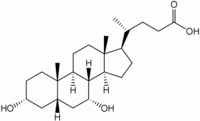
Chenodeoxycholic acid
| Template:Chembox header| Chenodeoxycholic acid | |
|---|---|
| |
| Systematic name | chenodiol 3α,7α-dihydroxy-5β-cholanic acid 5β-cholanic acid-3α,7α-diol |
| Chemical formula | C24H40O4 |
| Molecular mass | xx.xx g/mol |
| Density | x.xxx g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 165-167 °C |
| Boiling point | xx.x °C |
| CAS number | [474-25-9] |
| SMILES | C[C@@]34[C@] (CC[C@@H]4[C@@H] (CCC(O)=O)C) ([H])[C@]2([H]) [C@H](O)C[C@]1 ([H])C[C@H](O) CC[C@@](C)1 [C@]([H])2CC3 |
| Template:Chembox header | Disclaimer and references | |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Chenodeoxycholic acid (also known as chenodesoxycholic acid) is a bile acid, a white crystalline substance insoluble in water, with melting point at 165-167 °C. Its salts is called chenodeoxycholates. Chenodeoxycholic acid is one of the 4 main organic acids produced by the liver. It is soluble in alcohol and acetic acid.
Chenodeoxycholic acid is synthesized in the liver from cholesterol.
This compound, when altered by bacteria in the colon, will result in conversion to its secondary bile acid known as lithocholic acid. Both of these bile acids, in addition to the others, can be conjugated to taurine or glycine. Conjugation, a function carried out by the liver will result in a lowered pKa and therefore, the compounds will remain ionized. These ionized compounds will stay in the gastrointestinal tract until reaching the ileum where they will be reabsorbed. The purpose of this conjugation is to keep the bile acids in the tract until the end to facilitate lipid digestion all the way to the ileum.
In cases where bacteria overgrow in the small intestine, often due to a blind loop in the intestine retaining chyme in one place, the bacteria will de-conjugate the bile acids and therefore impede fat digestion and absorption. This can lead to steatorrhea.
Chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid are the most important human bile acids. Some other mammals synthesize predominantly deoxycholic acid.
Potential applications
The Australian biotechnology company Giaconda has developed a treatment for Hepatitis C infection that combines chenodeoxycholic acid with bezafibrate.
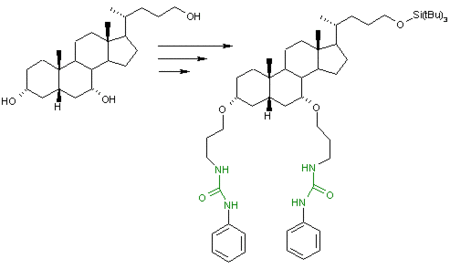
In supramolecular chemistry molecular tweezers based on a chenodeoxycholic acid scaffold is an urea receptor [2] which can contain anions in its binding pocket in order of affinity: H2PO4- (dihydrogen phosphate) > Cl- > Br- > I- reflecting their basicities (tetrabutylammonium counter ion).[1]