased excretion of potassium. These effects are less likely to occur with the synthetic derivatives except when used in large doses. However, since fludrocortisone acetate is a potent mineralocorticoid, both the dosage and salt intake should be carefully monitored in order to avoid the development of hypertension, edema or weight gain. Periodic checking of serum electrolyte levels is advisable during prolonged therapy; dietary salt restriction and potassium supplementation may be necessary. All corticosteroids increase calcium excretion.
- Patients should not be vaccinated against smallpox while on corticosteroid therapy. Other immunization procedures should not be undertaken in patients who are on corticosteroids, especially on high dose, because of possible hazards of neurological complications and a lack of antibody response.
- The use of fludrocortisone acetate in patients with active tuberculosis should be restricted to those cases of fulminating or disseminated tuberculosis in which the corticosteroid is used for the management of the disease in conjunction with an appropriate antituberculous regimen. If corticosteroids are indicated in patients with latent tuberculosis or tuberculin reactivity, close observation is necessary since reactivation of the disease may occur. During prolonged corticosteroid therapy these patients should receive chemoprophylaxis.
- Children who are on immunosuppressant drugs are more susceptible to infections than healthy children. Chicken pox and measles, for example, can have a more serious or even fatal course in children on immunosuppressant corticosteroids. In such children, or in adults who have not had these diseases, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. If exposed, therapy with variicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) or pooled intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), as appropriate, may be indicated. If chicken pox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Most adverse reactions are caused by the drug's mineralocorticoid activity (retention of sodium and water) and include hypertension, edema, cardiac enlargement, congestive heart failure, potassium loss, and hypokalemic alkalosis.
- When fludrocortisone is used in the small dosages recommended, the glucocorticoid side effects often seen with cortisone and its derivatives are not usually a problem; however the following untoward effects should be kept in mind, particularly when fludrocortisone is used over a prolonged period of time or in conjunction with cortisone or a similar glucocorticoid.
- Musculoskeletal—muscle weakness, steroid myopathy, loss of muscle mass, osteoporosis, vertebral compression fractures, aseptic necrosis of femoral and humeral heads, pathologic fracture of long bones, and spontaneous fractures.
- Gastrointestinal—peptic ulcer with possible perforation and hemorrhage, pancreatitis, abdominal distention, and ulcerative esophagitis.
- Dermatologic—impaired wound healing, thin fragile skin, bruising, petechiae and ecchymoses, facial erythema, increased sweating, subcutaneous fat atrophy, purpura, striae, hyperpigmentation of the skin and nails, hirsutism, acneiform eruptions and hives; reactions to skin tests may be suppressed.
- Neurological—convulsions, increased intracranial pressure with papilledema (psuedotumor cerebri) usually after treatment, vertigo, headache, and severe mental disturbances.
- Endocrine—menstrual irregularities; development of the cushingoid state; suppression of growth in children; secondary adrenocortical and pituitary unresponsiveness, particularly in times of stress (e.g., trauma, surgery, or illness); decreased carbohydrate tolerance; manifestations of latent diabetes mellitus; and increased requirements for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents in diabetics.
- Ophthalmic—posterior subcapsular cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, and exophthalmos.
- Metabolic—hyperglycemia, glycosuria, and negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism.
- Other adverse reactions that may occur following the administration of a corticosteroid are necrotizing angiitis, thrombophlebitis, aggravation or masking of infections, insomnia, syncopal episodes, and anaphylactoid reactions.
Postmarketing Experience
- There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Fludrocortisone Acetate in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- When administered concurrently, the following drugs may interact with adrenal corticosteroids.
- Amphotericin B or potassium-depleting diuretics (benzothiadiazines and related drugs, ethacrynic acid and furosemide)—enhanced hypokalemia. Check serum potassium levels at frequent intervals; use potassium supplements if necessary.
- Digitalis glycosides—enhanced possibility of arrhythmias or digitalis toxicity associated with hypokalemia. Monitor serum potassium levels; use potassium supplements if necessary.
- Oral anticoagulants— decreased prothrombin time response. Monitor prothrombin levels and adjust anticoagulant dosage accordingly.
- Antidiabetic drugs (oral agents and insulin)—diminished antidiabetic effect. Monitor for symptoms of hyperglycemia; adjust dosage of antidiabetic drug upward if necessary.
- Aspirin— increased ulcerogenic effect; decreased pharmacologic effect of aspirin. Rarely salicylate toxicity may occur in patients who discontinue steroids after concurrent high-dose aspirin therapy. Monitor salicylate levels or the therapeutic effect for which aspirin is given; adjust salicylate dosage accordingly if effect is altered.
- Barbiturates, phenytoin, or rifampin—increased metabolic clearance of fludrocortisone acetate because of the induction of hepatic enzymes. Observe the patient for possible diminished effect of steroid and increase the steroid dosage accordingly.
- Anabolic steroids (particularly C-17 alkylated androgens such as oxymetholone, methandrostenolone, norethandrolone, and similar compounds)—enhanced tendency toward edema. Use caution when giving these drugs together, especially in patients with hepatic or cardiac disease.
- Vaccines—neurological complications and lack of antibody response.
- Estrogen—increased levels of corticosteroid-binding globulin thereby increasing the bound (inactive) fraction; this effect is at least balanced by decreased metabolism of corticosteroids. When estrogen therapy is initiated, a reduction in corticosteroid dosage may be required, and increased amounts may be required when estrogen is terminated.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): Teratogenic effects: Category C
- Adequate animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with fludrocortisone acetate. However, many corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in laboratory animals at low doses. Teratogenicity of these agents in man has not been demonstrated. It is not known whether fludrocortisone acetate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Fludrocortisone acetate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Pregnancy: Nonteratogenic Effects
- Infants born of mothers who have received substantial doses of fludrocortisone acetate during pregnancy should be carefully observed for signs of hypoadrenalism.
- Maternal treatment with corticosteroids should be carefully documented in the infant's medical records to assist in follow up.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Fludrocortisone Acetate in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Fludrocortisone Acetate during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Corticosteroids are found in the breast milk of lactating women receiving systemic therapy with these agents. Caution should be exercised when fludrocortisone acetate is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in children have not been established.
- Growth and development of infants and children on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should be carefully observed.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fludrocortisone Acetate with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fludrocortisone Acetate with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fludrocortisone Acetate with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fludrocortisone Acetate in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fludrocortisone Acetate in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fludrocortisone Acetate in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Fludrocortisone Acetate in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
- There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Fludrocortisone Acetate in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
- There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Fludrocortisone Acetate in the drug label.
Overdosage
- Development of hypertension, edema, hypokalemia, excessive increase in weight, and increase in heart size are signs of overdosage of fludrocortisone acetate. When these are noted, administration of drugs should be discontinued, after which the symptoms will usually subside within several days; subsequent treatment with fludrocortisone acetate should be with a reduced dose. Muscular weakness may develop due to excessive potassium loss and can be treated by administering a potassium supplement. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and serum electrolytes can help to prevent overdosage.
Pharmacology
| |
| |
Fludrocortisone Acetate
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
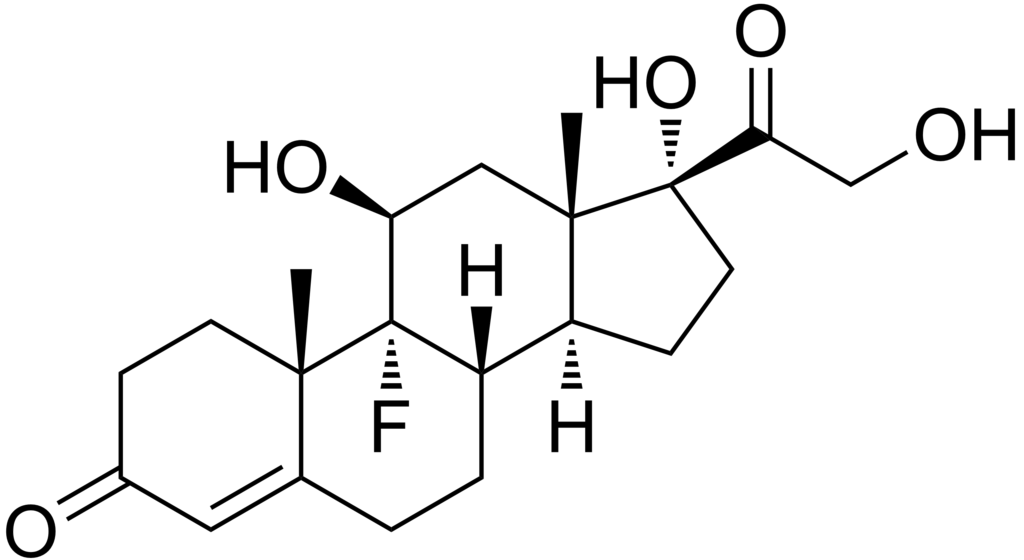
| 9-fluoro-11,17-dihydroxy-17- (2-hydroxyacetyl)- 10,13-dimethyl- 1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12, 13,14,15,16,17- tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | H02 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 380.45 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Protein binding | High |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Half life | 3.5 hours |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
C |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
- Corticosteroids are thought to act at least in part, by controlling the rate of synthesis of proteins. Although there are a number of instances in which the synthesis of specific proteins is known to be induced by corticosteroids, the links between the initial actions of the hormones and the final metabolic effects have not been completely elucidated.
- The physiologic action of fludrocortisone acetate is similar to that of hydrocortisone. However, the effects of fludrocortisone acetate, particularly on electrolyte balance, but also on carbohydrate metabolism, are considerably heightened and prolonged. Mineralocorticoids act on the distal tubules of the kidney to enhance the reabsorption of sodium ions from the tubular fluid into the plasma; they increase the urinary excretion of both potassium and hydrogen ions. The consequence of these three primary effects together with similar actions on cation transport in other tissues appear to account for the entire spectrum of physiological activities that are characteristic of mineralocorticoids. In small oral doses, fludrocortisone acetate produces marked sodium retention and increased urinary potassium excretion. It also causes a rise in blood pressure, apparently because of these effects on electrolyte levels.
- In larger doses, fludrocortisone acetate inhibits endogenous adrenal cortical secretion, thymic activity, and pituitary corticotropin excretion; promotes the deposition of liver glycogen; and, unless protein intake is adequate, induces negative nitrogen balance.
- The approximate plasma half-life of fludrocortisone (fluorohydrocortisone) is 3.5 hours or more and the biological half-life is 18 to 36 hours.
Structure
- Fludrocortisone Acetate Tablets USP, 0.1 mg contain fludrocortisone acetate, a synthetic adrenocortical steroid possessing very potent mineralocorticoid properties and high glucocorticoid activity; it is used only for its mineralocorticoid effects. The chemical name for fludrocortisone acetate is 9-fluoro-11β, 17, 21-trihydroxypregn-4-ene-3, 20- dione 21-acetate; its structural formula is:

- Fludrocortisone acetate tablets USP, 0.1 mg are available for oral administration as scored tablets providing 0.1 mg fludrocortisone acetate per tablet. Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium NF, lactose monohydrate NF, magnesium stearate NF, and microcrystalline cellulose NF.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Fludrocortisone Acetate in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Fludrocortisone Acetate in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Fludrocortisone Acetate in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Fludrocortisone Acetate in the drug label.
How Supplied
- Fludrocortisone Acetate Tablets USP, 0.1 mg—Each white to off-white, round, convex tablet debossed with a "7033" on one side and with a bisect on the other side.
- 10 tablets per card 5 cards per carton......NDC 50268-330-15
Storage
- Store at controlled room temperature 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F)(see USP). Avoid excessive heat.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Fludrocortisone Acetate |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel


{{#ask: Label Page::Fludrocortisone Acetate |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Information for Patients
- The physician should advise the patient to report any medical history of heart disease, high blood pressure, or kidney or liver disease and to report current use of any medicines to determine if these medicines might interact adversely with fludrocortisone acetate.
- Patients who are on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids should be warned to avoid exposure to chicken pox or measles and, if exposed, to obtain medical advice.
- The patient's understanding of his steroid-dependent status and increased dosage requirement under widely variable conditions of stress is vital. Advise the patient to carry medical identification indicating his dependence on steroid medication and, if necessary, instruct him to carry an adequate supply of medication for use in emergencies.
- Stress to the patient the importance of regular follow-up visits to check his progress and the need to promptly notify the physician of dizziness, severe or continuing headaches, swelling of feet or lower legs, or unusual weight gain.
- Advise the patient to use the medicine only as directed, to take a missed dose as soon as possible, unless it is almost time for the next dose, and not to double the next dose.
- Inform the patient to keep this medication and all drugs out of the reach of children.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Fludrocortisone Acetate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- FLUDROCORTISONE ACETATE®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "fludrocortisone acetate tablet".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Fludrocortisone Acetate
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Fludrocortisone Acetate |Label Name=Fludrocortisone Acetate11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Fludrocortisone Acetate |Label Name=Fludrocortisone Acetate11.png
}}