Diabetes mellitus type 1 natural history, complications, and prognosis
|
Diabetes mellitus type 1 Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Diabetes mellitus type 1 from other Diseases |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management |
|
Case Studies |
|
Diabetes mellitus Main page |
|
Patient Information |
|---|
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vishal Devarkonda, M.B.B.S[2]Anahita Deylamsalehi, M.D.[3]
Overview
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually develop in the first decade of life, and start with non-specific symptoms of classic new onset type 1 diabetes or acute symptoms with diabetic ketoacidosis. If left untreated, patients with type 1 DM may develop acute complications of the hyperglycemia state, such as diabetes ketoacidosis and hyperglycemia hyperosmolar state. In addition other complications related to microvascular or macrovascular changes, such as retinopathy, autonomic neuropathy, dermatology diseases, coronary heart disease, peripheral arterial disease and macular edema. Prognosis is generally good with compliance with medications.
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Natural History
- The symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually develop in the first decade of life, and start with non-specific symptoms of classic new onset type 1 diabetes or acute symptoms with diabetic ketoacidosis. Without treatment, the patient will develop complications of type 1 diabetes.[1]
Complications
- Complications of type 1 diabetes include:[2][3][4][5]
| Complications of Diabetes | |
|---|---|
| Acute Complications due to hyperglycemia | |
| Microvascular complications | Eye disease
Neuropathy Sensory and motor (mono- and polyneuropathy) and Autonomic neuropathy Nephropathy (albuminuria and declining renal function) |
| Macrovascular complications | Coronary heart disease |
| Other | Gastrointestinal (gastroparesis, diarrhea)
Genitourinary (uropathy/sexual dysfunction) Cheiroarthropathy (thickened skin and reduced joint mobility) Fatty liver disease Low testosterone in men |
- In a control study patients with type 1 diabetes had significantly lower total body bone mineral density (BMD) z-score values. Lower levels of osteocalcin, C-terminal telopeptide, calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium have been found in patients with type 1 diabetes, compared to control group.[6]
- A study demonstrated that children with type 1 diabetes mentioned barriers for physical activity (eg, fear of hypoglycemia, loss of control of diabetes and low fitness). This study report significant improvement with parental support. [7]
- Based on a systematic review, type 1 diabetic patients have worse executive function performance, working memory and task switching, compared to the control group.[8]
- There have been a reported association between early childhood onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus and mild cerebral atrophy and reduced intellectual performance in adulthood.[9]
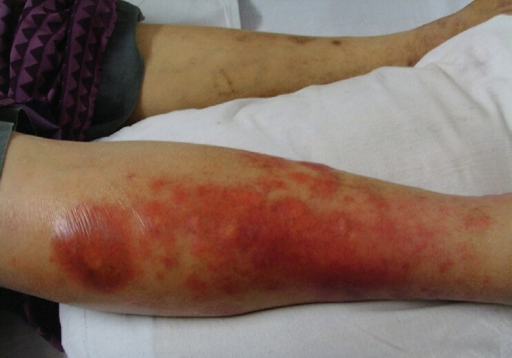
- The followings are some related dermatological consequences of type 1 diabetes:[10]
- Scleroderma-like skin changes: Pathogenesis is not fully understood, nevertheless advanced glycosylation end products and sugar alcohols buildup in the upper dermis is believed to effect the strengthening of collagen.
- Cheiroarthropathy (thickened skin and reduced joint mobility)
- Scleredema diabeticorum
- Necrobiosis lipoidica
- Bullosis diabeticorum
- Xerosis
- Eruptive xanthomas: Although xanthomas are routinely related to hypertriglyceridemia, type 1 diabetic patients may develop eruptive xanthomas with normal levels of triglyceride. Prevelance of Eruptive xanthomas in type 1 diabetes is approximately 1%.
Prognosis
- Diabetes is a lifelong disease and there is no cure. Tight control of blood glucose can prevent or delay diabetes complications. But these problems can occur, even in people with good diabetes control.[12]
- When type 1 diabetes mellitus left untreated it can be fatal due to complications like diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Prognosis of type 1 diabetes mellitus is effected by factors such as blood glucose concentration, hemoglobin A1c ([[Glycosylated hemoglobin|HbA1c), lipids, blood pressure, and weight.
- There is a direct relationship between hemoglobin A1c level and long-term cognitive decline.[13]
- The most common cause of death among type 1 diabetes mellitus patients under 30 years old is acute metabolic complications, based on a study done on Norwegian patients who were diagnosed between 1973 and 1982.[14]
- The following factors have been related to longer life expectancy in patients with type 1 diabetes:[15]
- Proper (not necessarily optimal) glycaemic control
- High HDL-cholesterol levels
- Low insulin requirements (insulin sensitive)
- Normal body mass index (BMI)
- Proper blood pressure control
- Patients who do not smoke
- Absence of microalbuminuria after 15-20 years of type 1 diabetes onset
- Familial history of long life
References
- ↑ Achenbach P, Bonifacio E, Koczwara K, Ziegler AG (2005). "Natural history of type 1 diabetes". Diabetes. 54 Suppl 2: S25–31. PMID 16306336.
- ↑ "ADA".
- ↑ Type 1 Diabetes mellitus "Dennis Kasper, Anthony Fauci, Stephen Hauser, Dan Longo, J. Larry Jameson, Joseph Loscalzo"Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19e Accessed on December 27th,2016
- ↑ Type 1 Diabetes mellitus "Dennis Kasper, Anthony Fauci, Stephen Hauser, Dan Longo, J. Larry Jameson, Joseph Loscalzo"Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19e Accessed on December 27th,2016
- ↑ Teng, Zhi-Pan; Tian, Rui; Xing, Fen-Li; Tang, Hui; Xu, Jin-Jing; Zhang, Bing-Wen; Qi, Jian-Wei (2017). "An association of type 1 diabetes mellitus with auditory dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis". The Laryngoscope. 127 (7): 1689–1697. doi:10.1002/lary.26346. ISSN 0023-852X.
- ↑ Leão, Andreia Araújo Porchat; Fritz, Camilla Kapp; Dias, Marcia Regina Messaggi Gomes; Carvalho, Julienne Angela Ramires; Mascarenhas, Luis Paulo Gomes; Cat, Mônica Nunes Lima; Radominski, Rosana; Nesi-França, Suzana (2020). "Bone mass and dietary intake in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus". Journal of Diabetes and its Complications. 34 (6): 107573. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107573. ISSN 1056-8727.
- ↑ Jabbour, Georges; Henderson, Mélanie; Mathieu, Marie-Eve (2016). "Barriers to Active Lifestyles in Children with Type 1 Diabetes". Canadian Journal of Diabetes. 40 (2): 170–172. doi:10.1016/j.jcjd.2015.12.001. ISSN 1499-2671.
- ↑ Broadley, Melanie M.; White, Melanie J.; Andrew, Brooke (2017). "A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Executive Function Performance in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus". Psychosomatic Medicine. 79 (6): 684–696. doi:10.1097/PSY.0000000000000460. ISSN 0033-3174.
- ↑ Ferguson, S. C.; Blane, A.; Wardlaw, J.; Frier, B. M.; Perros, P.; McCrimmon, R. J.; Deary, I. J. (2005). "Influence of an Early-Onset Age of Type 1 Diabetes on Cerebral Structure and Cognitive Function". Diabetes Care. 28 (6): 1431–1437. doi:10.2337/diacare.28.6.1431. ISSN 0149-5992.
- ↑ Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, de Herder WW, Dungan K; et al. (2000). "Endotext". PMID 29465926.
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3987274/. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ "Diabetes in control".
- ↑ Zheng, Fanfan; Yan, Li; Yang, Zhenchun; Zhong, Baoliang; Xie, Wuxiang (2018). "HbA1c, diabetes and cognitive decline: the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing". Diabetologia. 61 (4): 839–848. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4541-7. ISSN 0012-186X.
- ↑ Skrivarhaug, T.; Bangstad, H.-J.; Stene, L. C.; Sandvik, L.; Hanssen, K. F.; Joner, G. (2005). "Long-term mortality in a nationwide cohort of childhood-onset type 1 diabetic patients in Norway". Diabetologia. 49 (2): 298–305. doi:10.1007/s00125-005-0082-6. ISSN 0012-186X.
- ↑ Distiller LA (2014). "Why do some patients with type 1 diabetes live so long?". World J Diabetes. 5 (3): 282–7. doi:10.4239/wjd.v5.i3.282. PMC 4058732. PMID 24936249.