Dosulepin hydrochloride
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 20 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
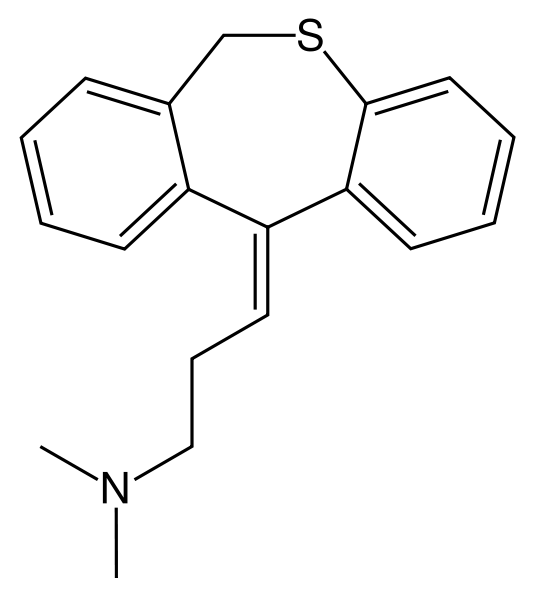
| Formula | C19H21NS |
| Molar mass | 331.9 g/mol |
Dosulepin hydrochloride (INN) (formerly the BAN dothiepin hydrochloride) is an antidepressant of the tricyclic family. It is sold under the brand names Prothiaden and Thaden.
Indications
Dosulepin is relatively mild and is used for low level anxiety depression and similar disorders, particularly where insomnia and/or loss of appetite are present. It can take between two and four weeks of regular usage to become effective, it is often started at a low level and the dosage increased if this is ineffective. The drug causes drowsiness as a side-effect, and this may be used as part of the treatment, since anxiety depressive patients may have difficulty sleeping, but it can be combined with other drugs such as temazepam.
Side effects
The most common side-effects are drowsiness and dry mouth. Other less common side-effects may include:
- Constipation
- Abnormally large stools
- Blurred vision
- Tachycardia
- Urinary retention
- tremors, especially of the hands
- Blood disorders
- Hypotension
- Sexual dysfunction
- Sweating
- Increased sensitivity to sunlight, increased vulnerability to sunburn
These side-effects cease when treatment ceases. Alcohol should be avoided whilst taking dosulepin as it may increase some side-effects.
Whilst dosulepin is not addictive, it should not be stopped suddenly as there is a risk of initial withdrawal symptoms which may be mistaken for some of the original indications for the drug:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
- Giddiness
- Chills
- Insomnia
- Anxiety
Contra-indications
Contra-indications include:
- Certain conditions of the heart, mainly those affecting the electrical impulses to the heart muscle, particularly arrhythmia or recent heart attack
- Mania.
- Liver disease or thyroid disease
- Epilepsy, phaeochromocytoma, glaucoma or diabetes
- Hypotension, vulnerability to dizziness or fainting
- History of urinary retention or porphyria
Drug interactions
The drug can interact dangerously with vasoconstrictors and should not be taken in combination with phenylephrine or adrenaline in particular.
This drug should not be started within 2 weeks of stopping a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) antidepressant, and should not be co-administered with any selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant such as fluoxetine), or any medication which affects the electrical impulses to the heart (e.g. astemizole, halofantrine or terfenadine).
The drug is not recommended for use by children nor taken in combination with some other drugs, including herbal remedies.
Overdose
The symptoms and the treatment of an overdose are largely the same as for the other tricyclic antidepressants.
See also
- Pages with script errors
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Analgesics
- Drugs