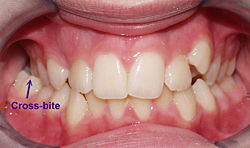
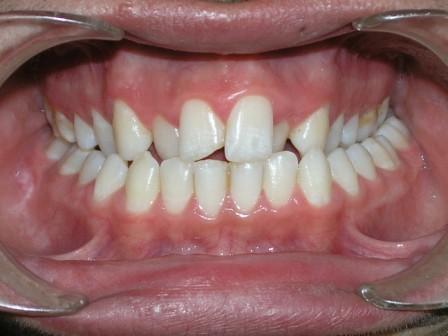
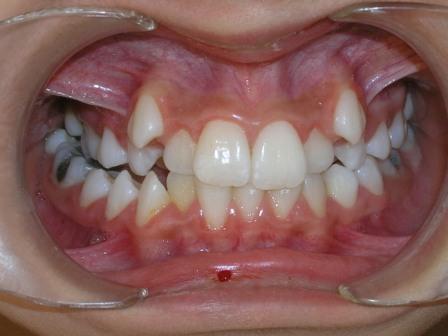
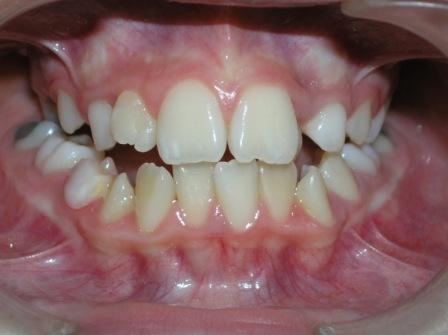
Crossbite
| Crossbite | |
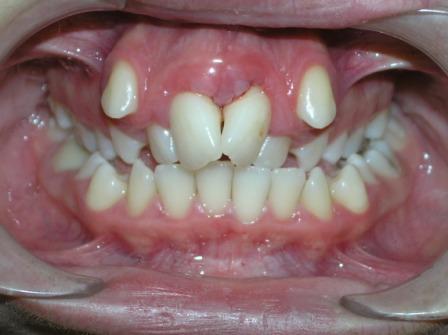 | |
|---|---|
| Crossbite (Image courtesy of Berna Zorkun DMD and copylefted) |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Crossbite |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Crossbite |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Crossbite at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Crossbite at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Crossbite
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Crossbite Discussion groups on Crossbite Directions to Hospitals Treating Crossbite Risk calculators and risk factors for Crossbite
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Crossbite |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor in Chief: Berna Zorkun DMD [1]
Overview
Crossbite is an occlusal irregular condition where a lower tooth has a more buccal position than the antagonist upper tooth. Crossbite can involve a single tooth or a group of teeth. Crossbite can be classified as anterior or posterior.
- Anterior crossbite can also be referred as negative overjet, and is typical of class III skeletal relations (Progenism).
- Posterior crossbite is often correlated to a narrow maxilla and upper dental arch. A posterior cross-bite can be unilateral or bilateral.
Unilateral cross-bite often determines a lateral shift of the mandibular position, which can become structural if left untreated for a long time during growth, leading to skeletal asymmetries.
Etiology
A crossbite may be associated with a pathological condition. A cleft palate patient may present both anterior and posterior crossbites with a narrow palate. Arthritis, acromegaly, Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy, condylar hyperplasia and osteochondroma are other factors. The majority of anterior crossbites a single tooth or a few teeth and are caused by dental factors: A congenitally-caused eruption pattern of the maxillary anteriors. Trauma to the primary dentition which leads to the displacement of the primary or permanent tooth bud. Trauma to permanent teeth that result in their being displaced by luxation.
Other factors include;
- Stomach sleeping posture
- Digit or pacifier sucking habits
- Oral respiration
- Low tongue position
- Tongue thrusting
Further Classification and Related Terminology
Buccal Crossbite
Buccal crossbite is due to the buccal displacement of the affected tooth or teeth as it relates to the antagonistic tooth or teeth in the posterior segments of the arch.
Lingual Crossbite
Lingual crossbite is due to the lingual displacement of the mandibular affected tooth or teeth as it relates to the antagonistic tooth or teeth.
Palatal Crossbite
Palatal crossbite is due to the palatal displacement of the maxillary affected tooth or teeth as it relates to the antagonistic tooth or teeth.
Complete Mandibular Buccal Crossbite
Complete mandibular buccal crossbite is present when all the mandibular teeth are lingually positioned to the maxillary teeth due to a narrower mandibular arch than the maxillary arch.
Complete Maxillary Palatal Crossbite
Complete maxillary palatal crossbite is present when all the maxillary teeth are palatal to the mandibular arch due to the narrower maxillary arch.
Both complete mandibular buccal crossbite and complete maxillary palatal crossbite could be referred as scissors-bite.
Complete Crossbite
Complete crossbite is found when all teeth in one arch are positioned either inside or outside to the all teeth in the opposing arch.
Scissors-bite
Scissors-bite is present when one or more of the adjacent posterior teeth are either positioned completely buccally or lingually to the antagonistic teeth and exhibit a vertical overlap.
Anterior crossbite
Anterior crossbite is a malocclusion in which one or more of the upper anterior teeth occlude lingually to the mandibular incisors; the lingual malpositions of one or more maxillary anterior teeth in relation to the mandibular anterior teeth when the teeth are in centric relation occlusion.
Posterior Crossbite
Posterior Crossbite is one or more posterior teeth locked in an abnormal relation with the opposing teeth of the opposite arch; can be either buccal or a lingual cross-bite and may be accompanied by a shift of the mandible.
Centric occlusion
Centric occlusion is a static reproducible position of the mandible in which there is maximal contact of the inclined planes of the opposing teeth with balanced, unstrained relationship in the temporomandibular articulation.
Treatment
There are several therapies that can be used to correct a cross bite:
- Multibrackets therapy (braces)
- Quad-Helix
- Hirex
- Removable Plates
- Invisalign
- Delaire Mask
The correct therapy should be decided by the orthodontist depending on the type and severity of the crossbite.
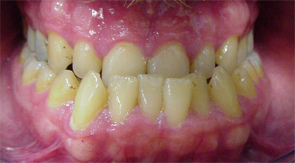
Image Gallery
-
Unilateral Posterior Crossbite
-
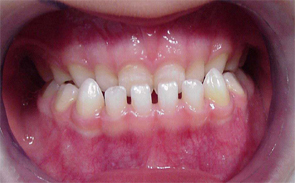
Crossbite
-
Crossbite
-
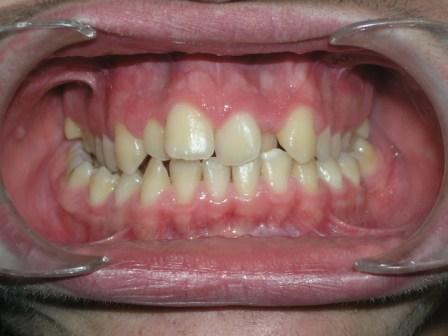
Crossbite
(Image courtesy of Berna Zorkun DMD and copylefted) -
Crossbite
(Image courtesy of Berna Zorkun DMD and copylefted) -
Crossbite
(Image courtesy of Berna Zorkun DMD and copylefted)
-
Crossbite
(Image courtesy of Berna Zorkun DMD and copylefted) -
Crossbite
(Image courtesy of Berna Zorkun DMD and copylefted)